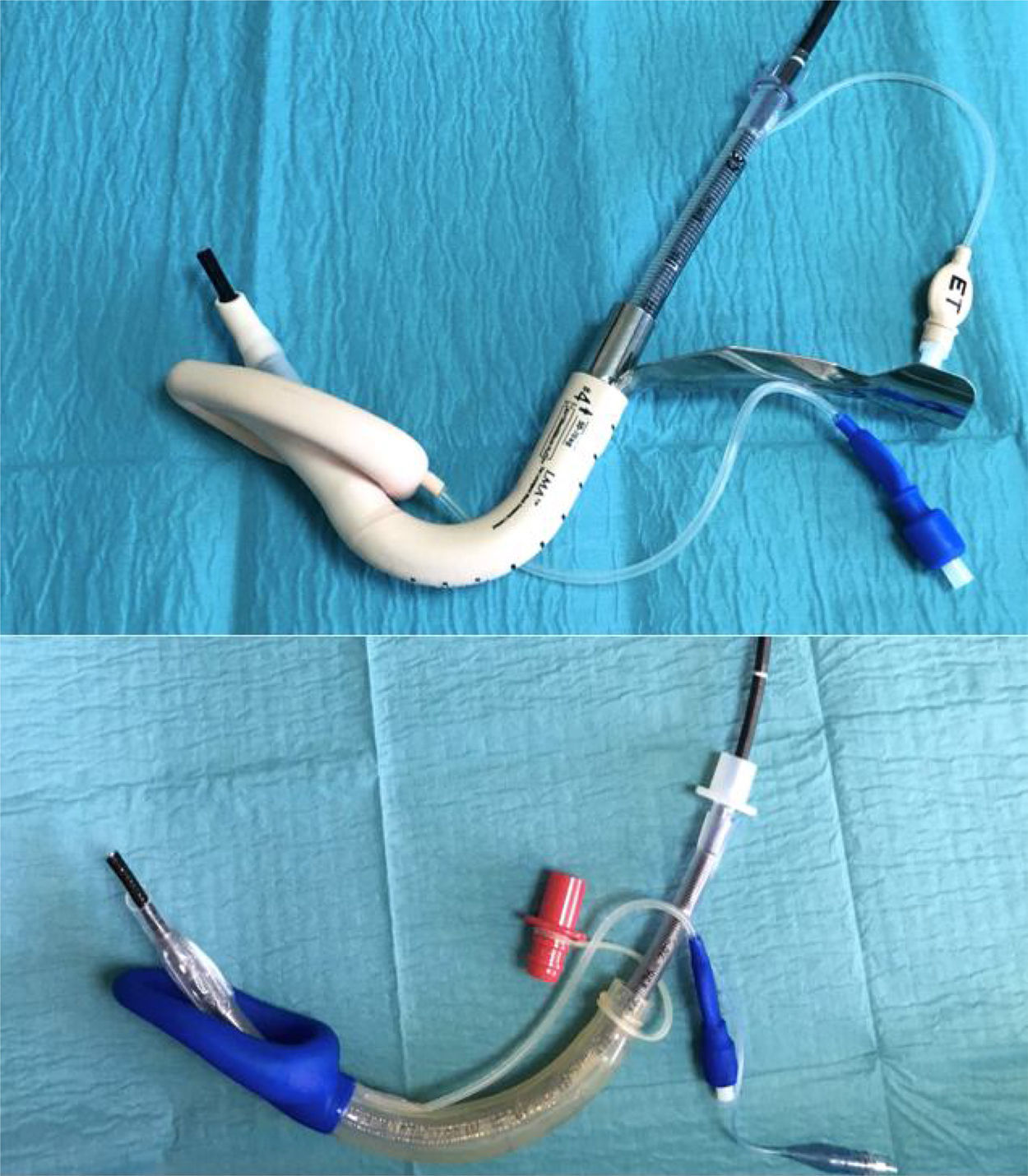
Airway management is still a major cause of anaesthesia-associated morbidity and mortality. Supraglottic devices are recommended in difficult airway management guidelines. The aim of this study was to compare the performance of the Air-Q® and the LMA Fastrach™ for fibreoptic guided tracheal intubation.
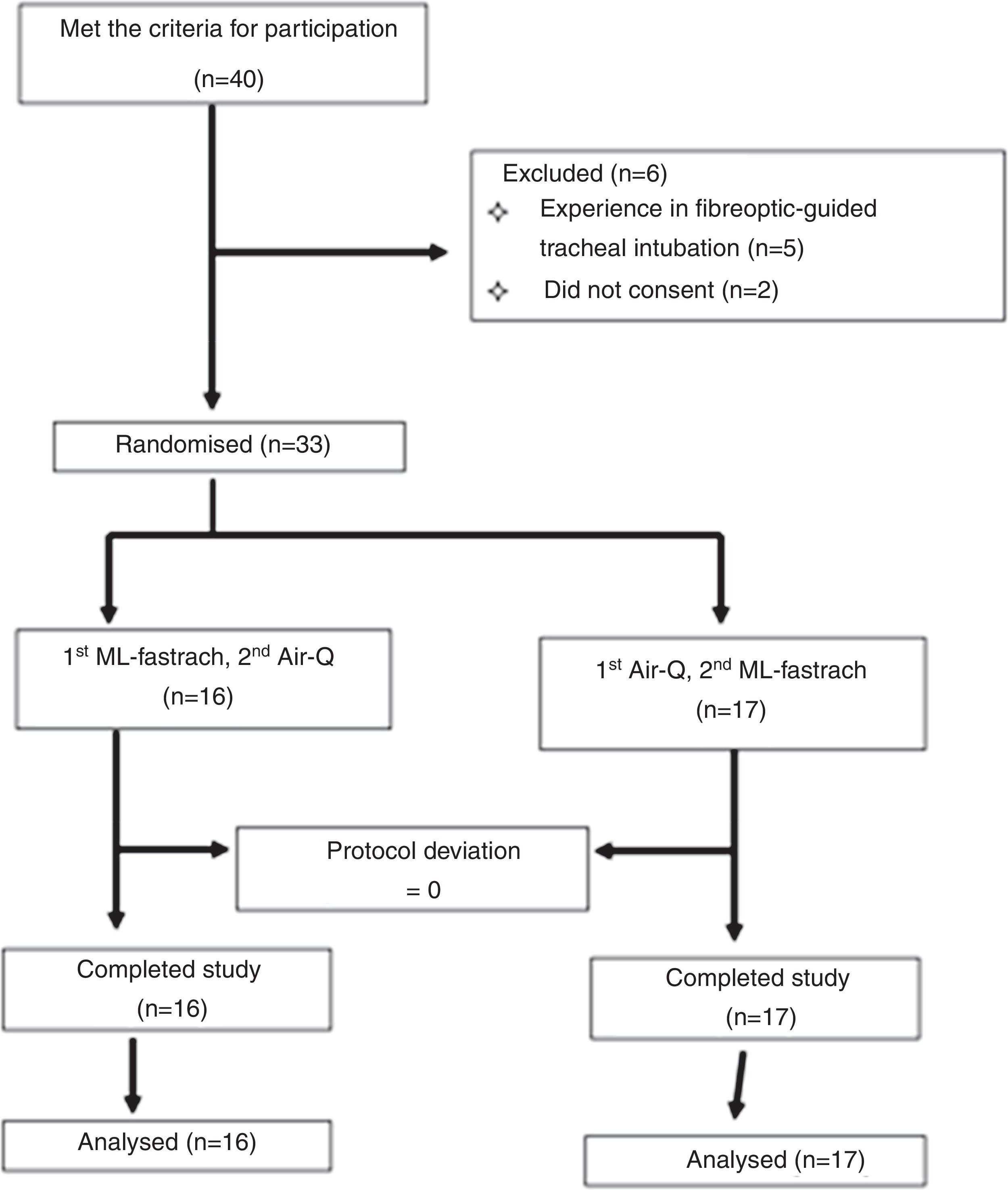
MethodsThirty-three anaesthesia trainees participated in this randomized crossover study. Time to insert the dedicated airways (insertion of the airway into the manikin and delivery of two breaths), time to tracheal intubation (fibreoptic-guided tracheal intubation), time to remove the dedicated airway (removal of the Air-Q®/LMA Fastrach™ over the tracheal tube) and the opinion of the ease of use of the anaesthesia trainees were measured.
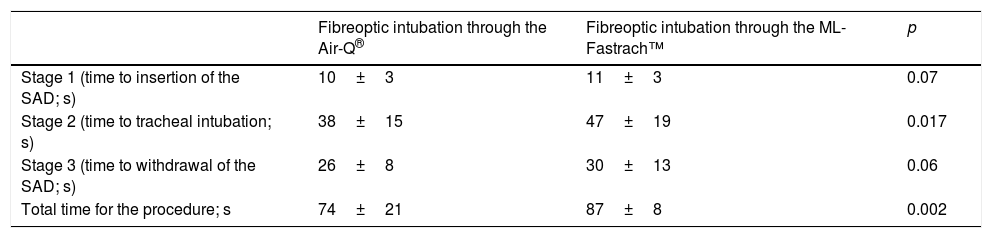
ResultsThere was 100% success rate for tracheal intubation with both devices on the first attempt. Time to insert the dedicated device and deliver two breaths was 10±3s for the Air-Q® and 11±3s for the LMA Fastrach™, p=0.07. Time taken to intubate the trachea was shorter with the Air-Q®, 38±15s, than with the LMA Fastrach™, 47±19s, p=0.017. Overall procedure time was significantly shorter with the Air-Q® as compared with the LMA Fastrach™, with a mean time of 74±21s and 87±28s respectively, p=0.002. Air-Q® removal was considered easier than LMA Fastrach™ removal, p=0.005. There were no tube dislodgements during the removal of the dedicated airways.
ConclusionsInexperienced anaesthesia residents can perform fibreoptic-guided intubation through Air-Q® and LMA Fastrach™ in a clinically acceptable time with high success.
Los dispositivos supraglóticos forman parte esencial en el manejo de la vía aérea difícil. El objetivo del presente estudio fue comparar las características de la intubación con fibrobroncoscopio a través del dispositivo Air-Q® versus la mascarilla laríngea Fastrach™ (ML-Fastrach™) por residentes de anestesia en maniquís.
MétodosEstudio aleatorizado y cruzado en el que participaron 33 residentes de anestesia. Se midió el tiempo de inserción (inserción del dispositivo en el maniquí y administración de 2 insuflaciones), el tiempo hasta la intubación traqueal (intubación guiada con el fibrobroncoscopio) y el tiempo para retirar los dispositivos (retirada de la Air-Q®/ML Fastrach™ sobre el tubo endotraqueal). Se evaluó la opinión de la facilidad de utilización.
ResultadosHubo una tasa de éxito del 100% para la intubación traqueal con ambos dispositivos al primer intento. El tiempo de inserción y administración de 2 ventilaciones fue de 10±3s para Air-Q® y de 11±3s para la ML-Fastrach™, p=0,07. El tiempo de intubación traqueal fue más corto con Air-Q®, 38±15s, que con la ML-Fastrach™, 47±19s, p=0,017. El tiempo total fue significativamente más corto con Air-Q® en comparación con la ML-Fastrach™, con un tiempo medio de 74±21 y 87±28s respectivamente, p=0,002. La retirada de la Air-Q® se consideró más fácil que la de la ML-Fastrach™, p=0,005. No se registraron desplazamientos del tubo endotraqueal durante la extracción de los dispositivos.
ConclusionesLos residentes de anestesia pueden realizar la intubación con fibrobroncoscopio a través de la Air-Q® y de la ML-Fastrach™ de forma exitosa y con tiempos clínicamente aceptables.