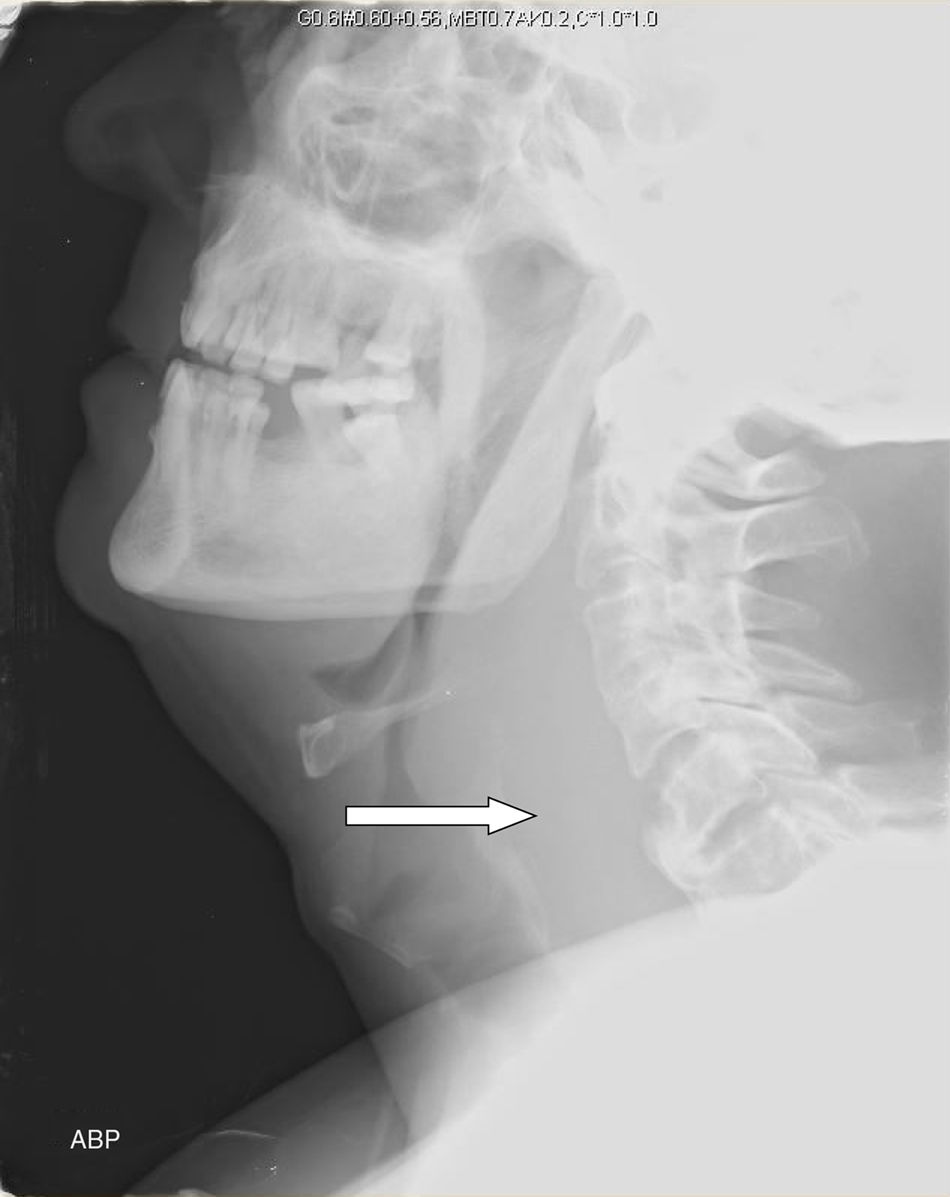
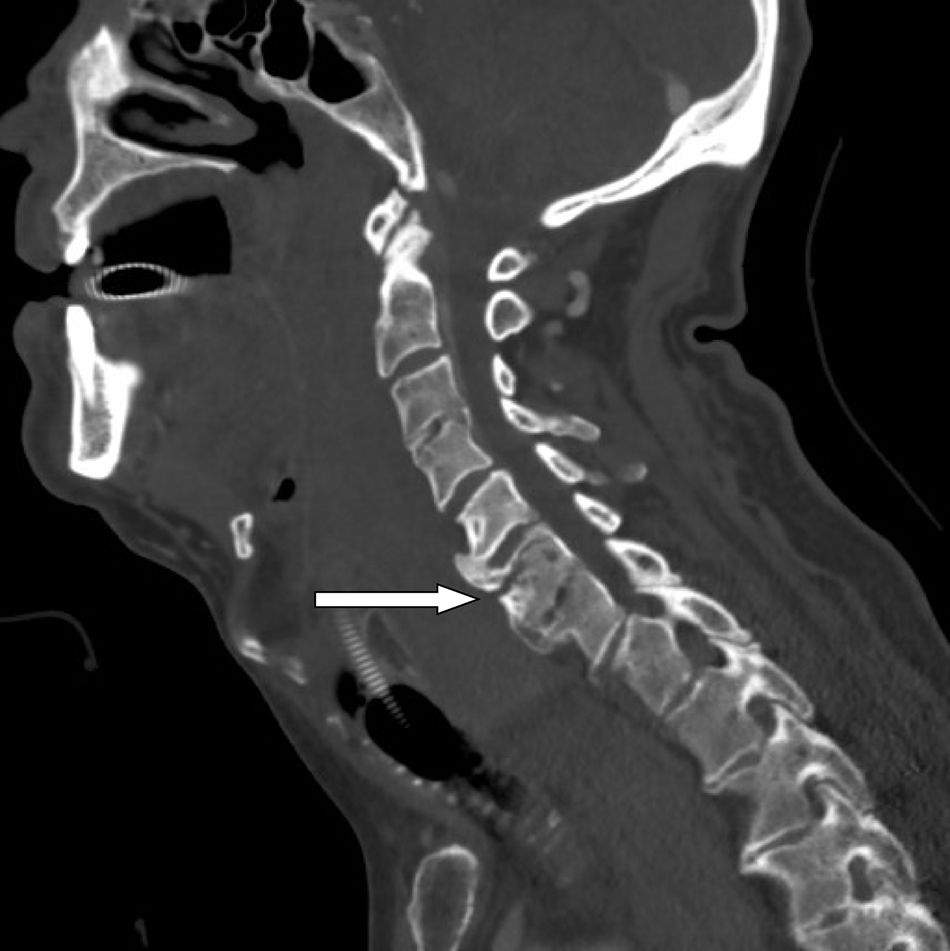
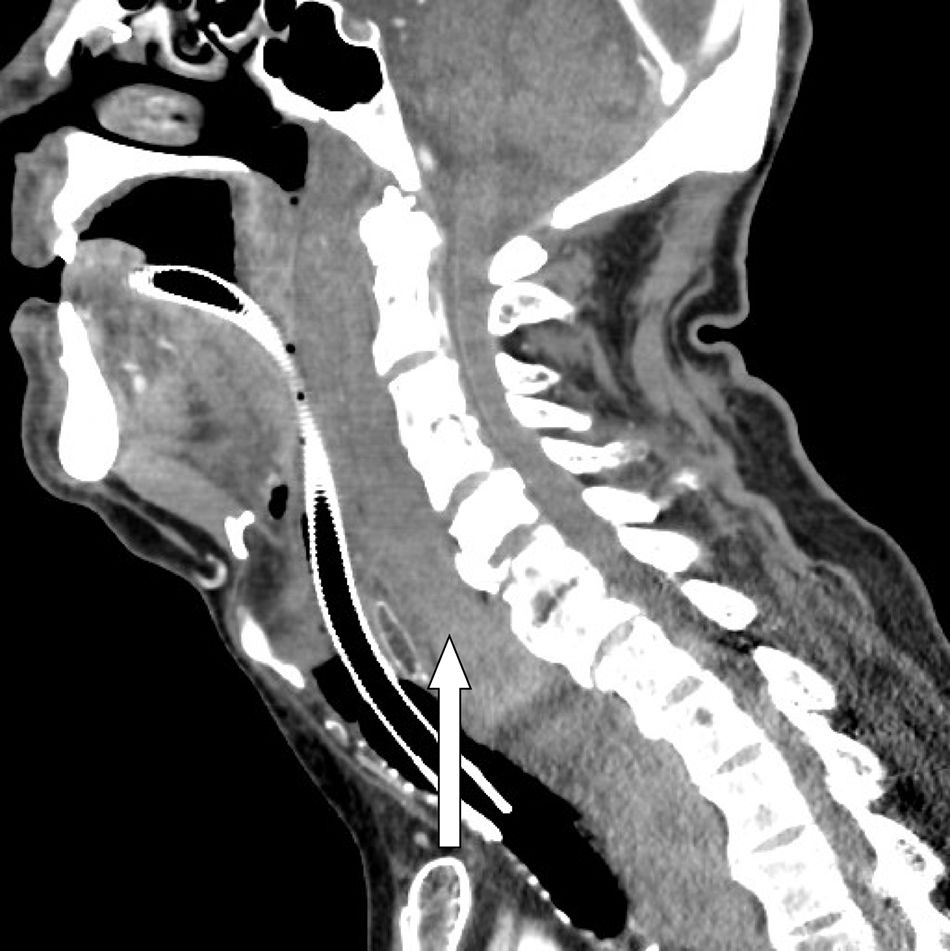
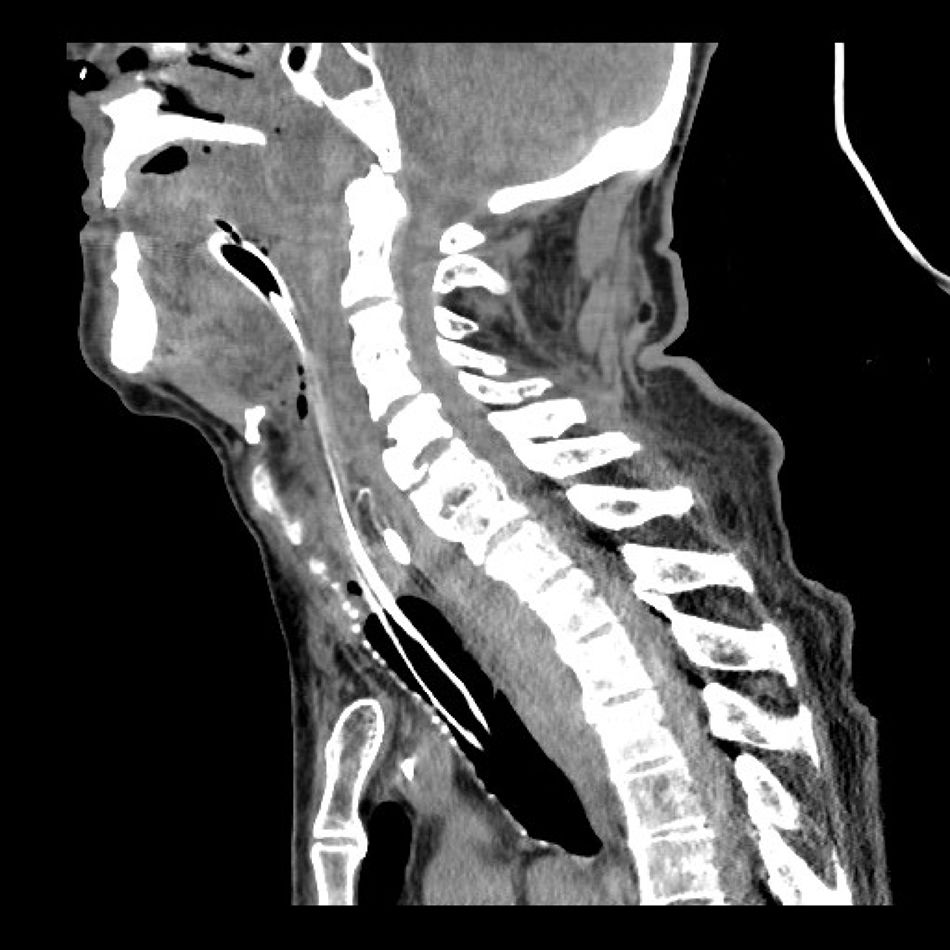
Retropharyngeal haematoma is a life-threatening clinical situation that can lead to a potential obstruction of the upper airway and requires rapid diagnosis. Clinically, it can be presented in different ways, depending on its size and growing speed. The first measure is to protect and manage the airway: in most cases this is a difficult airway situation. A retropharyngeal haematoma can be formed due to a previous traumatic history, with or without associated cervical fracture. Treatment of the haematoma is conservative in most cases, with close monitoring until it is reabsorbed in 3–4 weeks, although they can sometimes require surgical evacuation. We present the case of a patient who developed a large retropharyngeal haematoma after minor cervical trauma and describe an approach of the airway using the Airtraq® disposable optical laryngoscope.
Un hematoma retrofaríngeo es una situación clínica que puede poner en peligro la vida por la potencial obstrucción de la vía aérea superior y que requiere un rápido diagnóstico. Puede presentarse clínicamente de diferentes formas, según el tamaño y la velocidad en su desarrollo. La primera medida que tener en cuenta es la protección y el manejo de la vía aérea que, en la mayoría de las veces, es una situación de vía aérea difícil. En la aparición de un hematoma retrofaríngeo puede existir un antecedente traumático previo, con o sin fractura cervical asociada. El tratamiento del hematoma en la mayoría de los casos es conservador, con una estrecha vigilancia hasta su reabsorción en 3-4 semanas, aunque en ocasiones precisa de evacuación quirúrgica. Presentamos el caso clínico de un paciente que desarrolló un gran hematoma retrofaríngeo tras traumatismo cervical menor y describimos el abordaje de la vía aérea mediante el uso del laringoscopio óptico desechable Airtraq®.