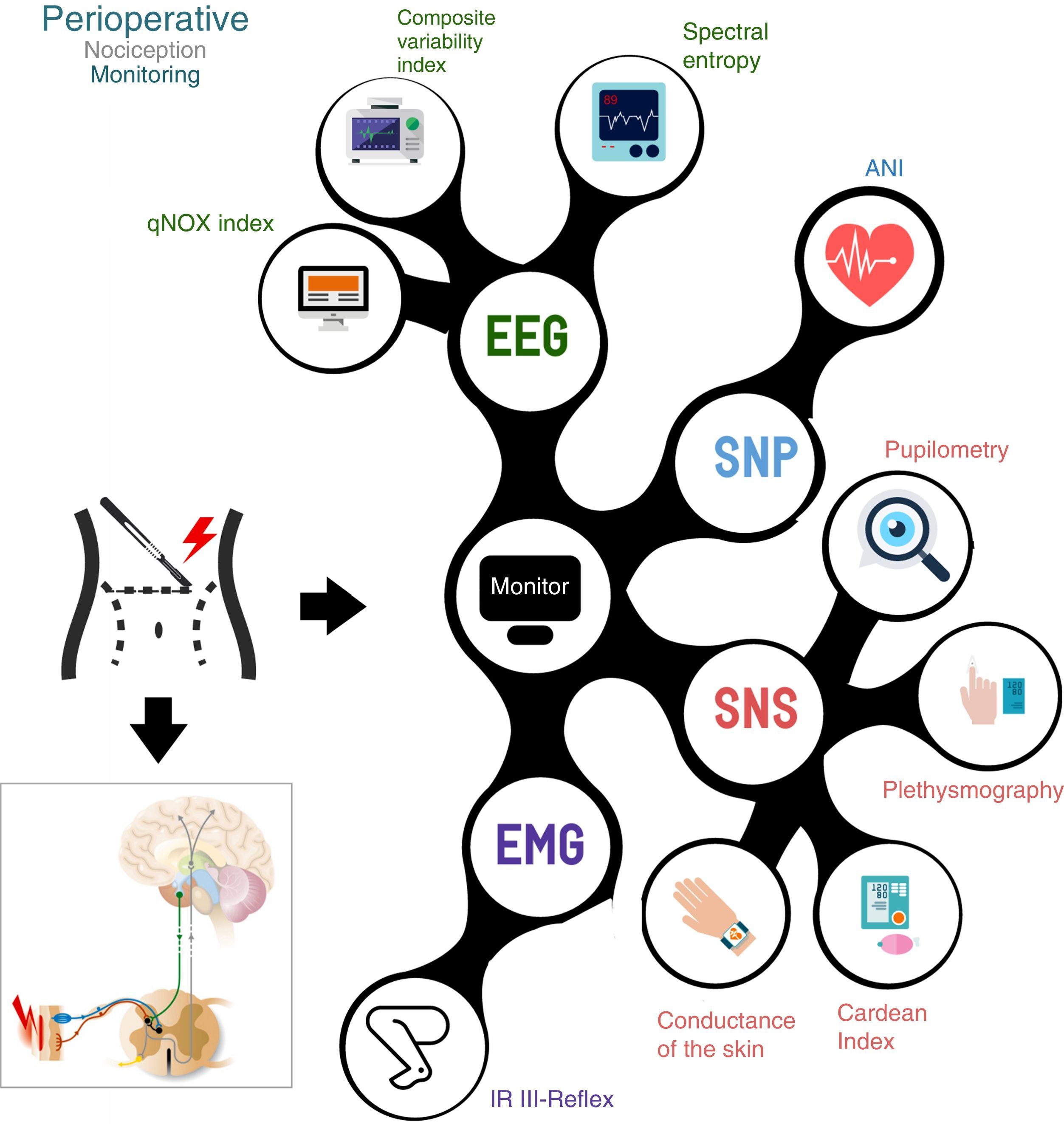
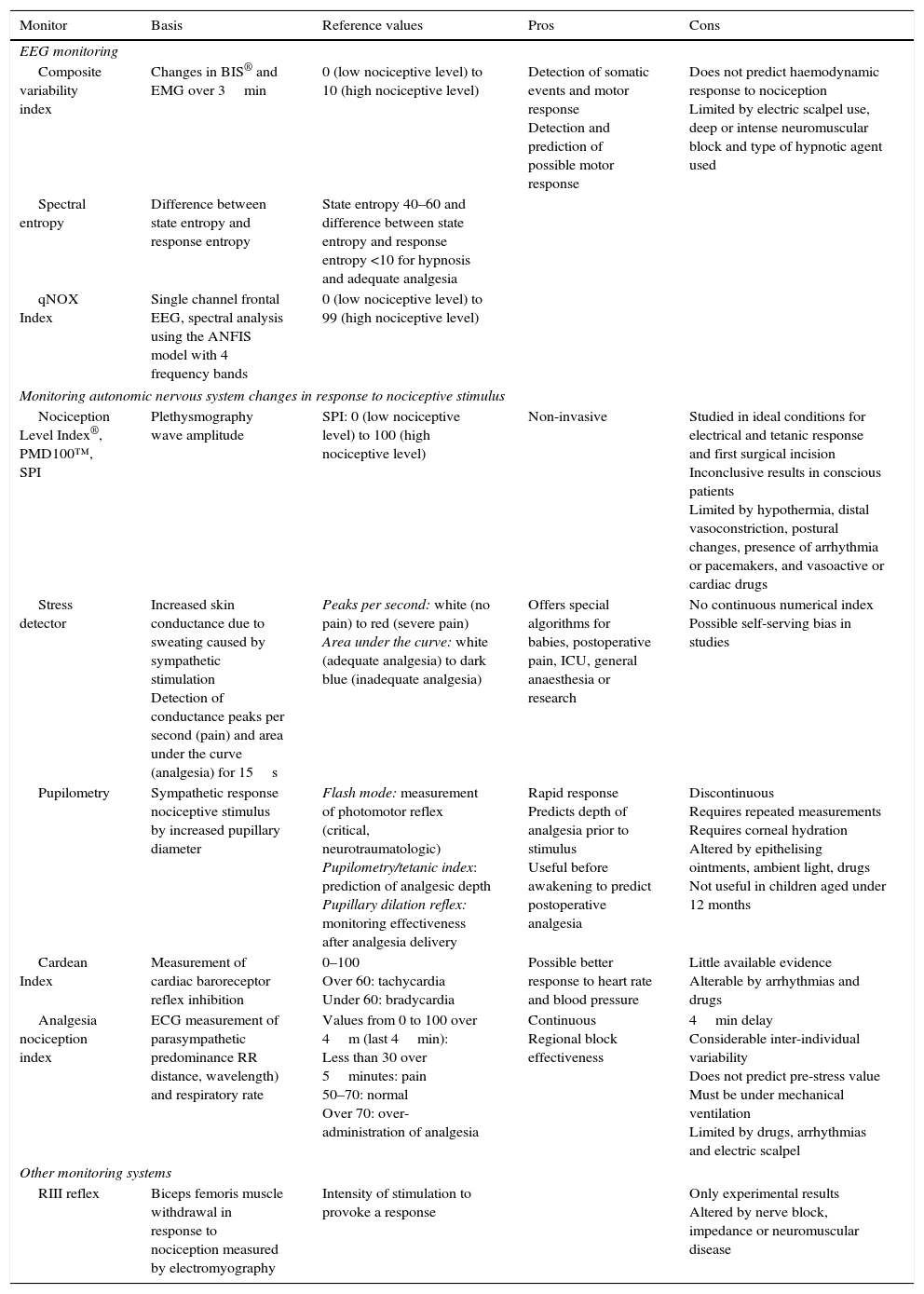
There are currently various projects underway that attempt to monitor the nociceptive responses caused by surgical stress and ensure patients the best analgesic conditions.
The systemic response to surgical stress has repercussions in the postoperative period, such as worse pain control, delayed recovery, greater complications, longer stay in resuscitation and hospital units, and increased healthcare costs. However, treatment with higher doses of opioids than necessary may lead to slower awakening, increased drowsiness and adverse effects, as well as situations of postoperative opioid-induced hyperalgesia.
There are 2 large groups of nociceptive monitoring according to the origin of the theoretical objective of monitoring response to the stimulus, that may derive from changes in the electroencephalogram or the response of the autonomic nervous system.
En la actualidad han aparecido diferentes proyectos para intentar monitorizar las respuestas nociceptivas provocadas por el estrés quirúrgico y para mantener a los pacientes en las mejores condiciones analgésicas.
La respuesta sistémica al estrés quirúrgico tiene repercusiones en el postoperatorio, como son el peor control del dolor, una recuperación más tardía, mayores complicaciones, mayor tiempo de estancia en unidades de reanimación y hospitalaria, e incremento del coste de los servicios sanitarios. Sin embargo, el tratamiento con mayores dosis de opiáceos de las necesarias puede suponer situaciones de despertar más lento, mayor somnolencia y efectos adversos, pero también situaciones de hiperalgesia postoperatoria por opiáceos.
Existen 2 grandes grupos de monitorización nociceptiva según el origen del objetivo teórico de vigilancia de la respuesta al estímulo, pudiendo ser derivados de cambios en el electroencefalograma o de la respuesta del sistema nervioso autónomo.