Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with rituximab (RTX) requires repeated cycles, but there is no well-established retreatment regimen in dose and frequency. The objective was to analyse the persistence of RTX treatment and factors that influence in terms of routine clinical practice.
MethodsRituximab in rheumatoid arthritis (RITAR Study) is an observational, retrospective study that analyses the persistence of RTX in a cohort from 2003 to 2015. Persistence was calculated by the Kaplan–Meier analysis; curves were compared with the Log-Rank test. Cox regression was used to quantify the risk of discontinuation and multivariate analyses were conducted to determine the factors associated with the persistence of the treatment.
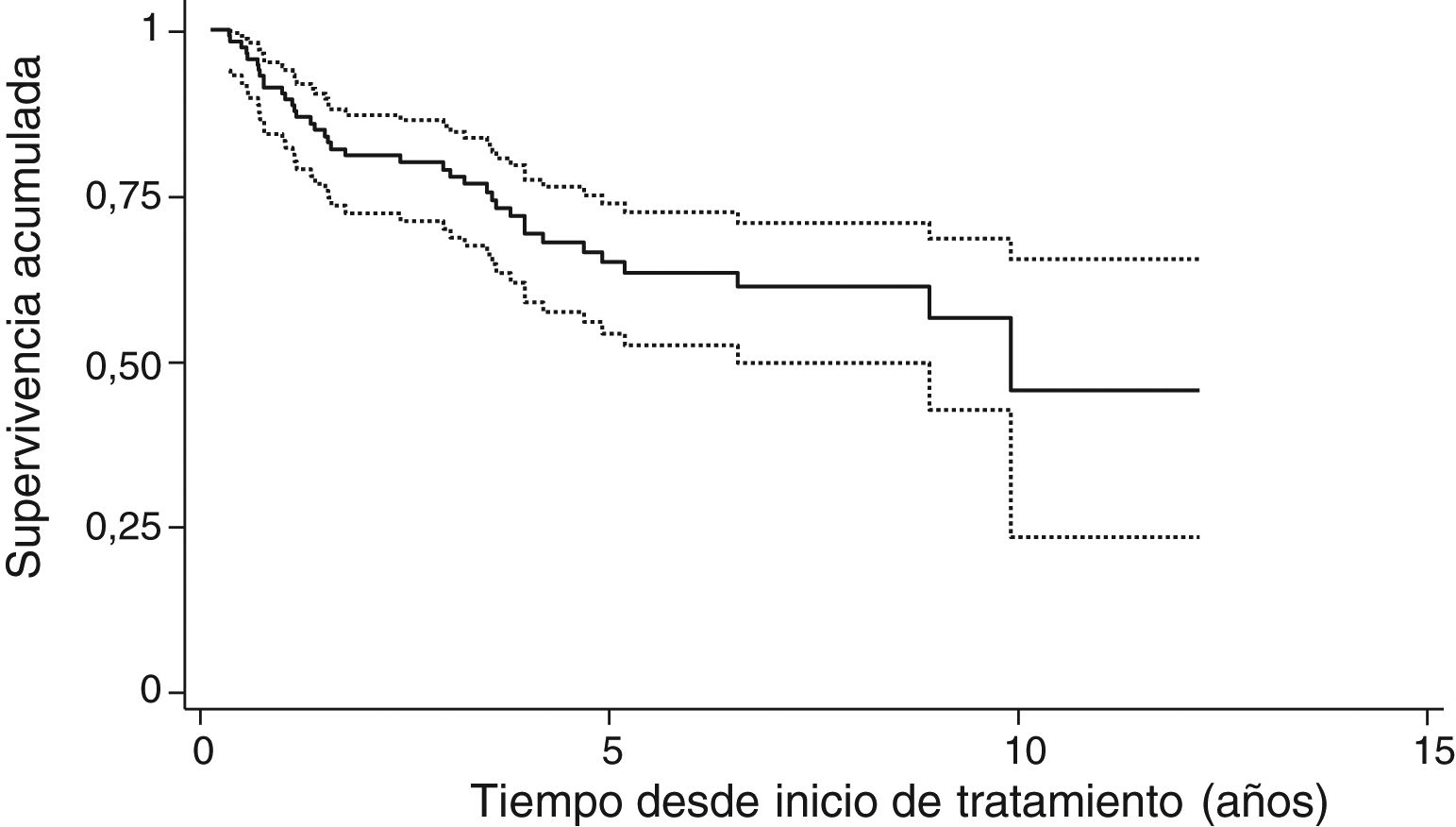
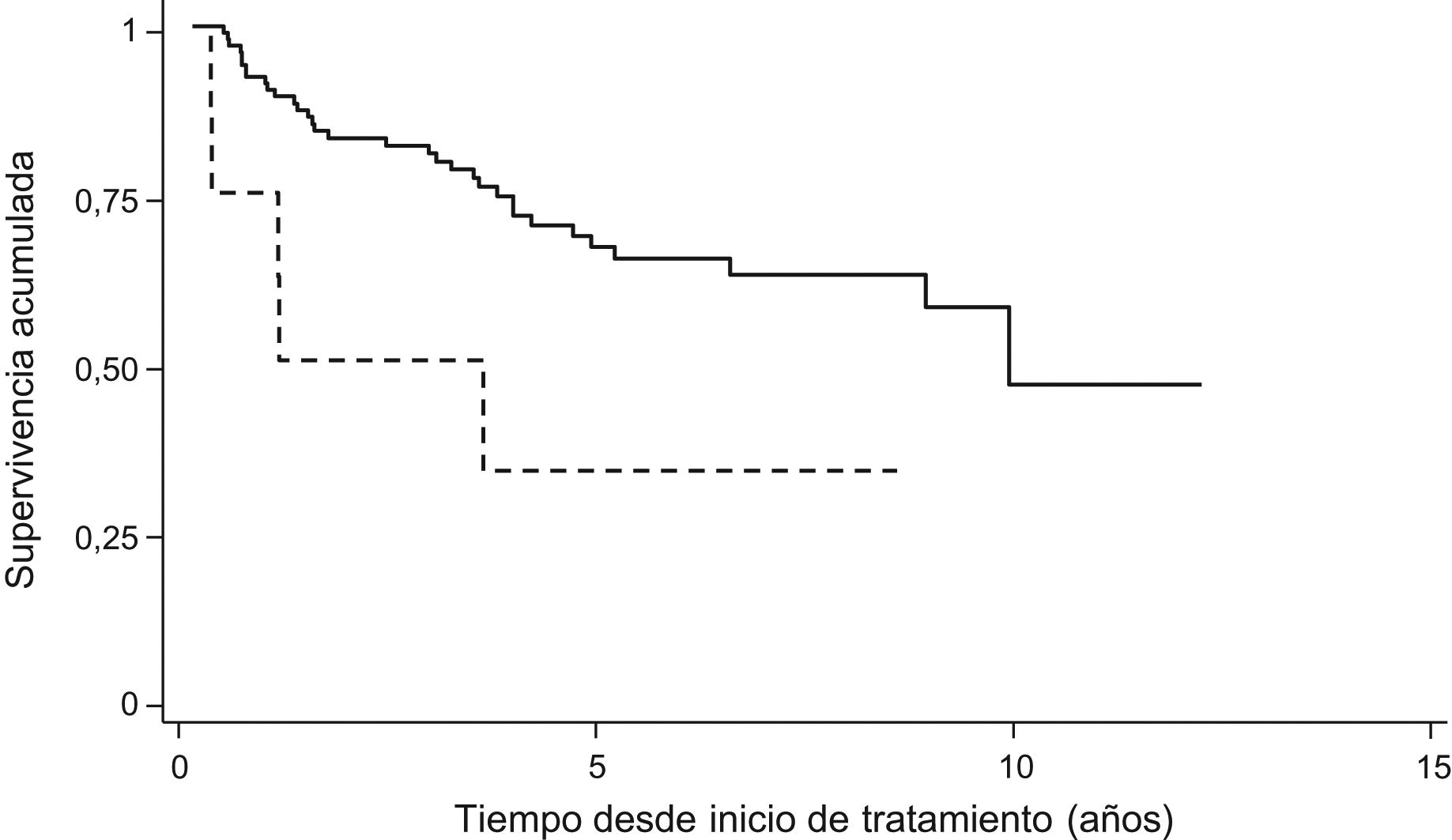
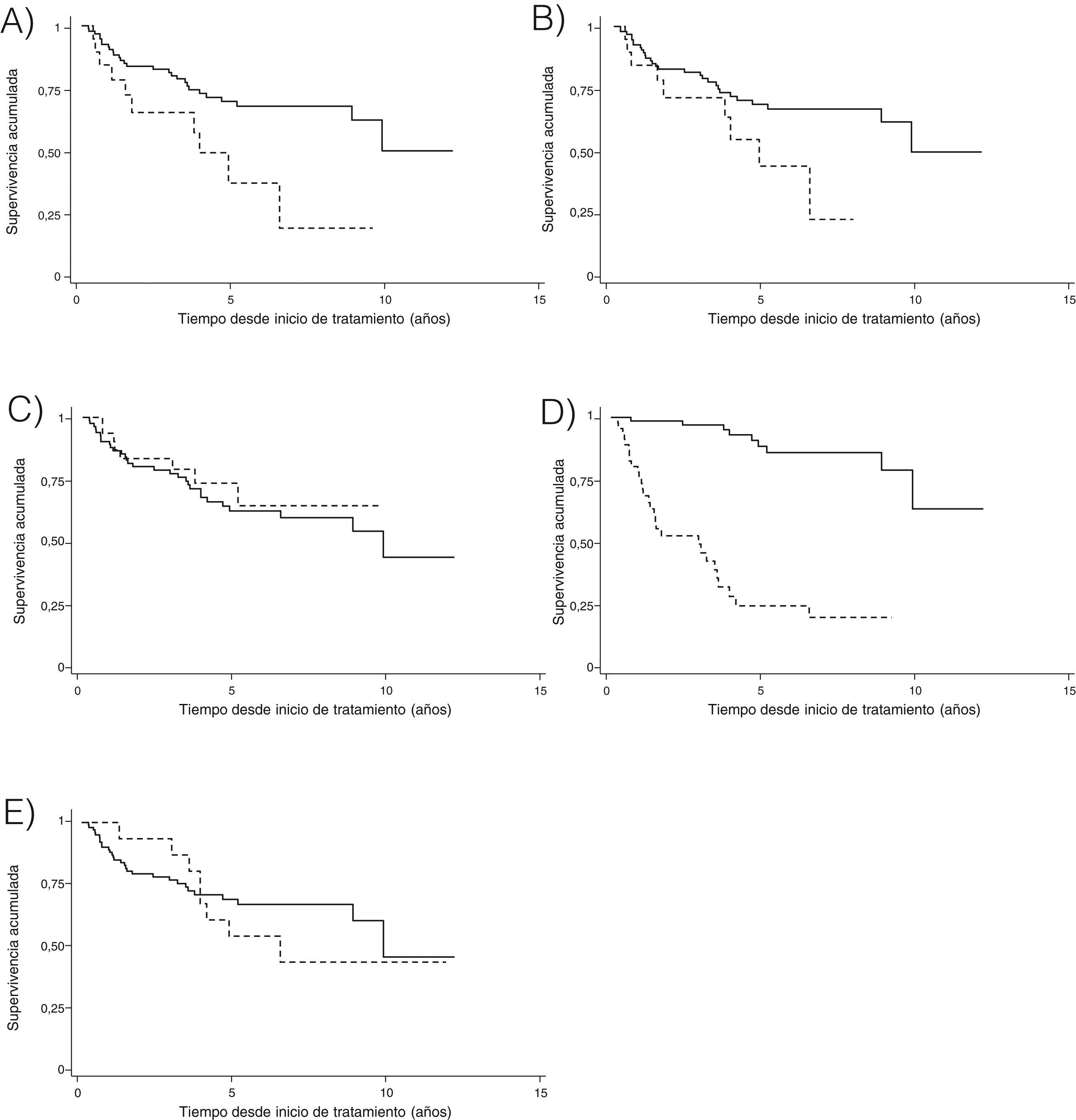
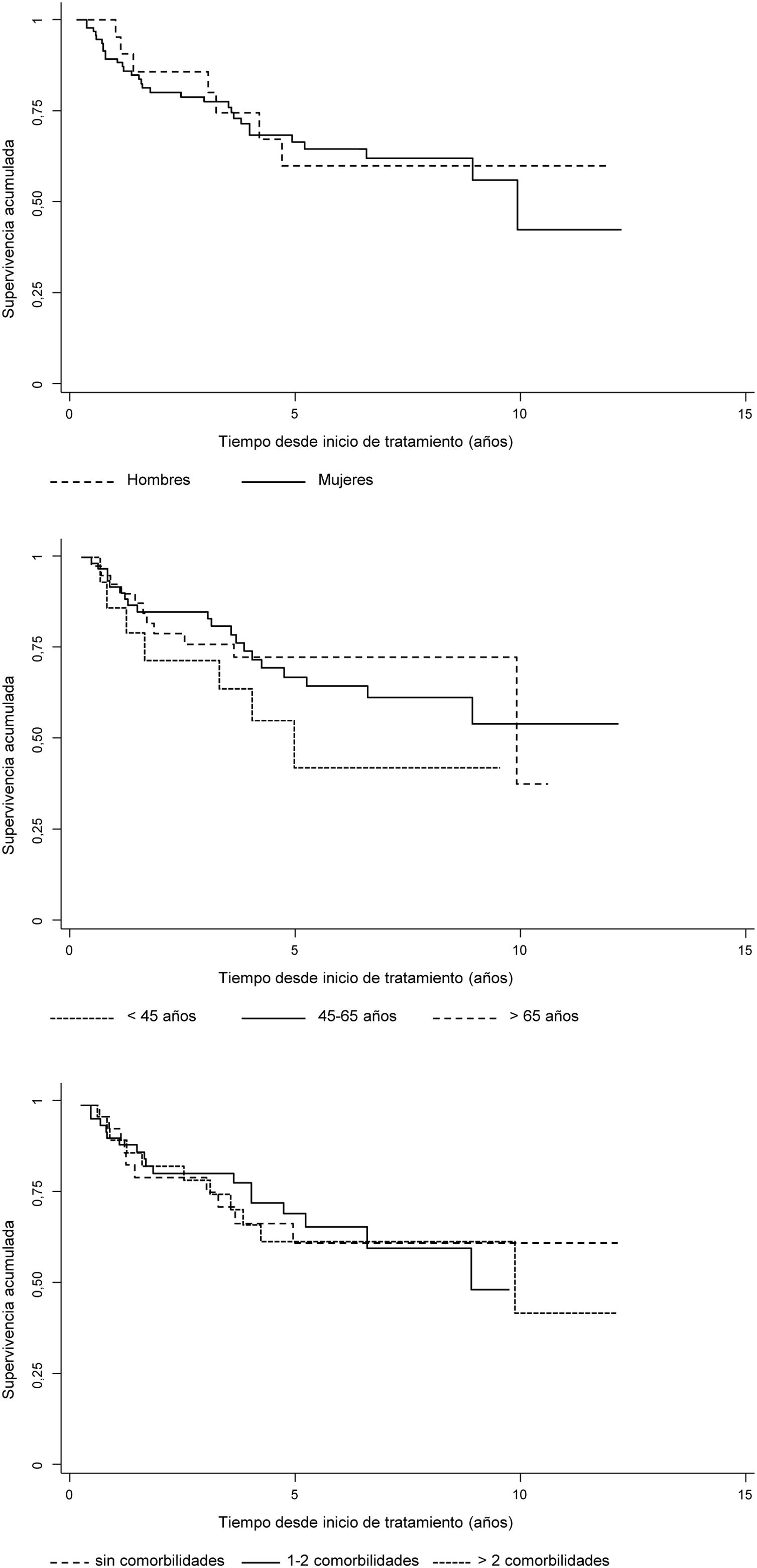
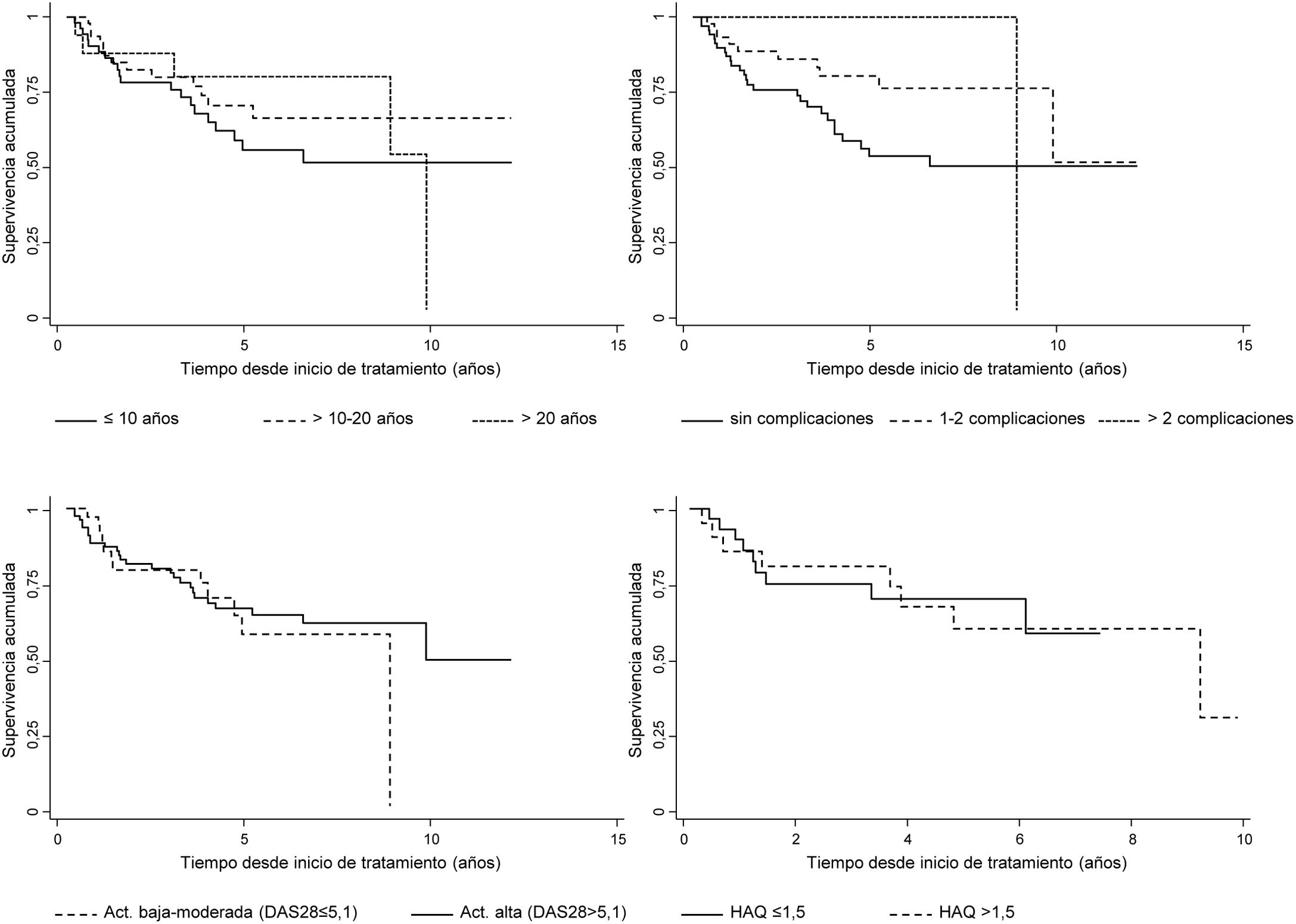
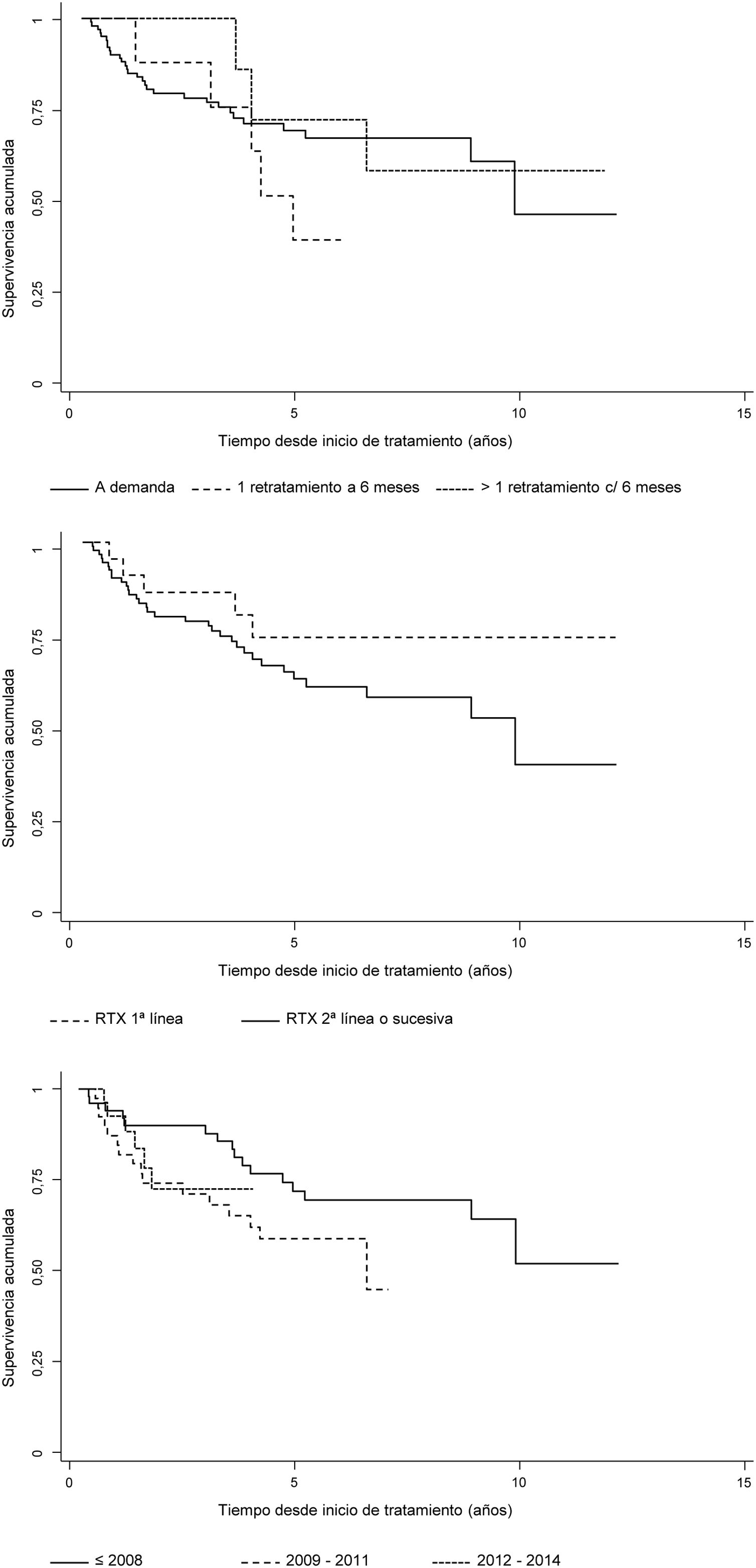
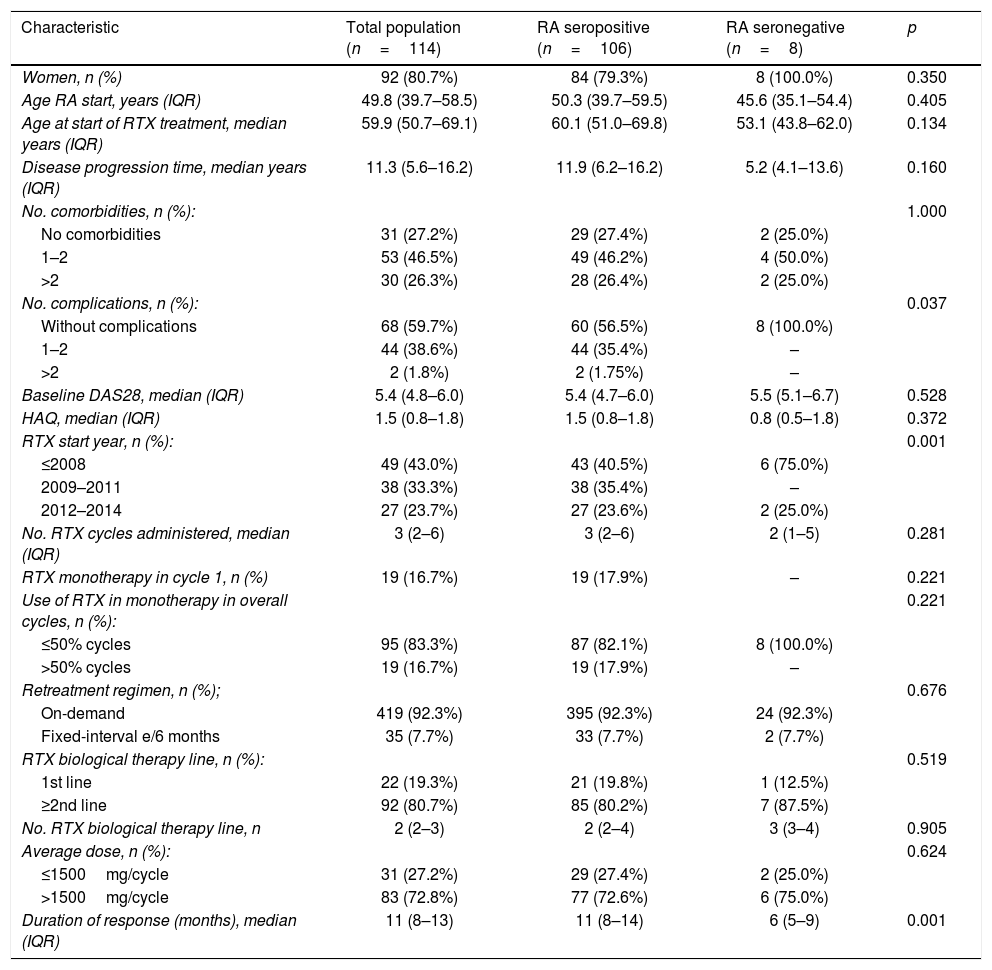
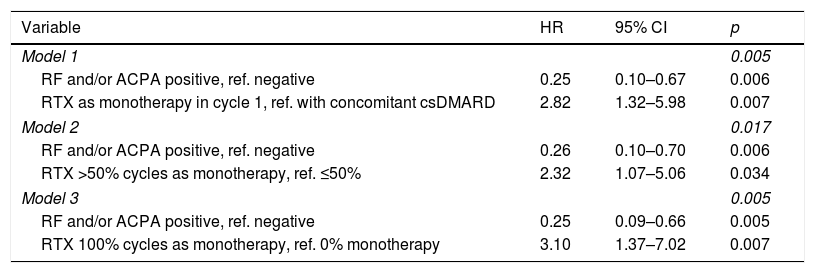
Results454 cycles of RTX in 114 patients were included. Median survival was 10.0 years and incidence rate of discontinuation was 7.7 per 100patients/year. Factors associated with persistence were autoantibody positivity and use of RTX in combination with csDMARDs. Sex, age, number of comorbidities, rheumatoid arthritis evolution, number of complications, basal DAS28, basal HAQ, number of lines of treatment, fixed or on demand retreatment and year of RTX starting were not associated. Multivariable models confirmed the relationship between autoantibody positivity, monotherapy and persistence of RTX.
ConclusionsThe persistence of RTX in clinical practice is higher in seropositive patients and in those who are treated with RTX associated with a csDMARD. Dose per cycle and retreatment frequency do not have a decisive role in rituximab persistence.
El tratamiento de la artritis reumatoide con rituximab (RTX) requiere ciclos repetidos y no existe una pauta bien establecida en dosis y frecuencia de retratamiento. El objetivo fue analizar la persistencia del tratamiento con RTX y los factores que influyen en condiciones de práctica clínica habitual.
Materiales y métodosRITuximab en Artritis Reumatoide (Estudio RITAR) es un estudio observacional, retrospectivo que analiza la persistencia de RTX en una cohorte desde 2003 hasta 2015. La persistencia se calculó por análisis de Kaplan-Meier, las curvas se compararon con el test del Log-Rank. Para cuantificar el riesgo de suspensión se utilizó la regresión de Cox, se realizaron análisis multivariables para determinar los factores asociados a la persistencia del tratamiento.
ResultadosSe incluyeon 454 ciclos de RTX pertenecientes a 114 pacientes. La mediana de supervivencia fue 10 años y la tasa de incidencia de suspensión 7,7 por cada 100 pacientes-año. Los factores asociados a la persistencia fueron la seropositividad, el uso de RTX combinado con FAMEsc. No estuvieron asociados sexo, edad, n.° de comorbilidades, tiempo de evolución, n.° de complicaciones, DAS28 basal, HAQ basal, número de líneas de tratamiento, pauta de retratamiento fijo o a demanda, año de inicio de RTX. Los modelos multivariables confirmaron la relación entre seropositividad, uso en monoterapia y persistencia de RTX.
ConclusionesLa persistencia de RTX en la práctica clínica es elevada en pacientes seropositivos y en aquellos que están tratados con RTX asociado a un FAMEsc. La dosis por ciclo y la frecuencia de retratamiento no tienen un papel determinante en la persistencia.