To achieve control of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) it is necessary to be able to evaluate its activity. The American College of Rheumatology (ACR) recommends for this purpose indexes of activity that can be performed by the patient (PAS-II and RAPID-3) and IA including medical evaluation with laboratory studies (DAS28 and SDAI) or without them (CDAI). The objective was to analyze the concordance between self-rated clinimetric evaluation and clinimetric evaluation performed by the physician.
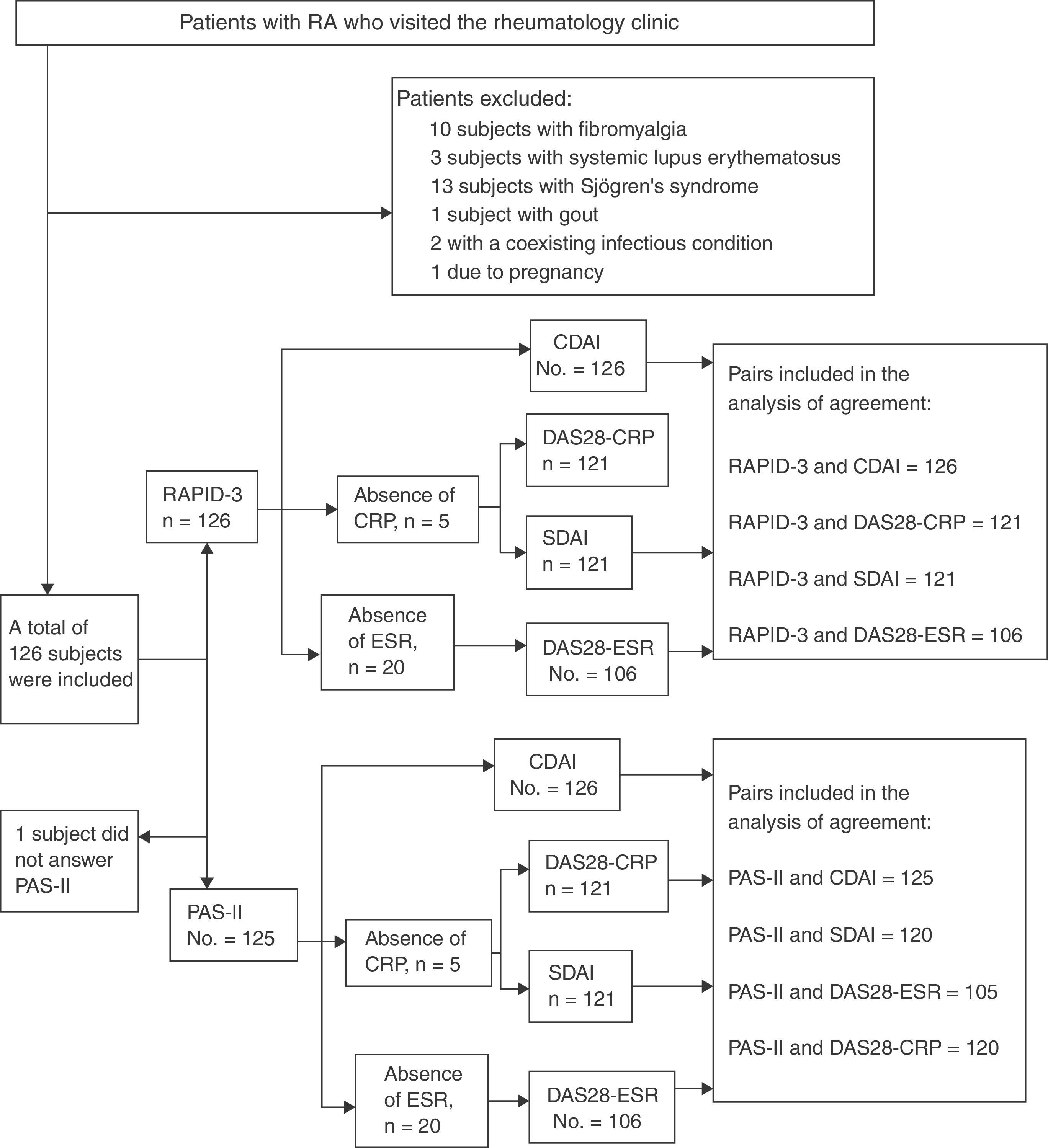
Patients and methodAnalytical cross-sectional study in 126 patients with RA. The agreement was evaluated through the weighted κ coefficient and the Krippendorff's α coefficient.
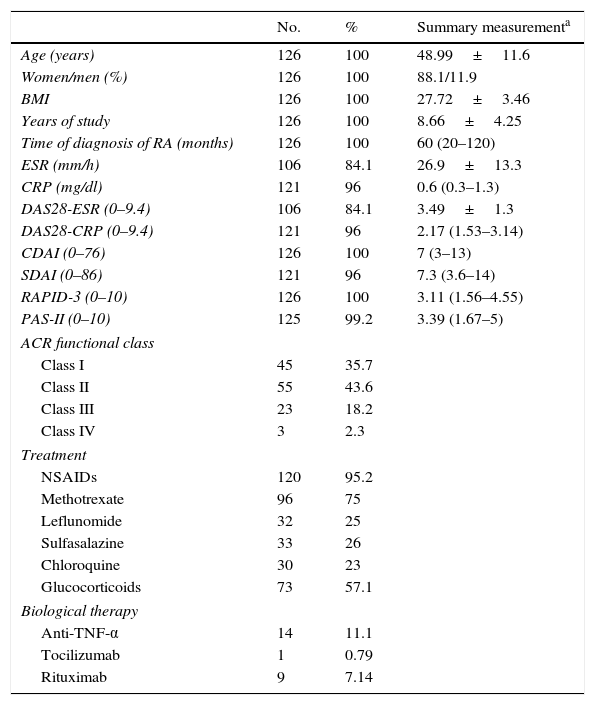
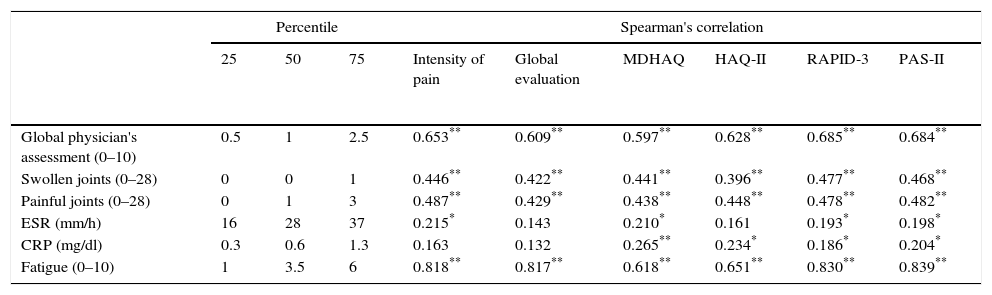
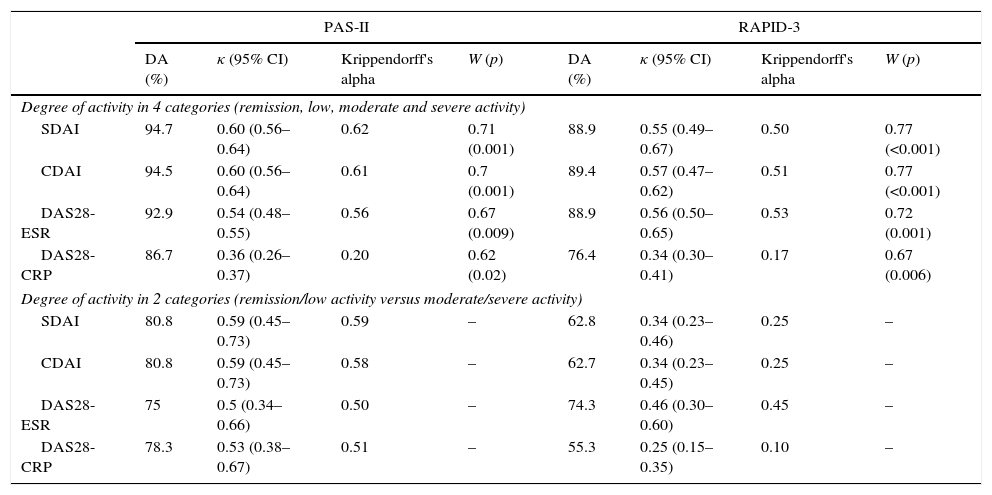
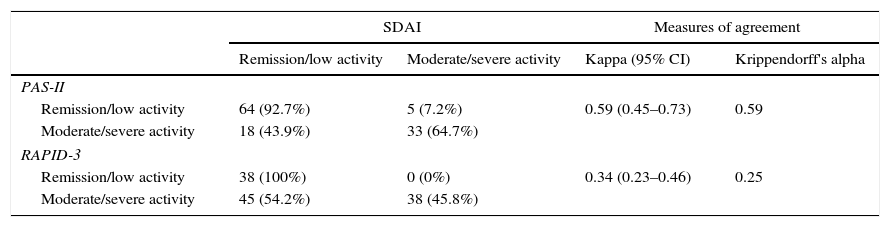
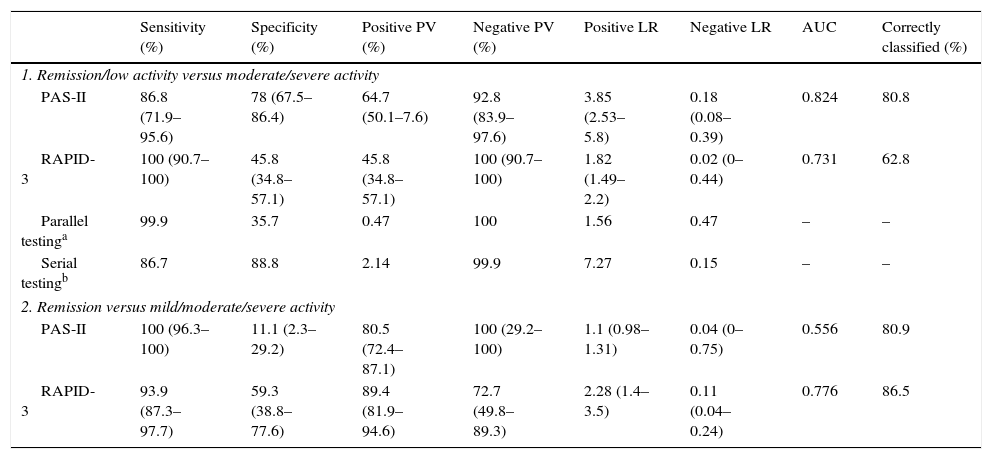
ResultsThe PAS-II and RAPID-3 significantly correlated with all variables included in the core set of measures recommended by the ACR/EULAR. The agreement between PAS-II and CDAI-SDAI was good (κ: 0.6, α: 0.61–0.62), and moderate with DAS28-ESR (κ: 0.53, α: 0.56). The concordance between RAPID-3 and CDAI-SDAI was moderate (κ: 0.55–0.57, α: 0.50–0.51), and moderate with DAS28-ESR (κ: 0.55, α: 0.53). When categorizing the activity in remission/low activity vs. moderate/severe activity, the agreement was greater with the PAS-II (0.59 vs. 0.34; P=.012).
ConclusionThe good concordance between PAS-II and SDAI supports their use in clinical practice, especially if biomarkers of inflammation or the possibility of joint count are not available. However, in order to recommend its routine application in clinical practice, it is necessary to perform longitudinal studies that assess its responsiveness.
Para lograr el control de la artritis reumatoide (AR) es necesario poder evaluar de forma objetiva su actividad. El American College of Rheumatology (ACR, «Colegio Americano de Reumatología») recomienda para este propósito índices de actividad que pueden ser realizados por el paciente (PAS-II y RAPID-3) y la evaluación médica con estudios de laboratorio (DAS28 y SDAI) o sin ellos (CDAI). Nuestro objetivo fue analizar la concordancia entre la autoclinimetría y la clinimetría realizada por el médico.
Pacientes y métodoEstudio transversal analítico en 126 pacientes con AR. La concordancia fue evaluada mediante el coeficiente κ ponderado y por el coeficiente α de Krippendorff.
ResultadosEl PAS-II y el RAPID-3 presentaron una correlación significativa con las variables incluidas en el core set del ACR/EULAR. La concordancia entre el PAS-II y el CDAI-SDAI fue buena (κ: 0,6, α: 0,61-0,62), y moderada con el DAS28-VSG (κ: 0,53, α: 0,56). La concordancia entre el RAPID-3 y el CDAI-SDAI fue moderada (κ: 0,55-0,57, α: 0,50-0,51), y moderada con el DAS28-VSG (κ: 0,55, α: 0,53). Al categorizar la actividad en remisión/baja actividad frente a actividad moderada/grave la concordancia favoreció al PAS-II (0,59 frente a 0,34; p=0,012).
ConclusiónLa buena concordancia entre el PAS-II y el SDAI apoya su uso en la práctica clínica, especialmente si no se dispone de biomarcadores de inflamación o de la posibilidad del recuento articular. Sin embargo, para recomendar su aplicación sistemática en la práctica clínica es necesario realizar estudios longitudinales que evalúen su sensibilidad al cambio.