Previous observational studies have suggested that low vitamin D status is associated with high circulating C-reactive protein levels, as well as other plasma inflammatory cytokines. However, there is no study to explore the relationship between vitamin D status and Lp-PLA2, a new biomarker of vascular-specific inflammation. The aim of this study was to examine the association between vitamin D status and circulating Lp-PLA2 levels in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Material and methodsThis descriptive cross-sectional study enrolled diabetic subjects who underwent physical examination at Taizhou People's Hospital between August 2016 and January 2017. Blood pressure, anthropometry, metabolic profiles, serum 25(OH)D levels and Lp-PLA2 mass levels were measured in all participants.
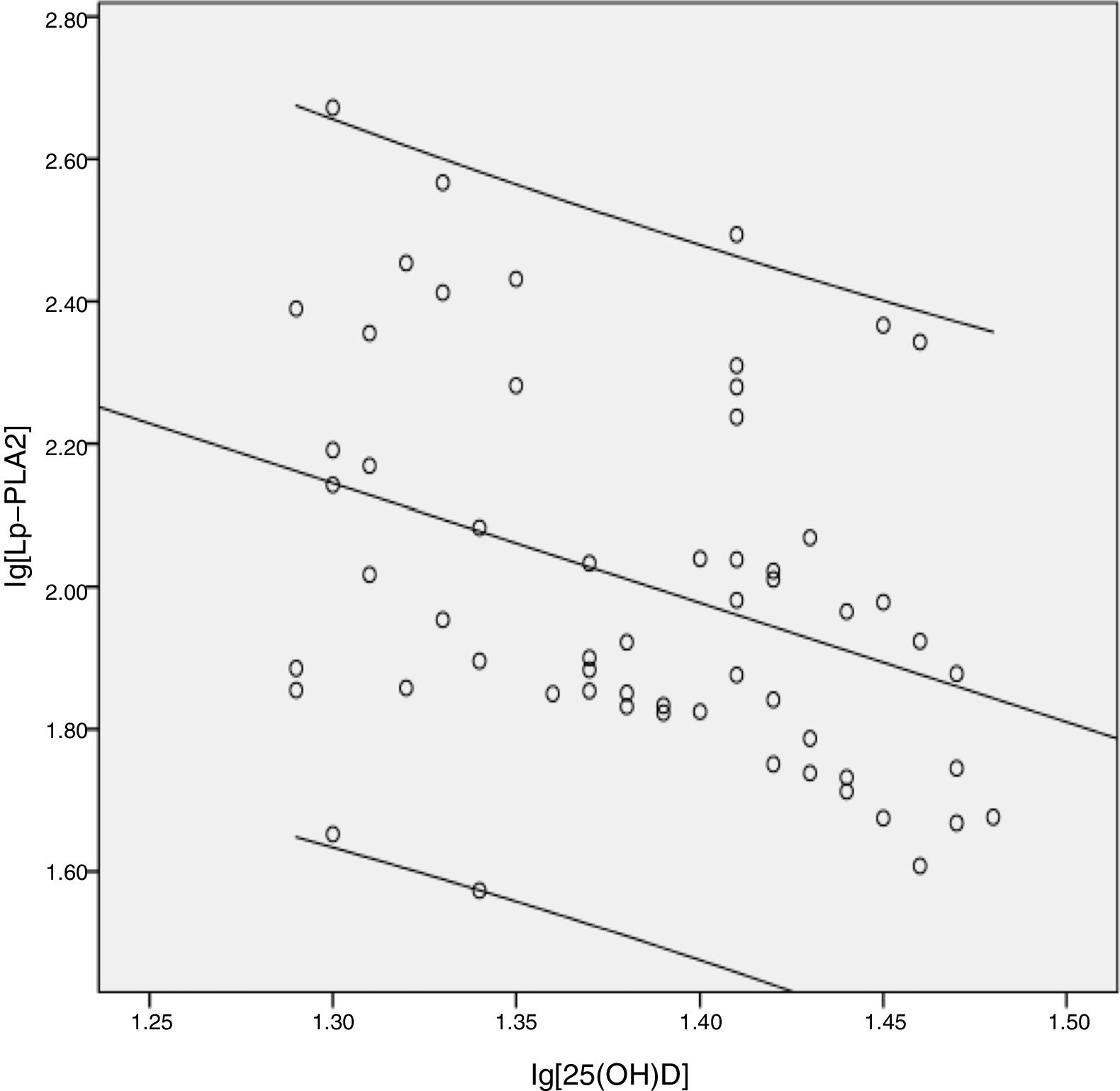
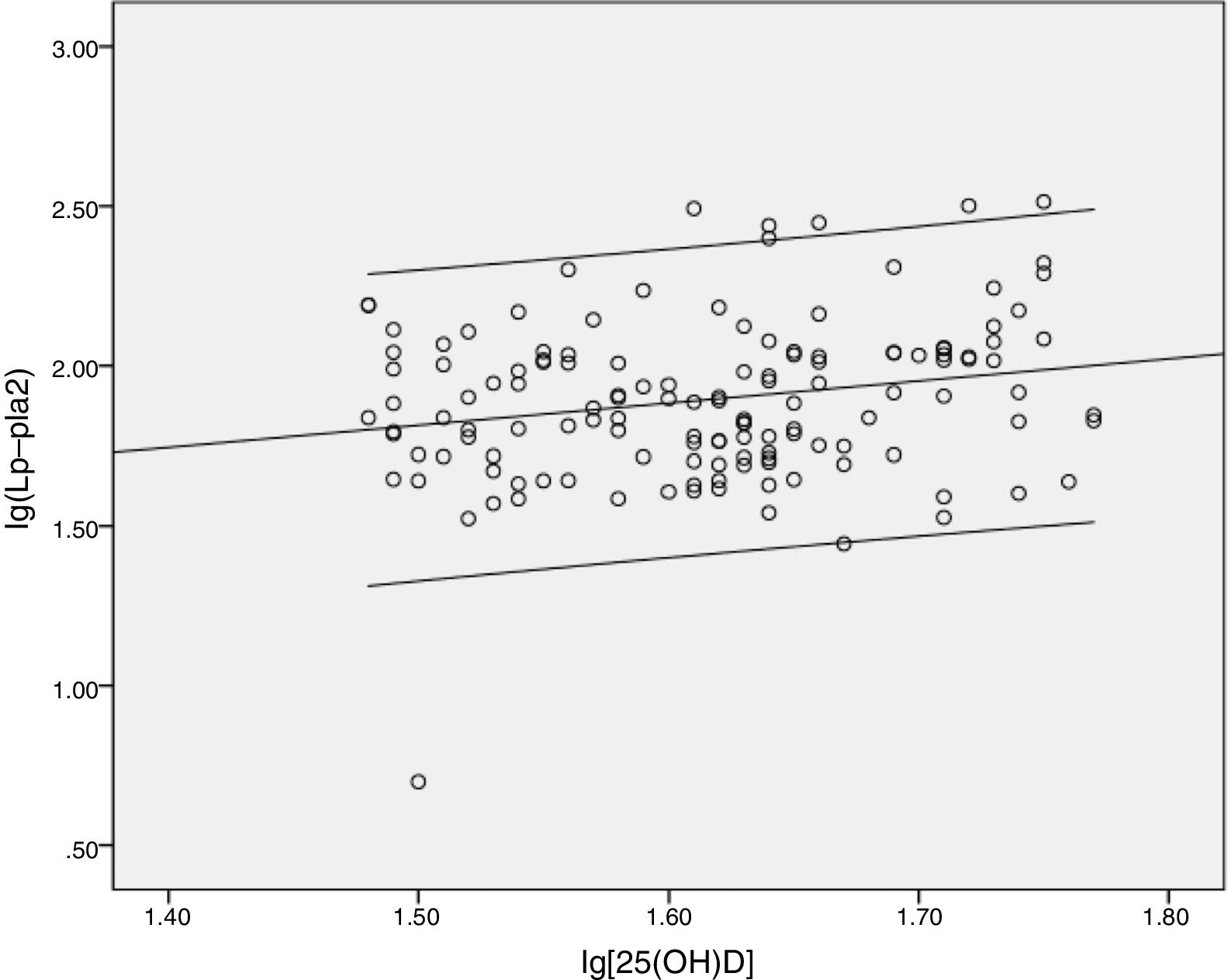
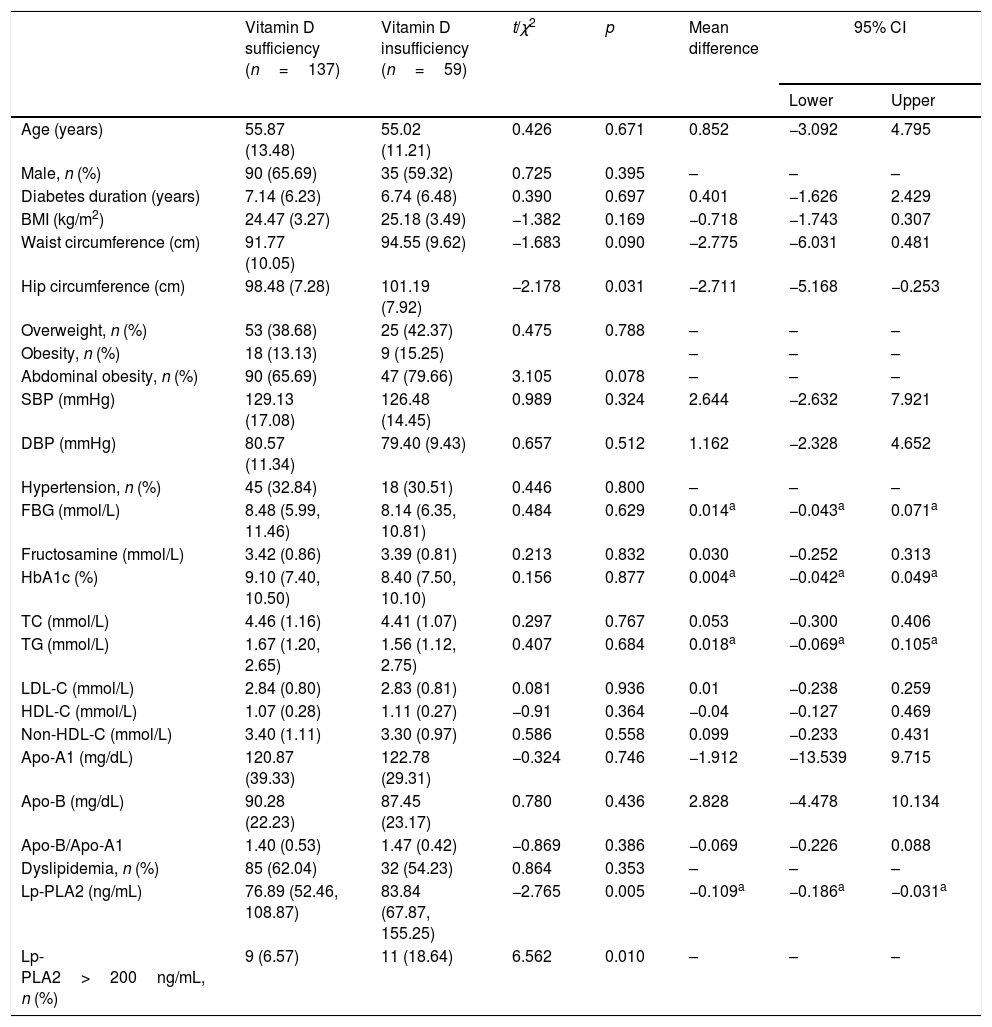
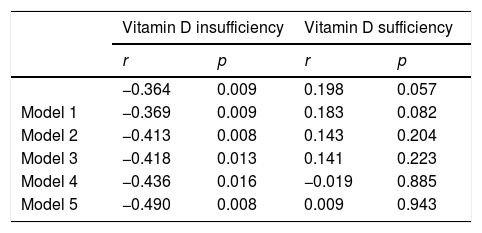
ResultsA total of 196 participants were recruited into this study. The vitamin D insufficiency group had higher serum LP-PLA2 levels than the vitamin D sufficiency group (t=−2.765, p=.005). A significant negative correlation was noted between Lp-PLA2 and 25(OH)D in the vitamin D insufficiency group (r=−0.364, p=0.009). However, no significant relationship between serum Lp-PLA2 concentration and 25(OH)D levels was observed in subjects with vitamin D sufficiency.
ConclusionsFrom this cohort of patients with type 2 diabetes, regardless of traditional cardiovascular risk factors, we observed a statistically significant inverse relation between Lp-PLA2 and 25(OH)D at levels <30ng/mL.
Los estudios observacionales previos han sugerido que la situación de los bajos niveles de la vitamina D está asociada a los altos niveles de la proteína C reactiva circulantes, así como a otras citoquinas inflamatorias en plasma. Sin embargo, no existe ningún estudio que explore la relación entre la situación de la vitamina D y la lipoproteína asociada a la fosfolipasa A2 (Lp-PLA2), un nuevo biomarcador de la inflamación específico vascular. El objetivo de este estudio fue examinar la asociación entre la situación de la vitamina D y los niveles circulantes de Lp-PLA2 en sujetos con diabetes mellitus tipo 2.
Material y métodosEstudio transversal descriptivo que incluyó sujetos diabéticos que fueron sometidos a un examen físico en el Hospital popular de Taizhou entre agosto de 2016 y enero de 2017. Se midieron en todos los participantes la presión arterial, la antropometría, los perfiles metabólicos, el suero de 25 (OH) niveles séricos de vitamina D y los niveles de masa de Lp-PLA2.
ResultadosUn total de 196 participantes fueron reclutados para este estudio. El grupo de insuficiencia de la vitamina D reflejó unos niveles superiores de Lp-PLA2 que el grupo con suficiencia de vitamina D (T=−2,765; p=0,005). Se observó una correlación negativa significativa entre Lp-PLA2 y 25(OH)D en el grupo con insuficiencia de vitamina D (R=−0,364; p=0,009). Sin embargo, no se observó ninguna relación significativa entre la concentración sérica de Lp-PLA2 y 25(OH)D en sujetos con niveles de suficiencia de vitamina D.
ConclusionesA partir de esta cohorte de pacientes con diabetes tipo 2, independientemente de los factores de riesgo cardiovascular, se observó una relación inversa entre Lp-PLA2, estadísticamente significativa, en los niveles de 25(OH)D<30ng/ml.