To study which variables involved in the process of selective sentinel node biopsy (SSNB) influence the intraoperative detection of the sentinel lymph node.
Material and methodsThis was a prospective cross-sectional study in 210 patients (mean age, 54 years) diagnosed with breast cancer who underwent SSNB. We recorded clinical, radiological, radioisotope administration, surgical, and histological data as well as follow-up data. We did a descriptive analysis of the data and an associative analysis using multivariable regression.
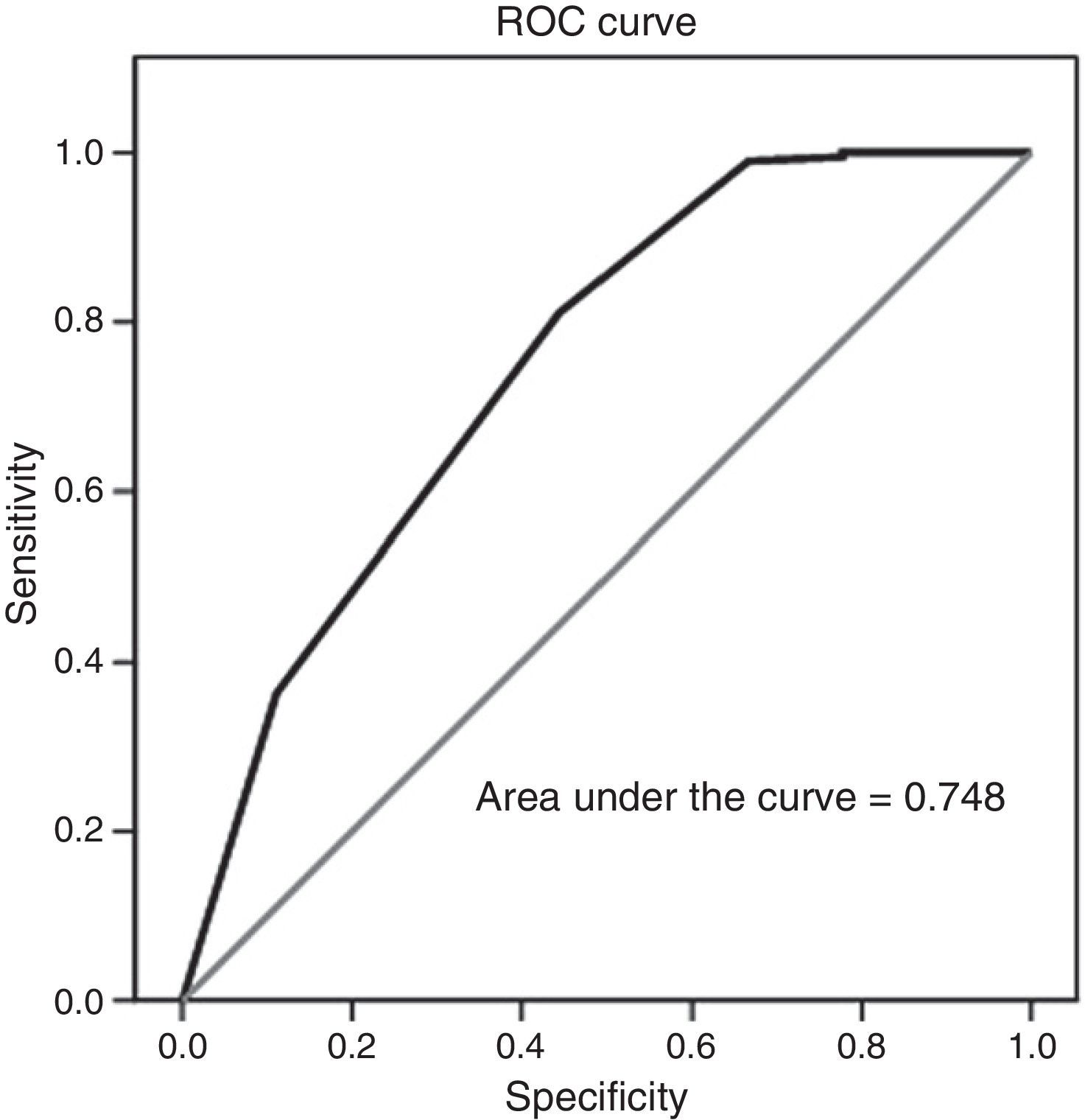
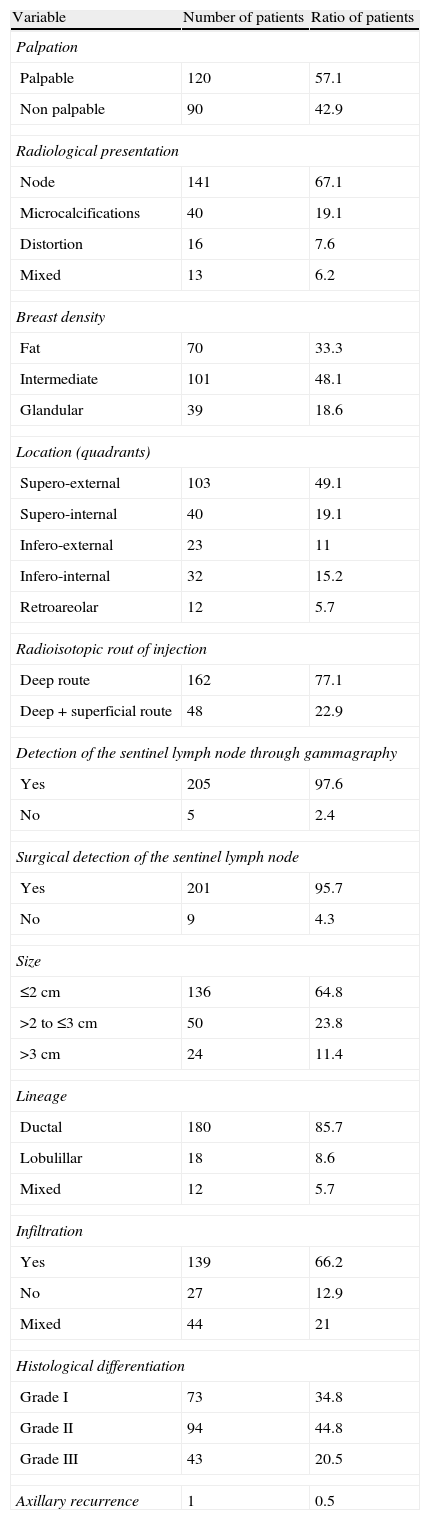
ResultsDeep injection alone was the most common route of radioisotope administration (72.7%). Most lesions were palpable (57.1%), presented as nodules (67.1%), measured less than 2cm in diameter (64.8%), were located in the upper outer quadrant (49.1%), were ductal carcinomas (85.7%), were accompanied by infiltration (66.2%), and had a histologic grade of differentiation of II (44.8%). Preoperative scintigraphy detected the sentinel node in 97.6% of cases and 95.7% were detected during the operation. One axillary relapse was observed. In the associative study, the variables “preoperative lymphoscintigraphy” and “histologic grade of differentiation of the tumor” were significantly associated with the detection of the sentinel lymph node during the operation.
ConclusionThe probability of not detecting the sentinel lymph node during the surgical intervention is higher in patients with high histologic grade tumors or in patients in whom preoperative lymphoscintigraphy failed to detect the sentinel node.
Estudiar qué variables implicadas en el proceso de la biopsia selectiva del ganglio centinela (BSGC) influyen en la detección intraoperatoria del ganglio centinela.
Material y métodosEstudio transversal prospectivo de 210 pacientes (edad media: 54 años) diagnosticadas de cáncer de mama a las que se les realizó BSGC. Se recogieron los datos clínicos y radiológicos, de la administración del radioisótopo, quirúrgicos, de anatomía patológica y de seguimiento, y se realizó un análisis descriptivo y asociativo mediante una regresión múltiple multivariante.
ResultadosLa vía de inyección del radioisótopo más utilizada fue la profunda aislada (72,7%). La mayoría de las lesiones fueron palpables (57,1%), se presentaron como nódulos (67,1%), fueron menores de 2cm (64,8%), se localizaron en el cuadrante supero-externo (49,1%), se trataba de carcinomas ductales (85,7%), con infiltración (66,2%) y el grado de diferenciación histológica fue II (44,8%). Con la gammagrafía prequirúrgica se detectó el ganglio centinela en el 97,6% de los casos, y en el quirófano el 95,7%. Se observó una recurrencia axilar. En el estudio asociativo, las variables «linfogammagrafía prequirúrgica» y «grado de diferenciación histológica del tumor» mostraron una asociación estadísticamente significativa con la detección del ganglio centinela en el quirófano.
ConclusiónLa probabilidad de no detectar el ganglio centinela durante la intervención quirúrgica es mayor en los pacientes con tumores de alto grado histológico o en las que no se ha conseguido verlo en la linfogammagrafía prequirúrgica.