To analyze whether there are significant differences in the objective quantitative parameters obtained in the postprocessing of dual-energy CT enterography studies between bowel segments with radiologic signs of Crohn's disease and radiologically normal segments.
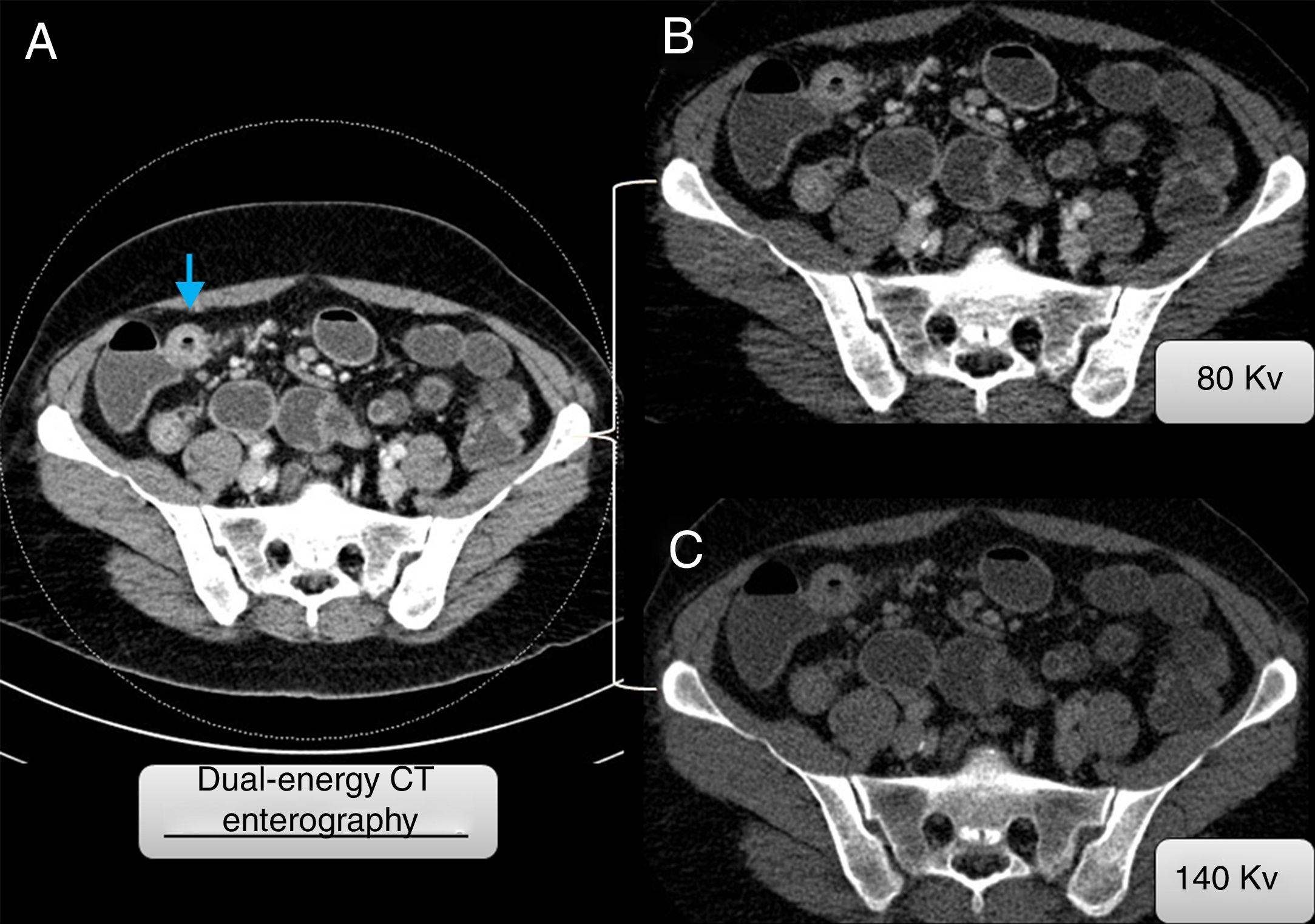
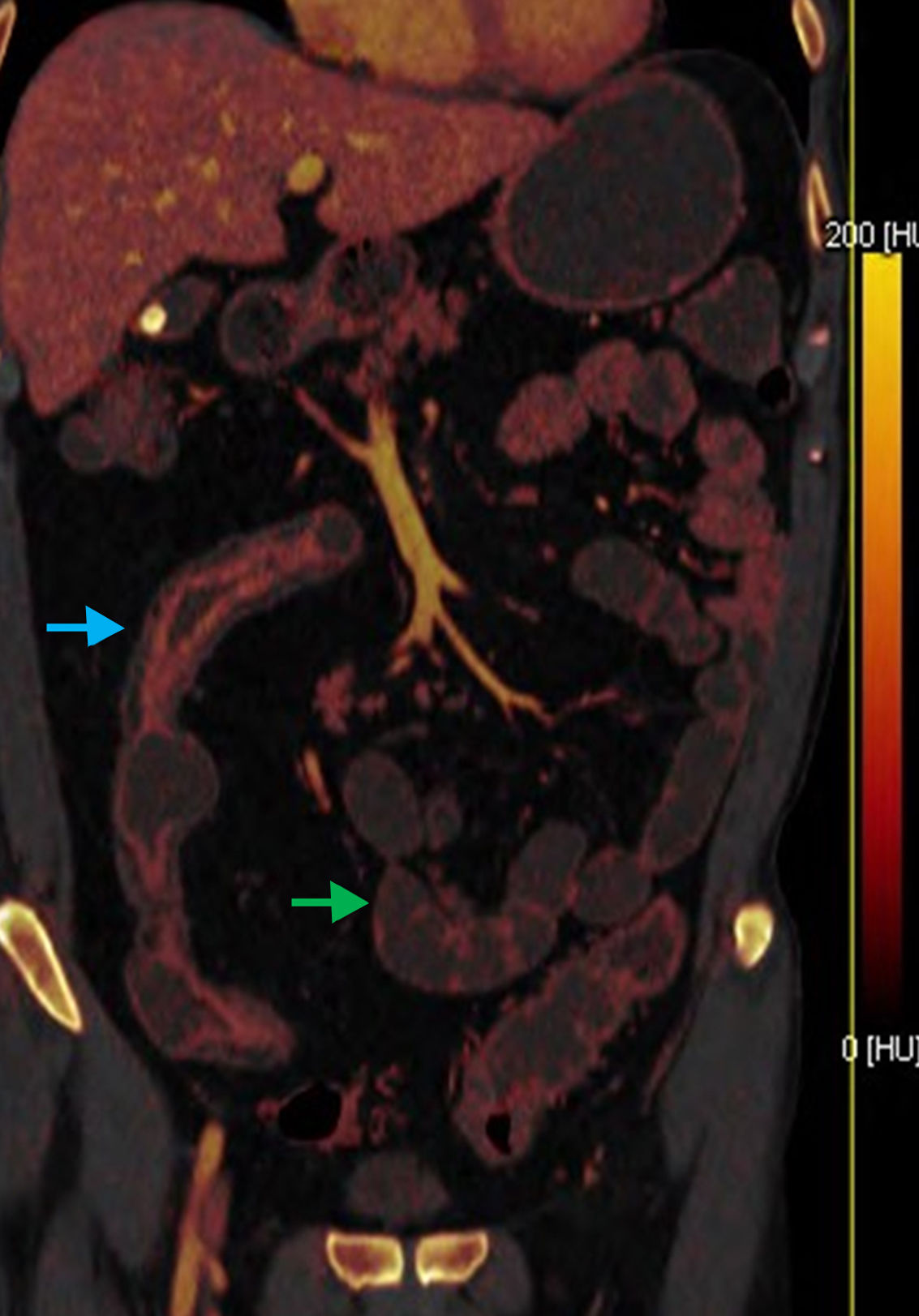
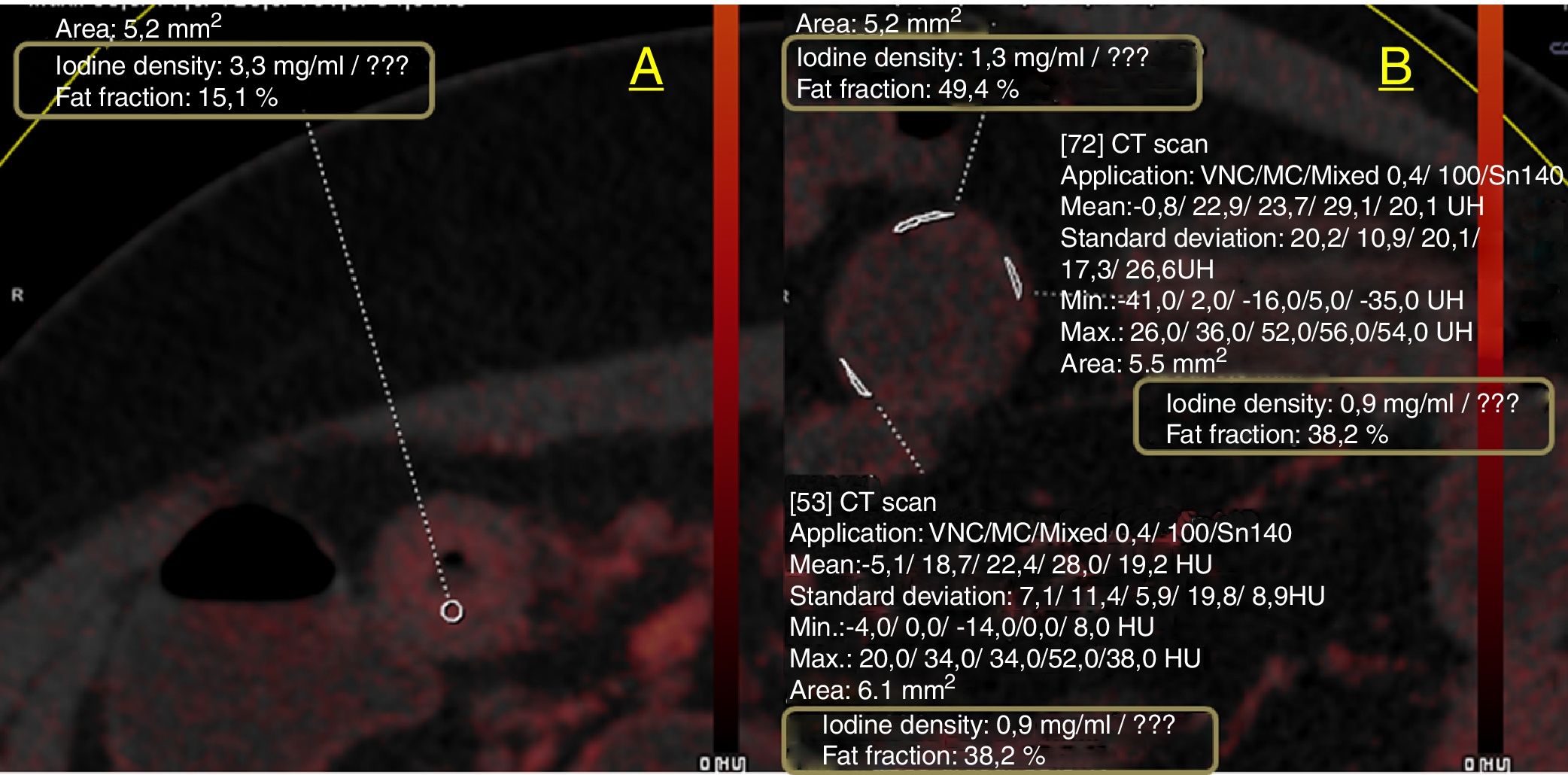
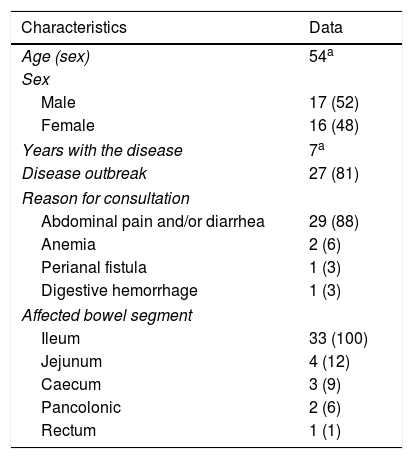
Material and methodsThis retrospective study analyzed 33 patients (16 men and 17 women; mean age 54 years) with known Crohn's disease who underwent CT enterography on a dual-energy scanner with oral sorbitol and intravenous contrast material in the portal phase. Images obtained with dual energy were postprocessed to obtain color maps (iodine maps). For each patient, regions of interest were traced on these color maps and the density of iodine (mg/ml) and the fat fraction (%) were calculated for the wall of a pathologic bowel segment with radiologic signs of Crohn's disease and for the wall of a healthy bowel segment; the differences in these parameters between the two segments were analyzed.
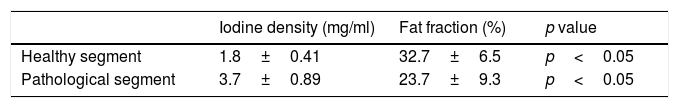
ResultsThe density of iodine was lower in the radiologically normal segments than in the pathologic segments [1.8±0.4mg/ml vs. 3.7±0.9mg/ml; p<0.05].
The fat fraction was higher in the radiologically normal segments than in the pathologic segments [32.42%±6.5 vs. 22.23%±9.4; p<0.05].
ConclusionThere are significant differences in the iodine density and fat fraction between bowel segments with radiologic signs of Crohn's disease and radiologically normal segments.
Analizar si existen diferencias significativas en los parámetros cuantitativos obtenidos en el posprocesado de estudios con enterografía por tomografía computarizada (entero-TC) de doble energía entre segmentos intestinales con signos radiológicos de enfermedad de Crohn (EC) y segmentos radiológicamente normales.
Material y métodosEstudio retrospectivo en el que se analizan 33 pacientes con EC conocida (16 hombres y 17 mujeres), con una media de edad de 54 años. Se seleccionan aquellos con una entero-TC con protocolo de doble energía. Todas las exploraciones están realizadas con una solución de sorbitol oral y contraste intravenoso en fase portal. Mediante técnicas de posprocesado de las imágenes adquiridas con doble energía se obtienen mapas de color (mapas de yodo). Sobre estos mapas de color, mediante la realización de regiones de interés se cuantifican en cada paciente la densidad de yodo (mg/ml) y la fracción de grasa (%) de la pared de un segmento intestinal patológico con signos radiológicos de EC y de un segmento sano, y se analiza si existen diferencias entre ambos.
ResultadosLa cuantificación de yodo en los segmentos sanos es 1,8 (± 0,4) mg/ml, y en los segmentos enfermos es 3,7 (± 0,9) mg/ml (p <0,05). La fracción de grasa presente en la pared de los segmentos sanos es del 32,42% (± 6,5), y en los segmentos afectados es del 22,23% (± 9,4) (p <0,05).
ConclusiónExisten diferencias significativas en la cuantificación de la densidad de yodo y la fracción de grasa entre segmentos intestinales con signos radiológicos de EC y segmentos radiológicamente normales.