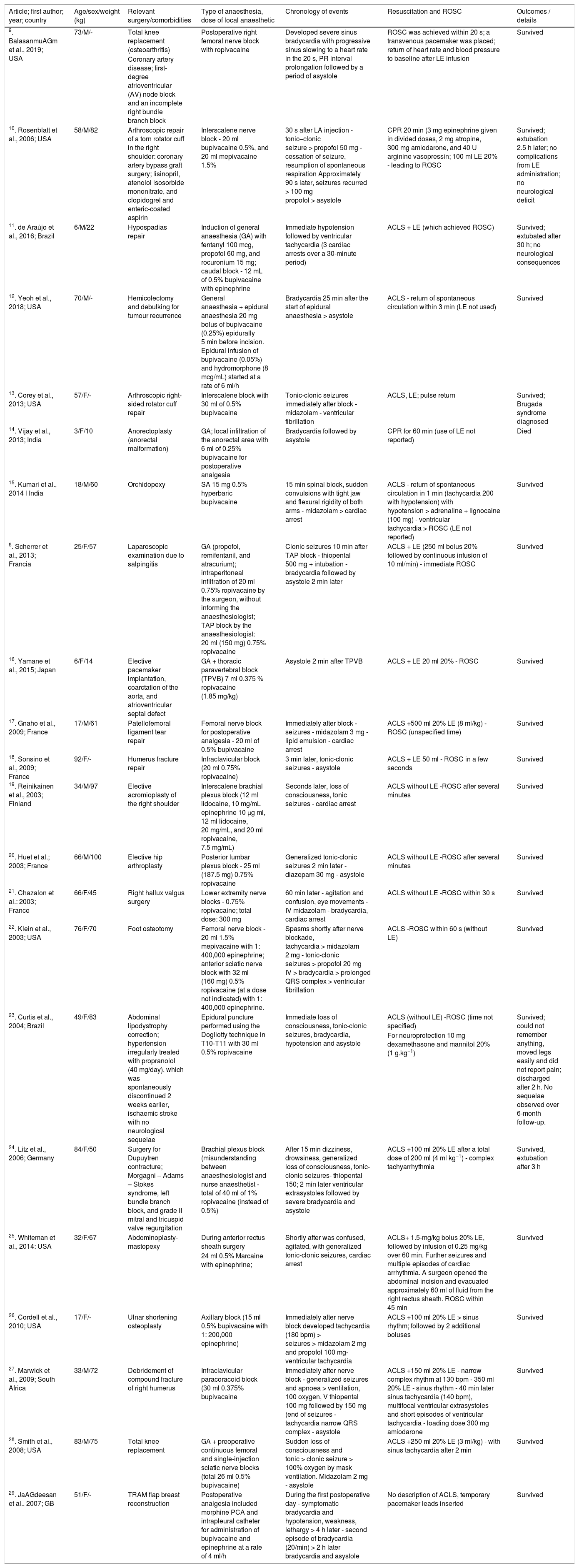
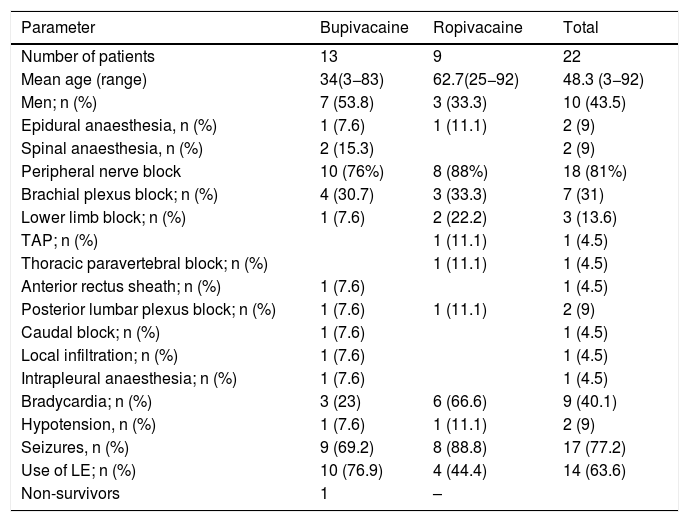
Regional anesthesia as a component of multimodal analgesia protocols has become more and more a part of modern perioperative pain management. The widespread adoption of ultrasound guidance in regional anesthesia has surely played an important role in that growth and it has significantly improved patient safety, decreased the incidence of block failure, cardiac arrest, and reduced complication rates. The objective of this systematic review is to extract, analyze, and synthesize clinical information about bupivacaine and ropivacaine related cardiac arrest that we might have a clearer picture of the clinical presentation. The literature search identified 268 potentially relevant publications and 22 relevant case reports were included in the review. Patients’ demographics, types of regional anesthesia, hypotension, heart rhythm disorders, seizures, cardiac arrest, fatal outcome, recommendations and limitations on prevention and treatment of bupivacaine and ropivacaine related cardiac arrest are analyzed and discussed in the systematic review. Both bupivacaine and ropivacaine-induced local anesthetic toxicity can result in cardiac arrest. Lipid emulsion, telemetry, local anesthetic toxicity resuscitation training appears to be promising in improvement of survival but more research is needed. Improvement and encouragement of reporting the local anesthetic toxicity are warranted to improve the quality of information that can be analyzed in order to make more precise conclusion.
La anestesia regional como componente de los protocolos de analgesia multimodal se ha ido convirtiendo de manera creciente en una parte del tratamiento moderno del dolor perioperatorio. Seguramente, la adopción generalizada de la guía ecográfica en la anestesia regional ha jugado un papel importante en dicho crecimiento y ha mejorado significativamente la seguridad del paciente, disminuyendo la incidencia de fallos de los bloqueos y de paradas cardiacas, y reduciendo las tasas de complicaciones. El objetivo de esta revisión sistemática es extraer, analizar y sintetizar información clínica sobre la parada cardiaca relacionada con la bupivacaína y la ropivacaína, para poder tener una imagen más clara de la presentación clínica. La búsqueda bibliográfica identificó 268 publicaciones potencialmente relevantes y se incluyeron 22 informes de casos relevantes en la revisión. En la revisión sistemática se analizan los datos demográficos de los pacientes, los tipos de anestesia regional, la hipotensión, los trastornos del ritmo cardiaco, las convulsiones, la parada cardiaca, el desenlace fatal, las recomendaciones y las limitaciones en la prevención y el tratamiento de la parada cardiaca relacionada con la bupivacaína y la ropivacaína. La toxicidad de la anestesia local inducida tanto por bupivacaína como ropivacaína puede provocar una parada cardiaca. La emulsión lipídica, la telemetría, y la formación en la reanimación de la toxicidad anestésica local parecen ser prometedoras para mejorar la supervivencia, pero se necesita más investigación. Deben garantizarse la mejora y el estímulo de informar sobre la toxicidad de los anestésicos locales, para mejorar la calidad de la información que puede analizarse para llegar a una conclusión más precisa.