Primary eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases (EGID) are chronic inflammatory disorders of the gastrointestinal tract with unknown etiology.
Features, utility, and evolution are still unknown in screening for EGID in adult patients with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE).
ObjectivesTo evaluate the prevalence, characteristics, comorbidities, and evolution of EGID in adults diagnosed with EoE and investigate differences between both groups.
MethodsProspective unicenter observational and analytical study. Gastric and duodenal biopsies were obtained during upper baseline endoscopy in all consecutive EoE adult patients evaluated. A colonoscopy with colon biopsies was performed upon persistent diarrhea and normal duodenal biopsies.
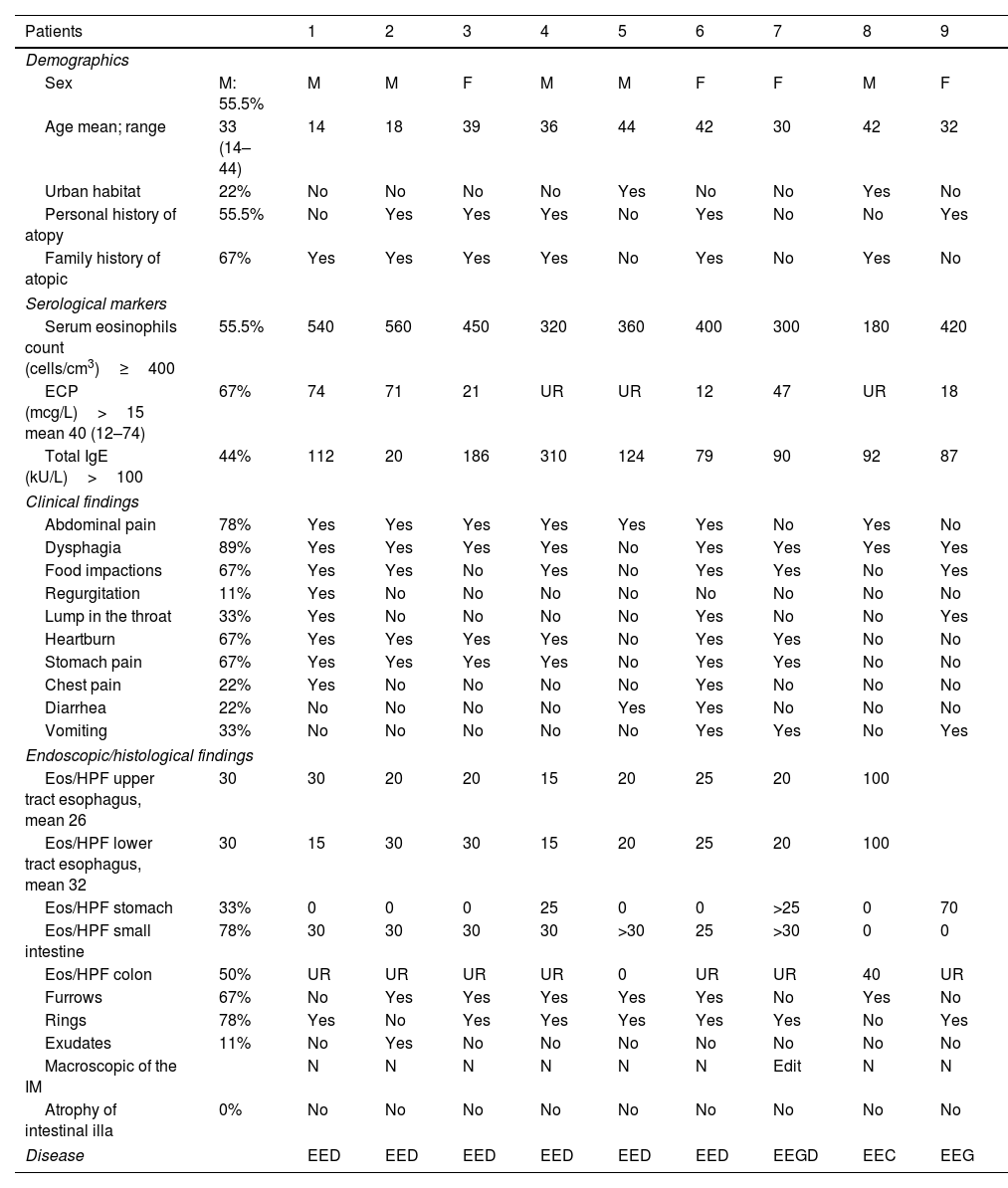
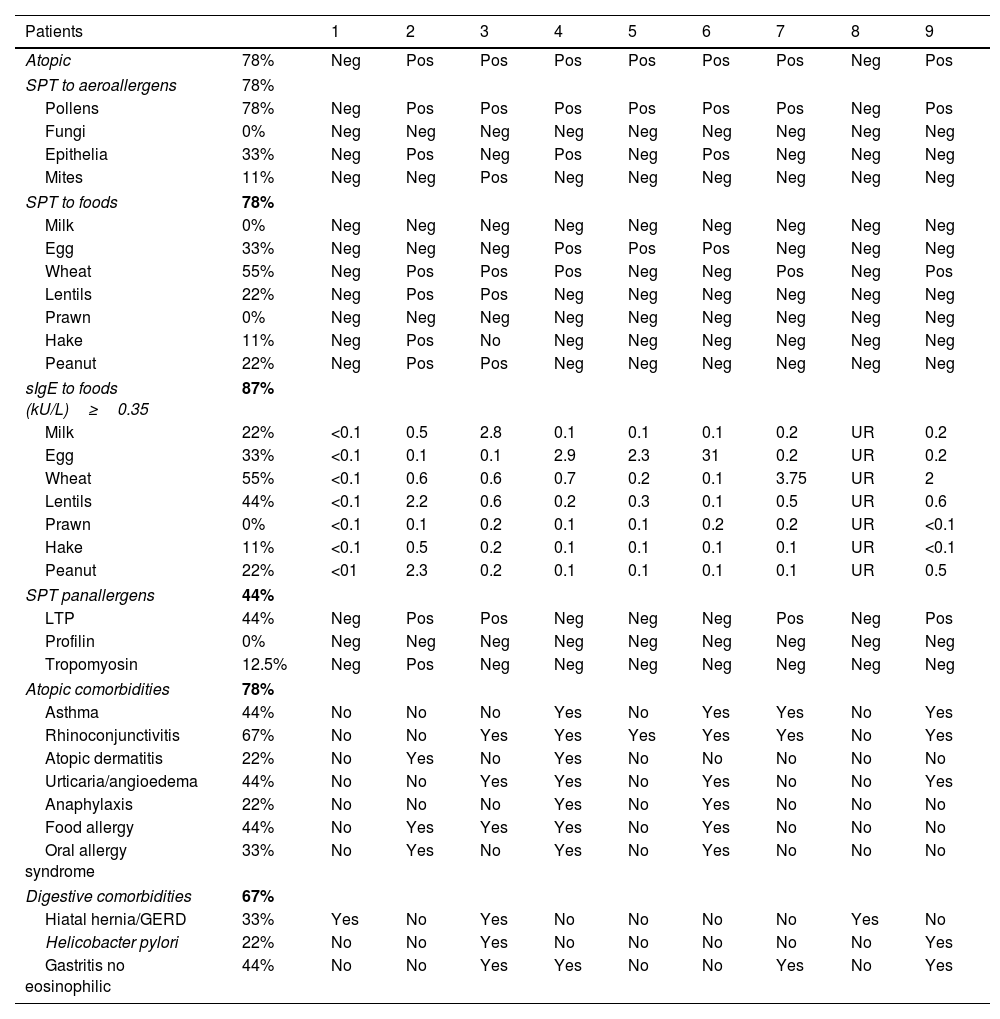
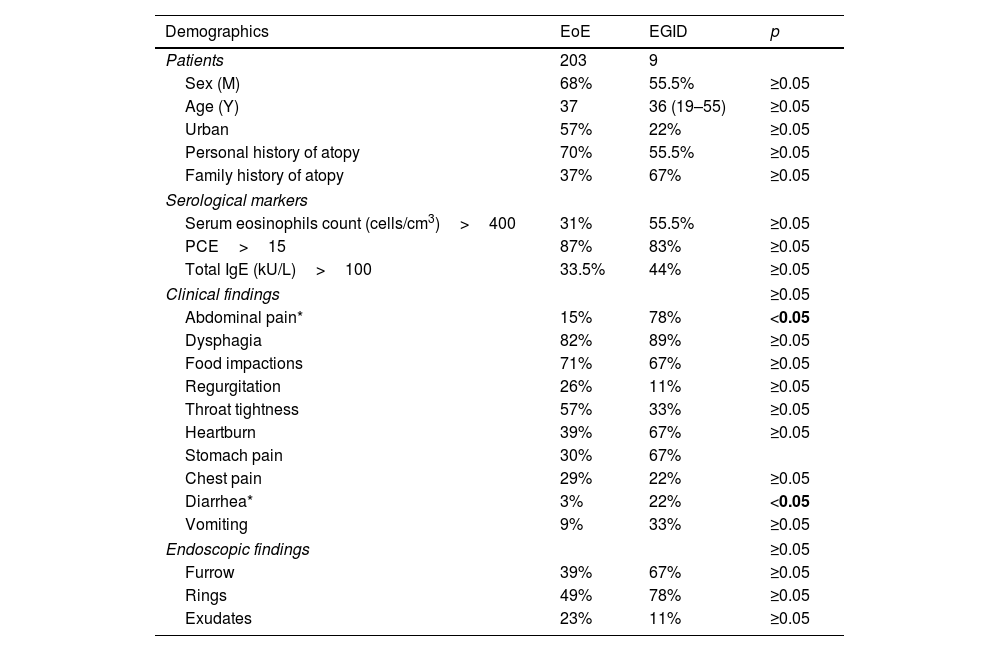
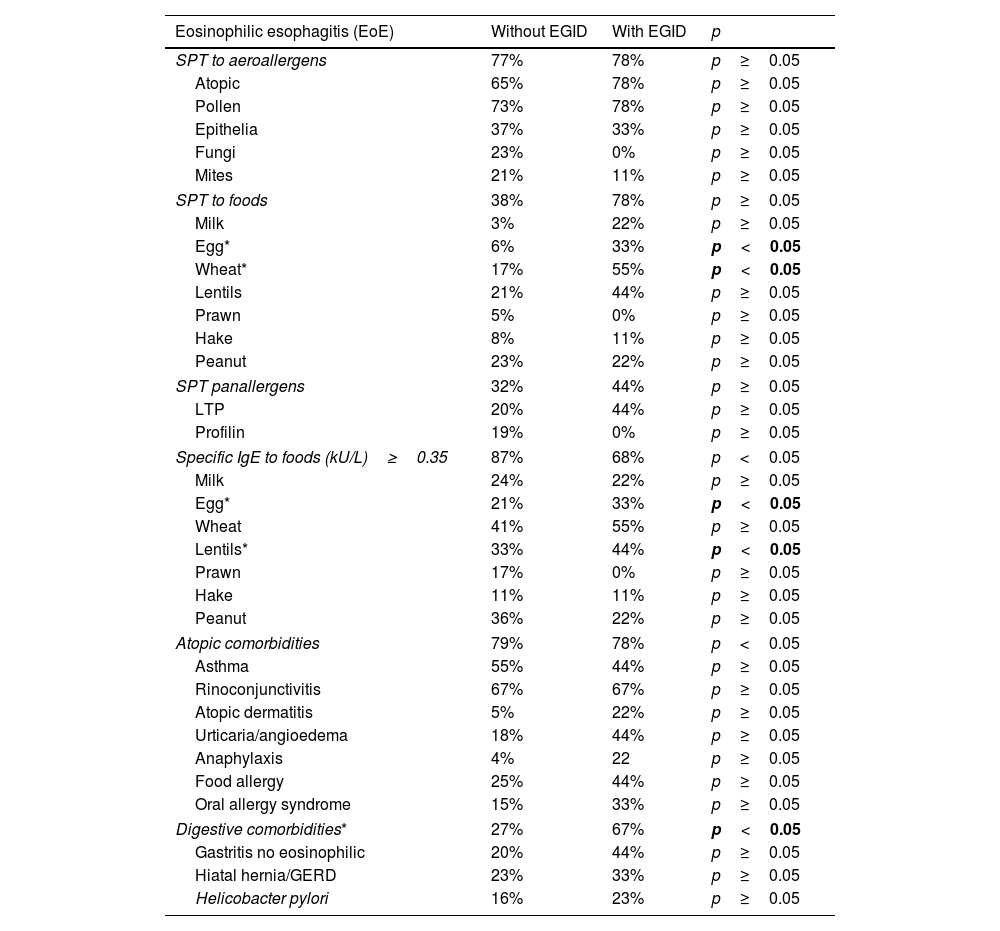
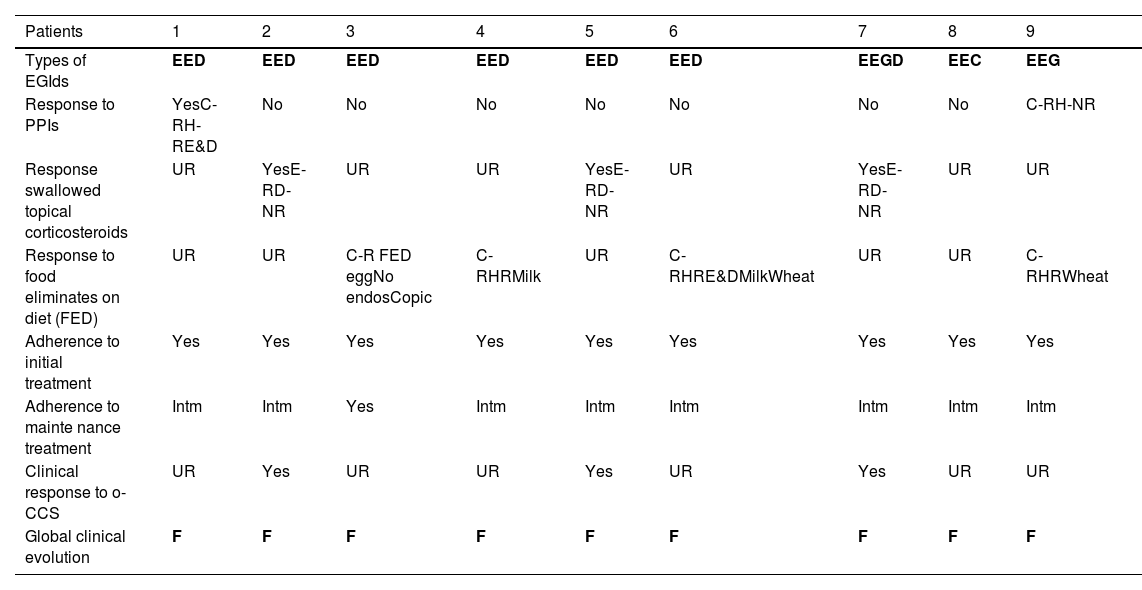
Results212 EoE patients were included. Nine patients (4.3%) also showed significant eosinophilic infiltration in at least one organ within the digestive tract. The most common site affected was the small bowel (78%). Gastrointestinal symptoms (43% vs. 100%, p<0.002) and, more specifically, either abdominal pain or diarrhea (17% vs. 78%, p<0.001), some food sensitizations, and digestive comorbidities (p<0.05) were significantly more common in patients with EGID. Gastrointestinal symptoms were present in 94/212 (44%) patients, of whom 9 (10%) had EGID. Considering only abdominal pain or diarrhea, 20% suffered from it.
ConclusionsEGID rarely coexist with EoE, even when gastrointestinal symptoms are present. These findings advise against routine gastric, duodenal, or colon biopsies in adult EoE patients with gastrointestinal symptoms. Most of the characteristics of EoE do not change due to having EGID except gastrointestinal symptoms, digestive comorbidities, and sensitizations to some foods. The evolution was generally favorable despite intermittent adherence to treatment, especially maintenance.
Las enfermedades gastrointestinales eosinofílicas primarias (EGIE) son trastornos inflamatorios crónicos del tracto gastrointestinal con etiología desconocida.
Aún se desconocen las características, la utilidad y la evolución en el cribado de EGIE en pacientes adultos con esofagitis eosinofílica (EoE).
ObjetivosEvaluar la prevalencia, características, comorbilidades y evolución de las EGIE en adultos diagnosticados de EoE e investigar las diferencias entre ambos grupos.
MétodosEstudio observacional y analítico prospectivo de un único centrro. Se obtuvieron biopsias gástricas y duodenales durante la endoscopia digestiva superior en todos los pacientes adultos con EoE consecutivos evaluados. Se realizó colonoscopia con biopsias de colon ante diarrea persistente y biopsias de duodeno normales.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 212 pacientes con EoE. Nueve pacientes (4,3%) también mostraron infiltración eosinofílica significativa en al menos un órgano dentro del tracto digestivo. El sitio más común afectado fue el intestino delgado (78%). Los síntomas gastrointestinales (43 vs. 100%, p < 0,002) y, más específicamente, dolor abdominal o diarrea (17 vs. 78%, p < 0,001), algunas sensibilizaciones alimentarias y comorbilidades digestivas (p < 0,05) fueron significativamente más comunes en pacientes con EGIE. Los síntomas gastrointestinales estuvieron presentes en 94/212 (44%) pacientes, de los cuales nueve (10%) tenían EGIE. Considerando solo dolor abdominal o diarrea, 20% la padecía.
ConclusionesLas EGIE rara vez coexisten con EoE, incluso cuando hay síntomas gastrointestinales. Estos hallazgos desaconsejan las biopsias gástricas, duodenales o de colon de rutina en pacientes adultos con EoE con síntomas gastrointestinales. La mayoría de las características de la EoE no cambian por tener EGIE, excepto los síntomas gastrointestinales, las comorbilidades digestivas y las sensibilizaciones a algunos alimentos. La evolución fue en general favorable a pesar de la adherencia intermitente al tratamiento, especialmente de mantenimiento.