To determine the most common clinical indications for different diagnostic neuroimaging tests. To analyze the diagnostic yield for each type of test in function of its clinical indication. To quantify the number of additional imaging tests generated as a consequence of pathological findings on the initial study or of the physician's requesting an inappropriate study.
Material and methodsWe reviewed the clinical indications and radiological report for computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) studies of the brain, head, and neck carried out during a 30-day period in three intermediate level hospitals with similar characteristics. We counted the studies with pathological findings and those with normal findings. We recorded cases that required additional imaging studies.
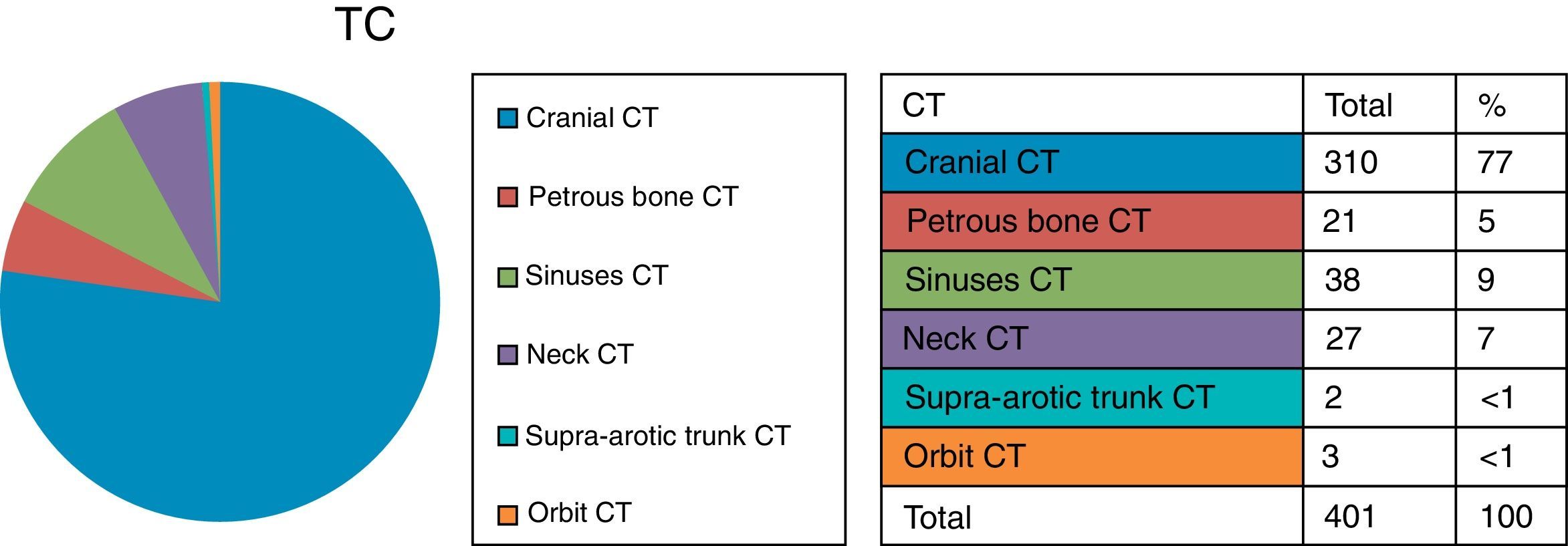
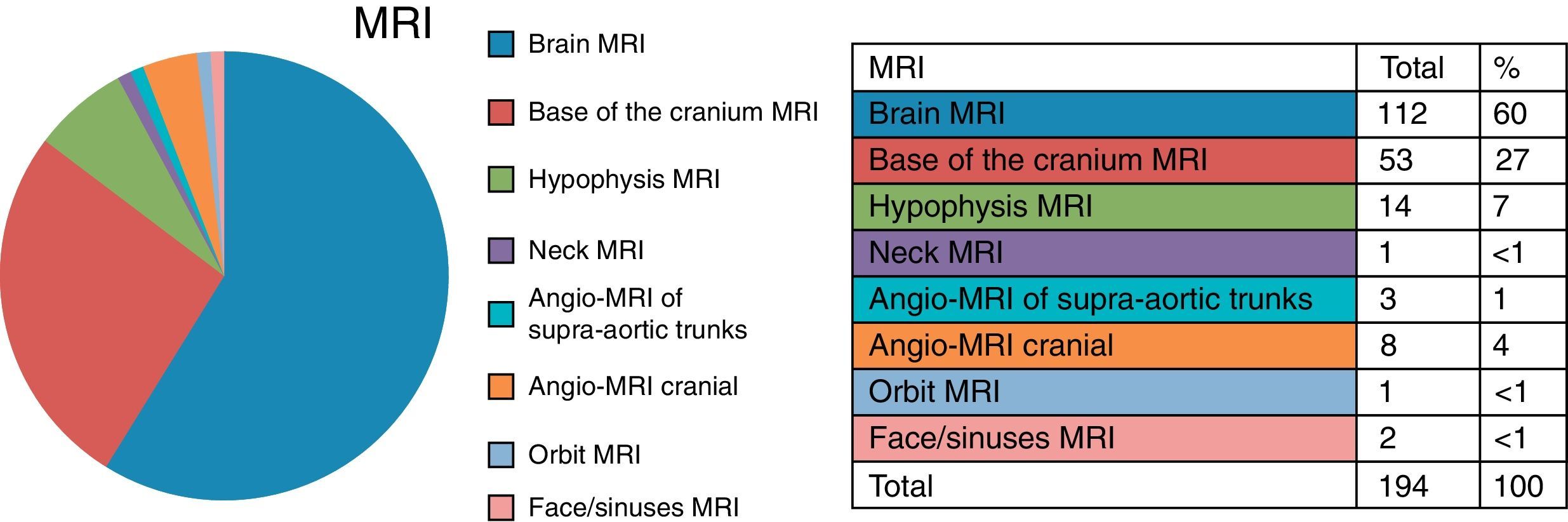
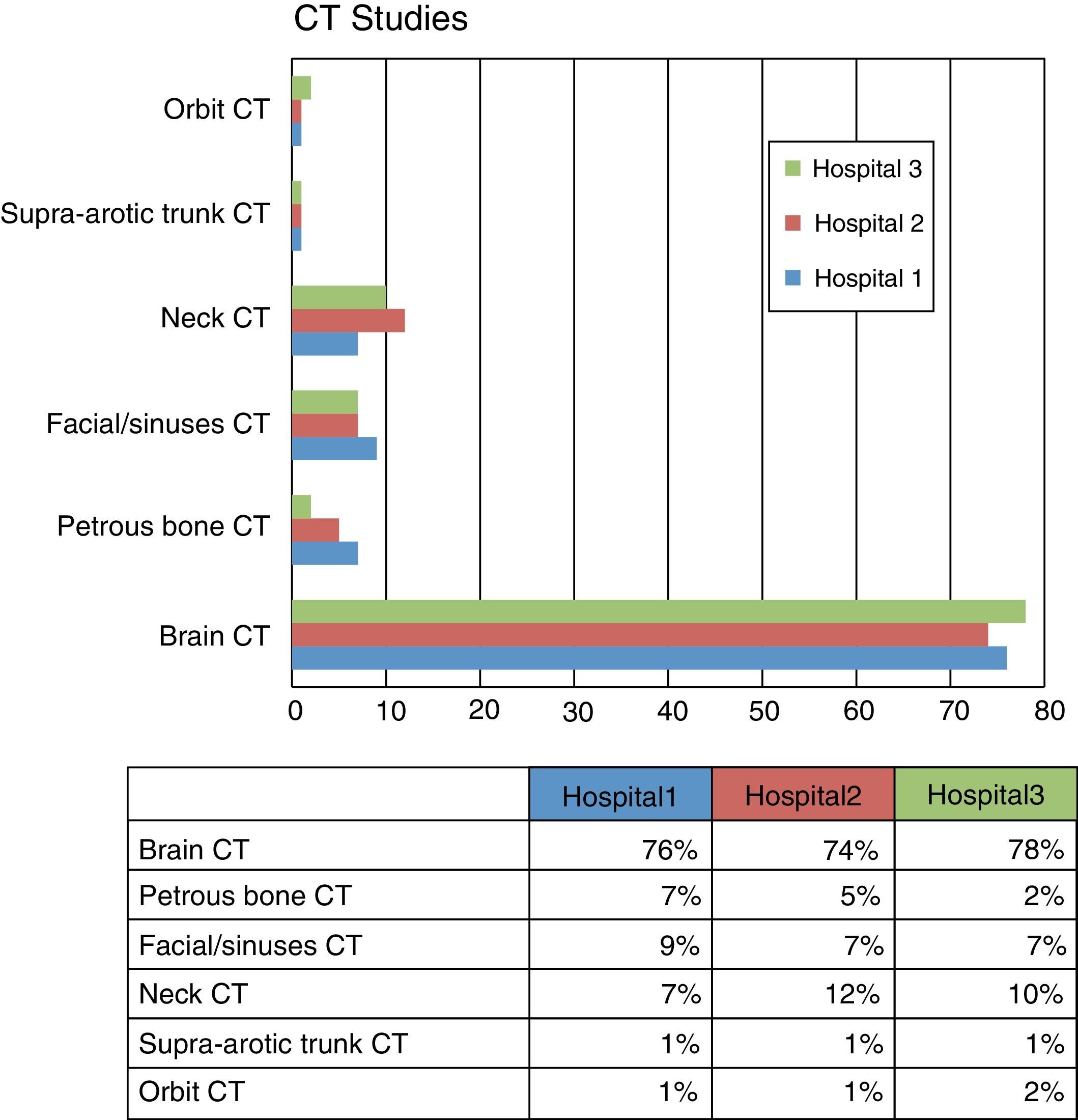
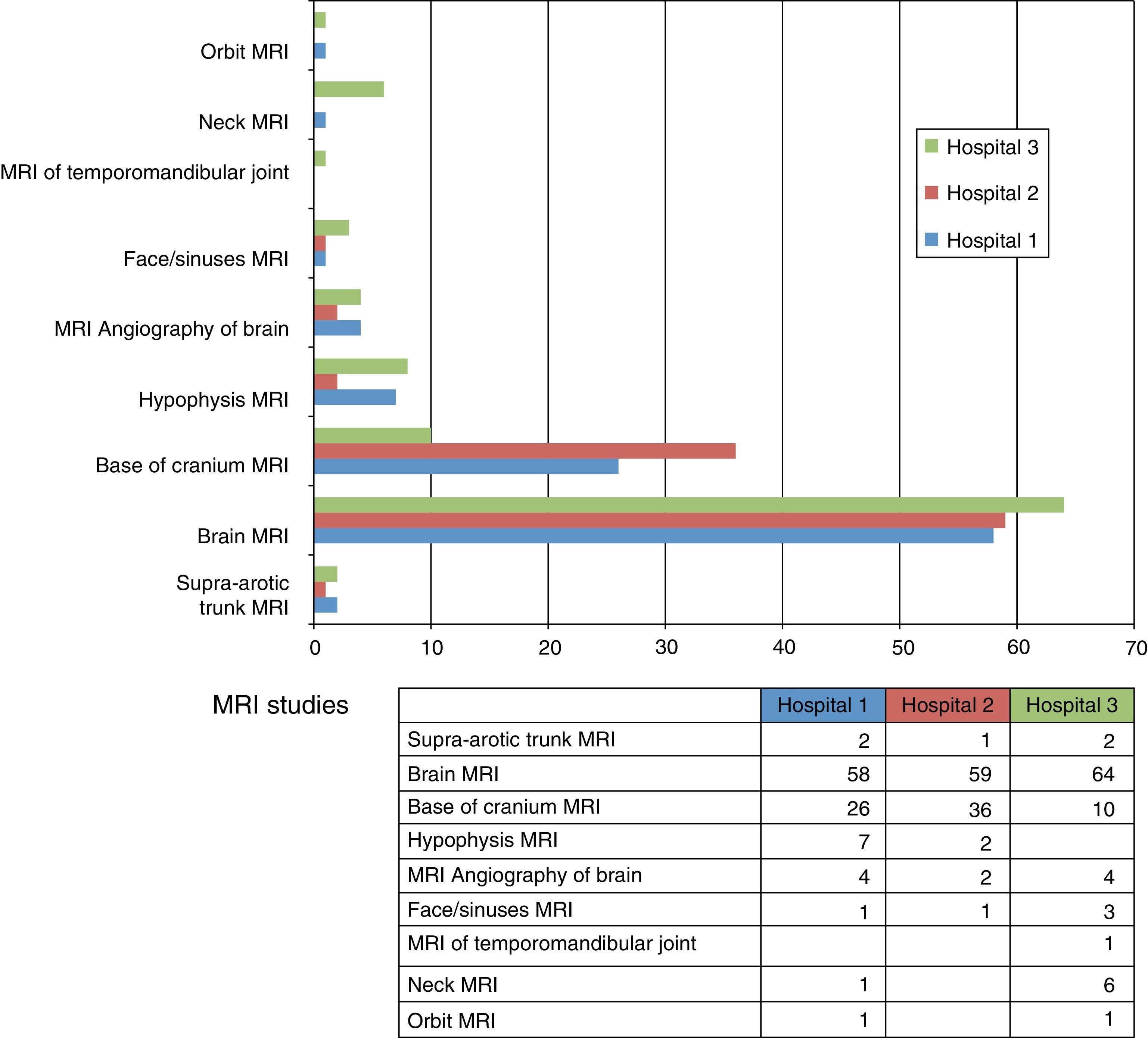
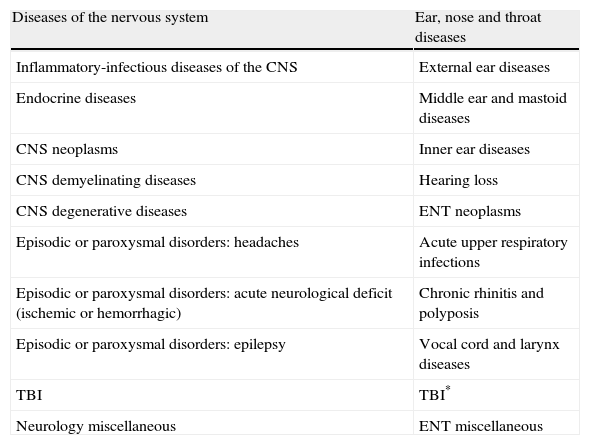
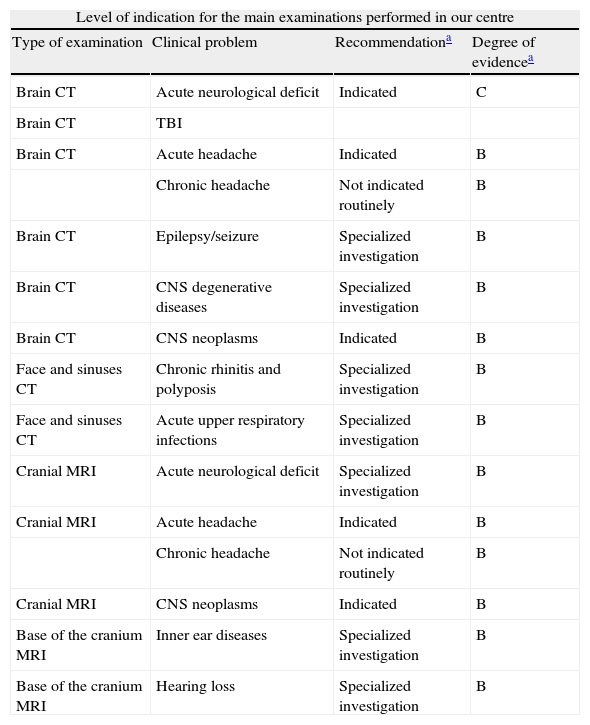
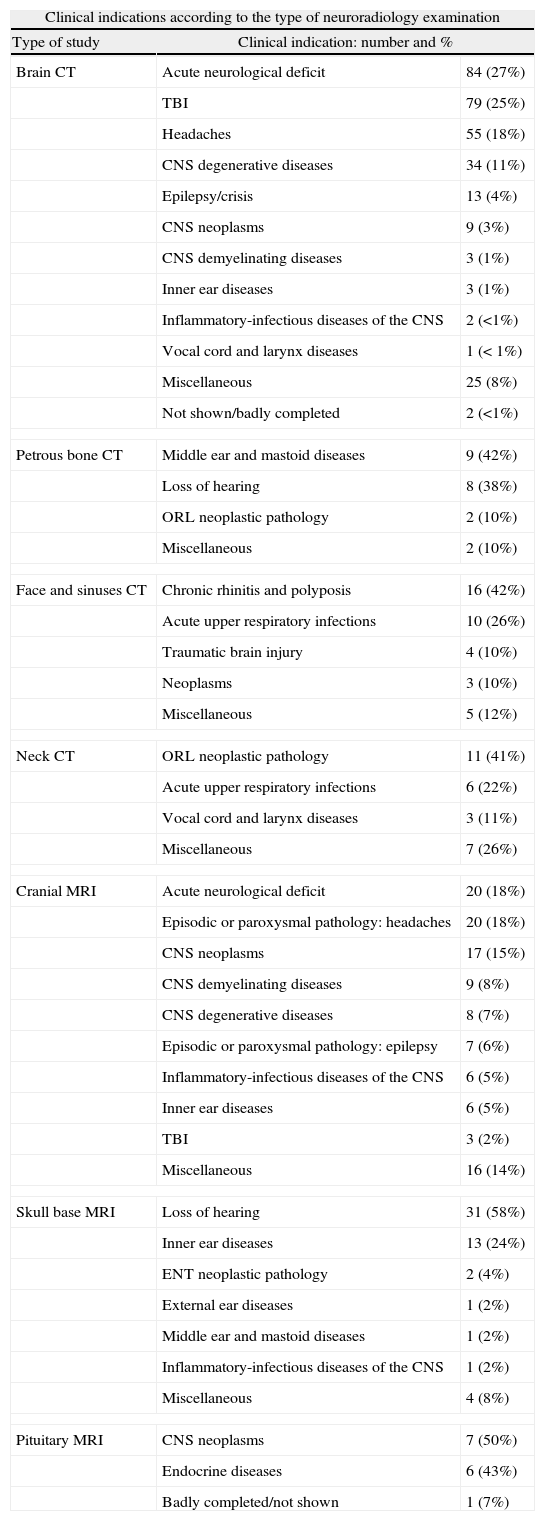
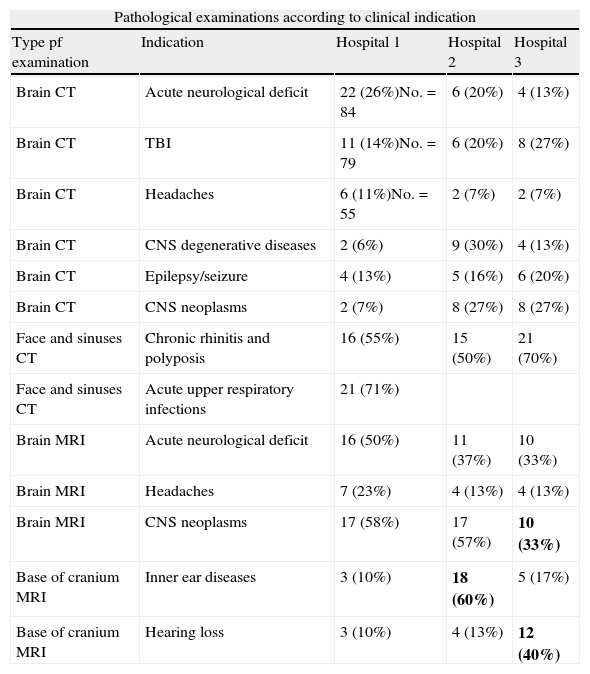
ResultsCT and MRI studies of the brain are the most frequently requested neuroimaging studies. The most common indications for examinations requested from the neurology department were headache, head trauma, and acute neurological deficit. The most common indication for examinations requested from the ear, nose, and throat department was hearing loss. The percentage of examinations with pathological findings ranged from 6% to 71% depending on the clinical indication. Additional imaging studies were necessary in 3.5% of the cases.
ConclusionsMost neuroimaging studies are performed for especially prevalent clinical indications; however, in many cases the degree of concordance between the clinical and radiological diagnosis shows there is much room for improvement.
Conocer las indicaciones clínicas más frecuentes que dan lugar a las distintas pruebas diagnósticas en neurorradiología. Analizar para cada tipo de exploración la rentabilidad diagnóstica de la prueba solicitada según la indicación clínica. Cuantificar el número de exploraciones radiológicas adicionales generadas como consecuencia de la detección de patología en el estudio inicial o de la solicitud de una exploración inadecuada por parte del médico peticionario.
Material y métodosSe ha revisado la indicación clínica y el informe radiológico de las exploraciones de tomografía computarizada (TC) y resonancia magnética (RM) de cerebro, cabeza y cuello realizadas durante un período de 30 días en tres hospitales de nivel intermedio de similares características. Se contabilizan los estudios que presentan hallazgos patológicos y los normales. Se recogen aquellos casos que precisaron de algún estudio radiológico adicional.
ResultadosLa TC de cerebro y la RM cerebral son las exploraciones más solicitadas. En el área de neurología son la cefalea, el traumatismo craneoencefálico y el déficit neurológico agudo las indicaciones que justifican la mayoría de los estudios. En el área otorrinolaringológica, la pérdida de audición es la indicación de mayor demanda. El porcentaje de exploraciones patológicas oscila entre el 6 y el 71% según la indicación clínica. En un 3,5% de los casos se precisaron exploraciones radiológicas adicionales.
ConclusionesLa mayoría de las exploraciones neurorradiológicas derivan de un grupo de indicaciones clínicas especialmente prevalentes; sin embargo, en muchos casos el grado de concordancia entre el diagnóstico clínico y el radiológico presenta un amplio margen de mejora.