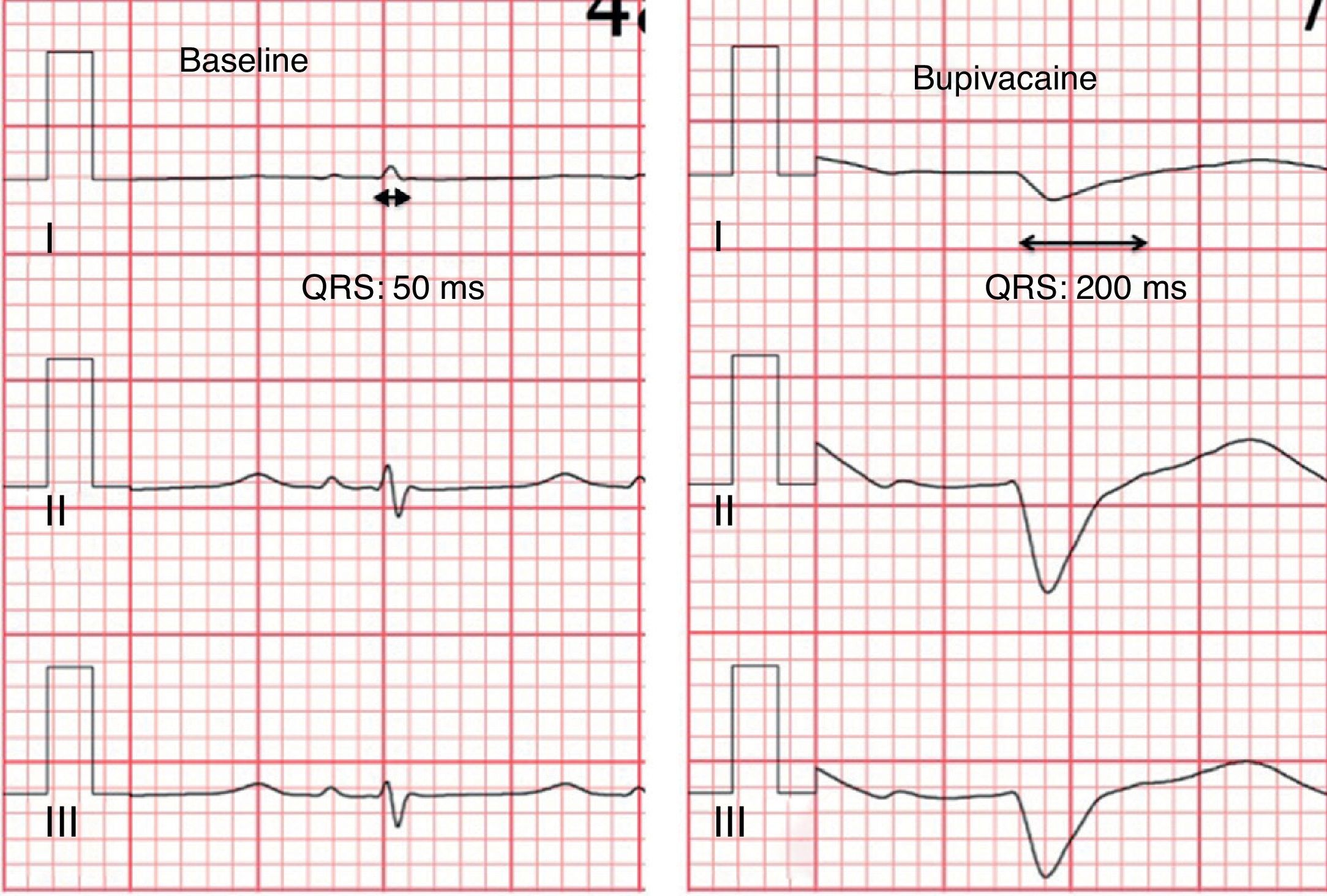
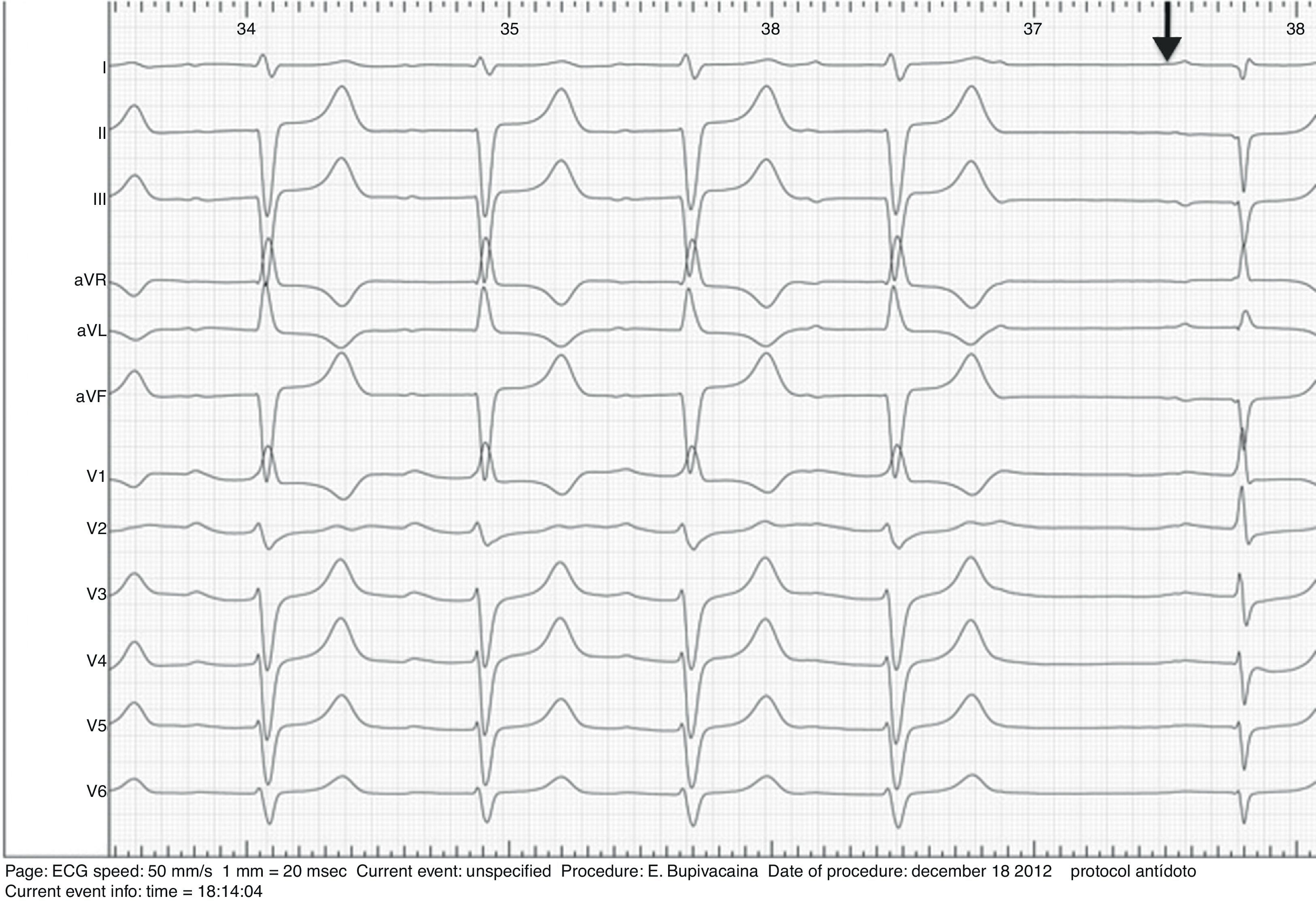
The principal mechanism of cardiac toxicity of bupivacaine relates to the blockade of myocardial sodium channels, which leads to an increase in the QRS duration. Recently, experimental studies suggest that lipid emulsion is effective in reversing bupivacaine cardiac toxicity. We aimed to evaluate the temporal evolution of the QRS widening induced by bupivacaine with the administration of Intralipid.
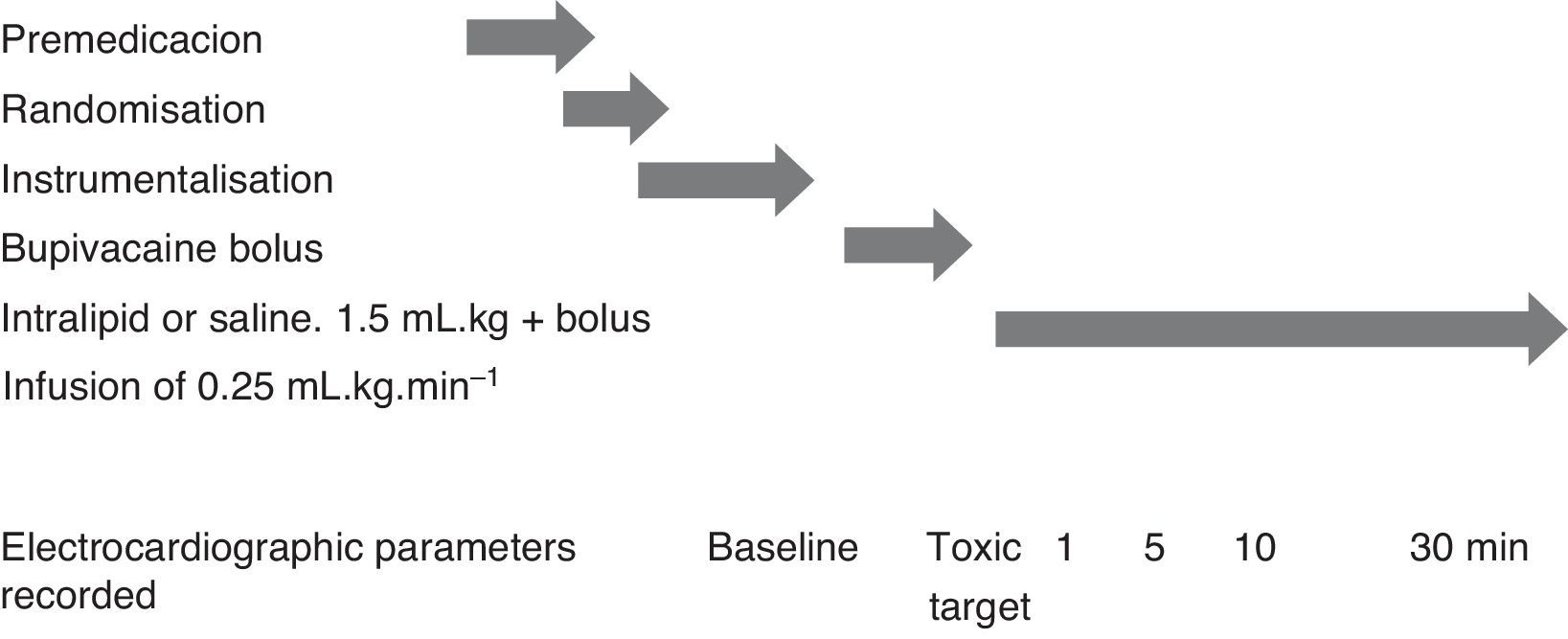
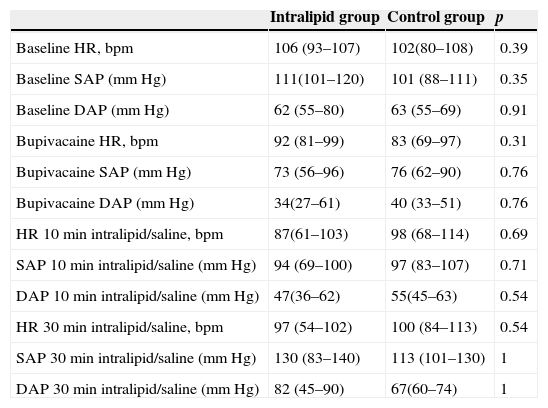
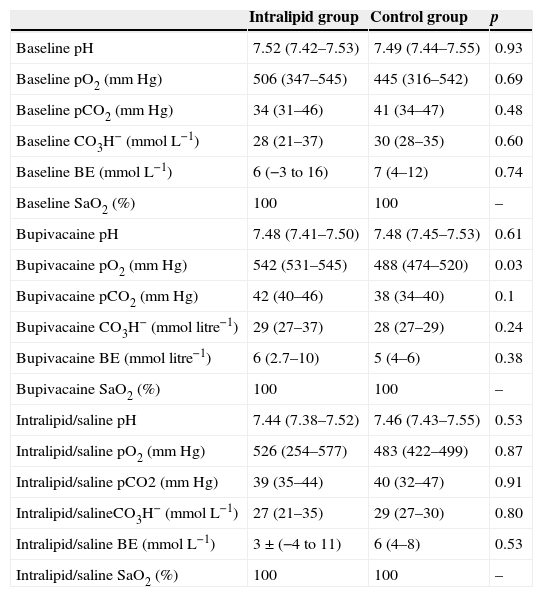
Material and methodsTwelve pigs were anesthetized with intravenous sodium thiopental 5mgkg−1 and sevoflurane 1 MAC (2.6%). Femoral artery and vein were canalized for invasive monitoring, analysis of blood gases and determination of bupivacaine levels. After instrumentation and monitoring, a bupivacaine bolus of 4–6mgkg−1 was administered in order to induce a 150% increase in QRS duration (defined as the toxic point). The pigs were randomized into two groups of six individuals. Intralipid group (IL) received 1.5mLkg−1 of IL over 1min, followed by an infusion of 0.25mLkgmin−1. Control group (C) received the same volume of a saline solution. The electrocardiographic parameters were recorded, and blood samples were taken after bupivacaine and 1, 5, 10 and 30min after Intralipid/saline administration.
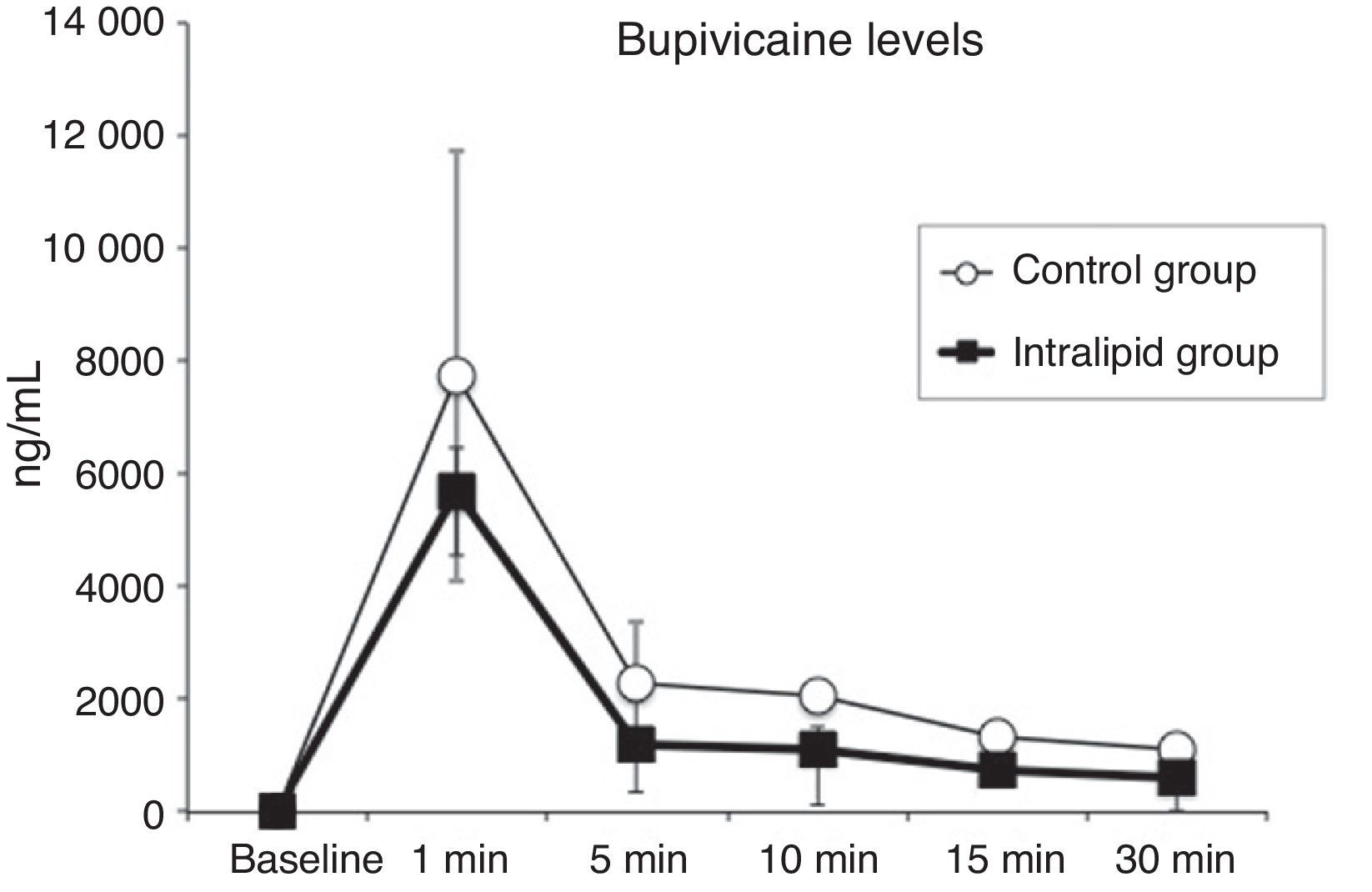
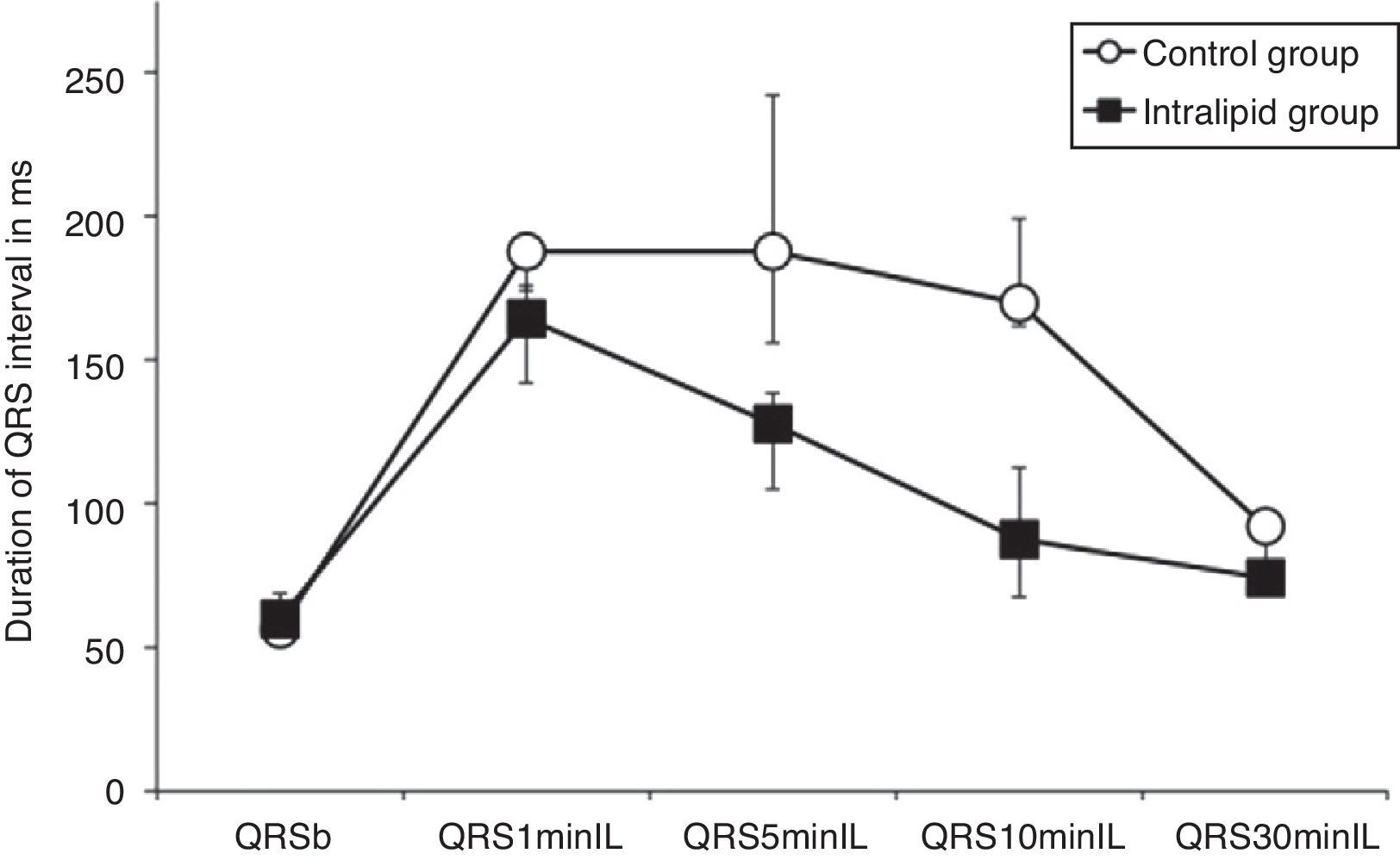
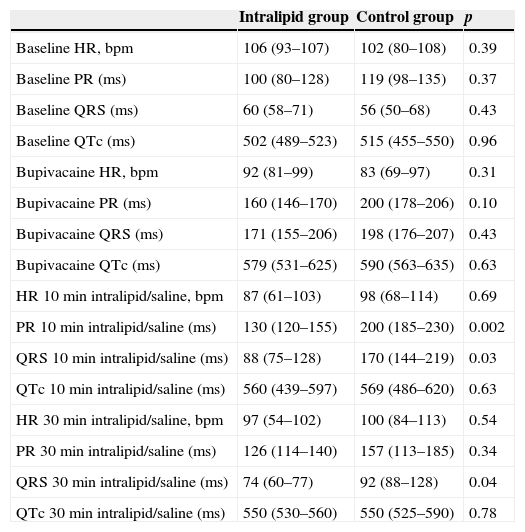
ResultsBupivacaine (4.33±0.81mg/kg in IL group and 4.66±1.15mg/kg in C group) induced similar electrocardiographic changes in both groups; mean maximal percent increase in QRS interval was 184±62% in IL group, and 230±56% in control group (NS). Lipid administration reversed the QRS widening previously impaired by bupivacaine. After 10min of the administration of IL, the mean QRS interval decreased to 132±56% vs. 15±76% relative to the maximum widening induced by bupivacaine, in IL and C group, respectively.
ConclusionIntralipid reversed the lengthening of QRS interval induced by the injection of bupivacaine. Time to normalization of electrocardiographic parameters can last more than 10min. While the phenomena of cardiac toxicity persist, resuscitation measures and adequate monitoring should be continued until adequate heart conduction parameters are restored.
La toxicidad cardiaca inducida por la bupivacaína (B) se relaciona con el bloqueo de los canales de sodio, que se traduce por un ensanchamiento del intervalo QRS. Estudios experimentales recientes, sugieren que el Intralipid (IL) es eficaz en revertir la toxicidad cardiaca de la B. Nuestro objetivo fue analizar la evolución temporal del ensanchamiento del QRS inducido por la B con la administración de IL.
Material y métodoDoce cerdos fueron anestesiados con tiopental sódico, 5mgkg−1, y sevoflurano a concentración alveolar mínima de 2,6%. Tras la instrumentalización se administró un bolo de B de 4–6mgkg−1 con el objetivo de inducir un aumento de 150% en la duración del QRS. El grupo IL recibió 1,5mLkg−1 de IL seguido de 0,25mLkg min−1; el grupo control (C) recibió salino. Se registraron los parámetros electrocardiográficos tras la infusión de B y a 1, 5,10 y 30min de la administración de Intralipid/salino.
ResultadosLa administración de B (4,33±0,81mg/kg en el grupo IL y 4,66±1,15mg/kg en el grupo C) indujo cambios electrocardiográficos similares en ambos grupos; el porcentaje medio de incremento máximo en el QRS fue de 184±62% en el grupo IL, y de 230±56% en el grupo C. El IL revirtió el ensanchamiento del QRS inducido por la B, a los 10min de su administración el intervalo QRS disminuyó 132±56% vs. 15±76%, en relación al máximo incremento inducido por la B, en el grupo IL y grupo C respectivamente.
ConclusiónEl IL revirtió eficazmente el ensanchamiento del intervalo QRS inducido por la B. El tiempo hasta la normalización de los parámetros electrocardiográficos puede prolongarse más de 10min. Mientras persistan los fenómenos de toxicidad cardíaca, las medidas de resucitación y monitorización deben continuarse hasta que los parámetros de conducción cardíaca se hayan restaurado de forma adecuada.