We present a case of postoperative pseudomeningocele that primarily manifested as headache, apnoea, and syncope. Our patient was a 64-year-old woman with history of arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, dyslipidaemia, and depression, who was assessed due to lumbar sciatic pain secondary to L5/S1 spinal disc herniation with right S1 root involvement. The lack of pain improvement with conservative medical treatment led to the surgical indication of right L5/S1 microdiscectomy, which had been performed 24 months earlier and once more 8 months earlier due to symptom relapse; in a follow-up MRI study performed after surgery, we observed significant residual compression of the S1 root in the right L5/S1 lateral recess, caused by calcified disc material. During the second surgical procedure, an additional right microdiscectomy was performed, with intraoperative repair of an incidental durotomy affecting the right S1 nerve root using an autologous fat patch with fibrin sealant (Tisseel®). Two months after the second surgical intervention, the patient experienced episodes of sudden-onset holocranial headache, characterised by intense stabbing pain predominantly affecting the bilateral occipital region. Pain radiated to the neck and manifested in the decubitus position and while standing, which was usually followed by transient, sudden-onset loss of consciousness, with no other prodromal signs, neck extension, flexion of the upper limbs, sweating, pallor, or low skin temperature. After the episodes, the patient fully recovered consciousness in less than a minute, with no subsequent confusion or disorientation. The frequency of these events progressively increased, from one every 2 weeks to 3 per week. The neurological examination revealed normal eye fundus and no relevant focal deficits; headache was triggered by palpation of a subcutaneous collection under the surgical scar (of otherwise healthy appearance) in the lumbosacral region, which was suggestive of tension pseudomeningocele. In addition to the clinical symptoms described, the patient also presented an episode of apnoea with spontaneous recovery while in the supine position, with no respiratory arrest. An additional postoperative lumbosacral MRI study (Fig. 1) showed a collection measuring a maximum of 7 cm in diameter (in the craniocaudal direction) in the subcutaneous space, compatible with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and apparently originating in the right L5/S1 lateral recess, which was diagnosed as postoperative pseudomeningocele. An emergency procedure was performed to repair the pseudomeningocele by identification and microsurgical suture of the edges of the durotomy affecting the right S1 nerve root; this procedure was uneventful. After the surgery, and during outpatient follow-up, we observed no further clinical episodes similar to those previously described.
Postoperative pseudomeningocele is an extravasated collection of CSF resulting from a persistent dural tear after surgery (spinal surgery, in our case). The literature reports a low incidence rate, between 0.068% and 2%.1 It is usually asymptomatic, although pseudomeningocele may also manifest as radiculopathy, persistent thoracolumbar pain, myelopathy, infection, meningeal symptoms,1–3 and headache.3–5 Some isolated reports describe decerebrate rigidity,1 transient anoxic seizures,2 syncope,3,6 communicating hydrocephalus,7 and diplopia.8,9 Our patient presented headache, accompanied by apnoea episodes and repeated syncope, when in the decubitus position and while sitting, with the symptoms being clearly elicitable by direct compression of the pseudomeningocele during examination. This palpation would cause an abrupt flow of CSF from the pseudomeningocele to the subarachnoid space and the resulting increase in pressure. Therefore, CSF hypertension is the mechanism that best explains the pathophysiology of our patient’s symptoms.2,6 CSF hypotension has also been proposed as a mechanism of these clinical manifestations in previous reports.3–5 Treatment of asymptomatic cases is usually conservative, but surgery is needed in patients presenting symptoms like those described.1–5
Please cite this article as: Sanabria Sanchinel AA, Lin Y, Rodríguez Rubio D. Seudomeningocele: cefalea, apnea y síncope. Neurología. 2021;36:654–656.




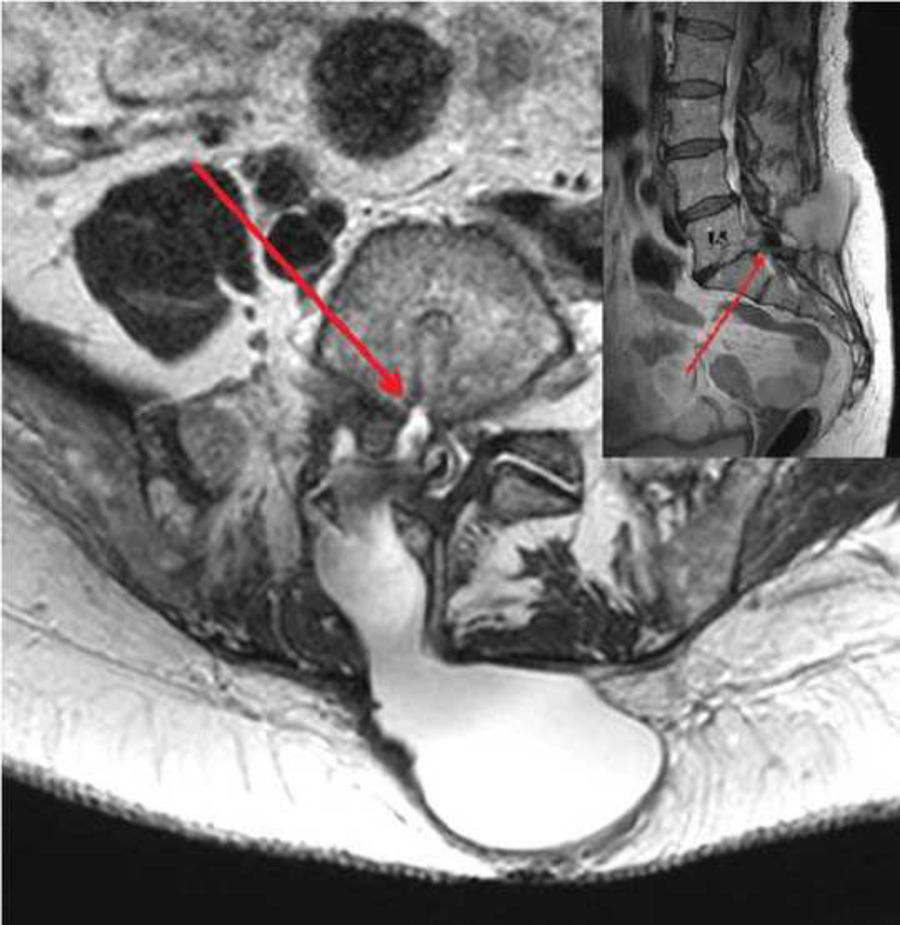
![MRI study (axial [main image] and sagittal [small window] T2-weighted sequences) showing pseudomeningocele in the subcutaneous space adjacent to the L5 vertebra and measuring a maximum diameter of 7 cm, with a fistula between the dural sac and the collection at the L5/S1 level. MRI study (axial [main image] and sagittal [small window] T2-weighted sequences) showing pseudomeningocele in the subcutaneous space adjacent to the L5 vertebra and measuring a maximum diameter of 7 cm, with a fistula between the dural sac and the collection at the L5/S1 level.](https://static.elsevier.es/multimedia/21735808/0000003600000008/v1_202110130604/S2173580821001012/v1_202110130604/en/main.assets/thumbnail/gr1.jpeg?xkr=ue/ImdikoIMrsJoerZ+w96p5LBcBpyJTqfwgorxm+Ow=)

