In Mexico, type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM2) presents epidemiological levels with a prevalence rate of 9.12% and with the highest overweight and obesity rates worldwide. To overcome this situation, strategies must be created focused on the identification of subjects at risk. The Triglyceride and Glucose (TyG) index, was created for the detection of insulin resistance, has recently been used in the prediction of DM. The objective of the present study was to determine the predictive power of the TyG index in a cohort from Mexico City.
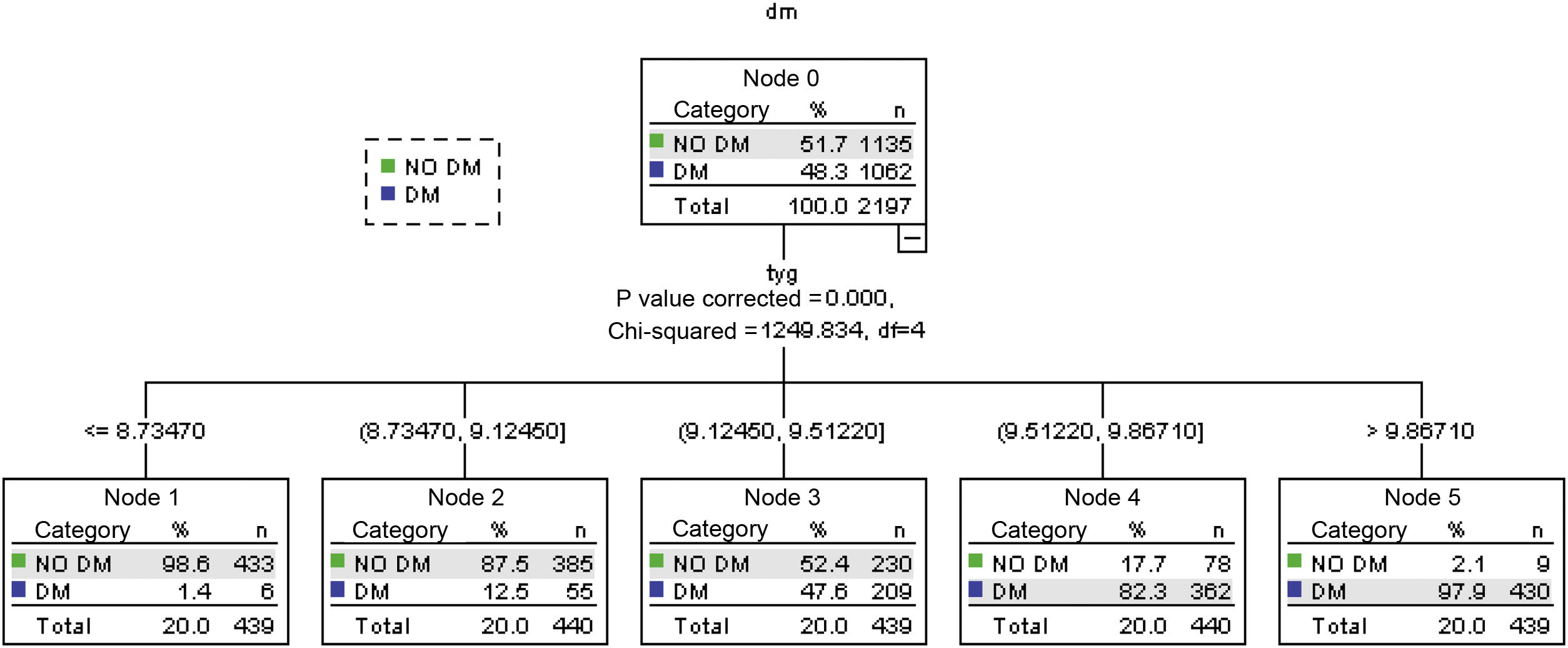
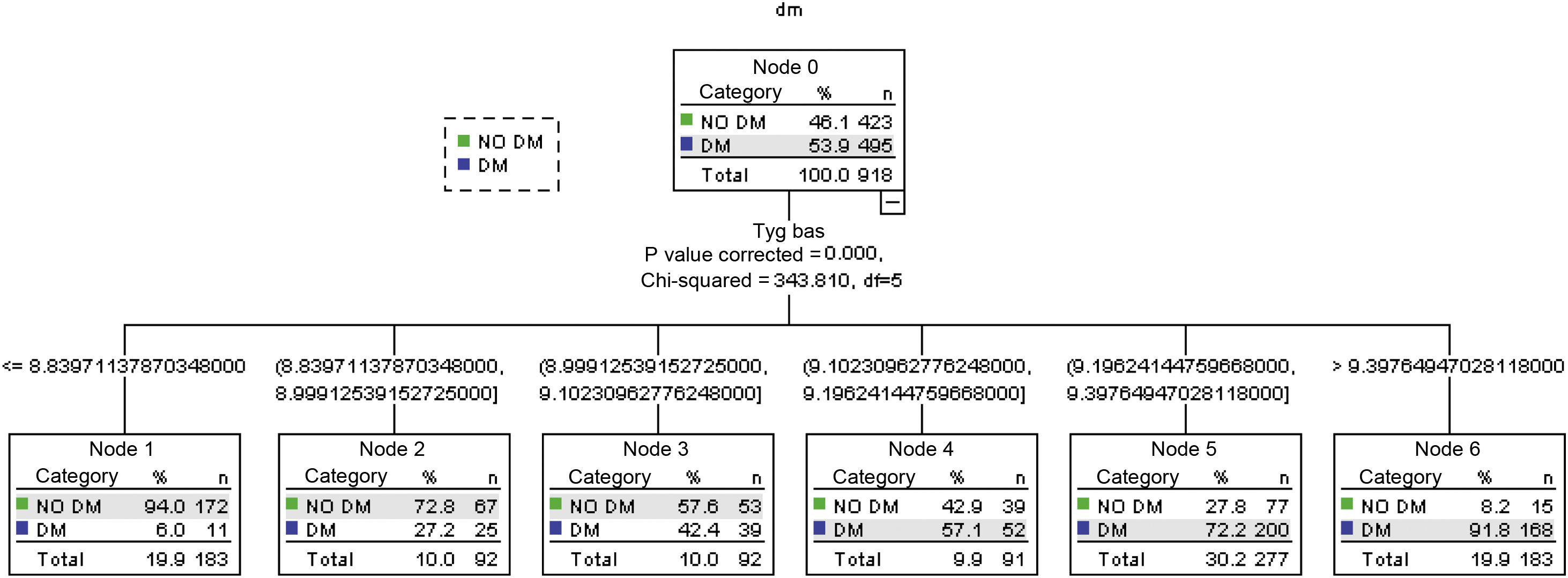
Methods3195 patients were selected from a cohort of patients from the chronic degenerative area of the Health Centers of the Public Health Services of Mexico City. The ability of the TyG index in predicting diabetes was evaluated as: ln [Fasting triglycerides (mg/dl) × fasting glucose (mg/dl)/2] after a follow-up of at least 4.5 years. A CHAID test was determined that was corroborated by a ROC test.
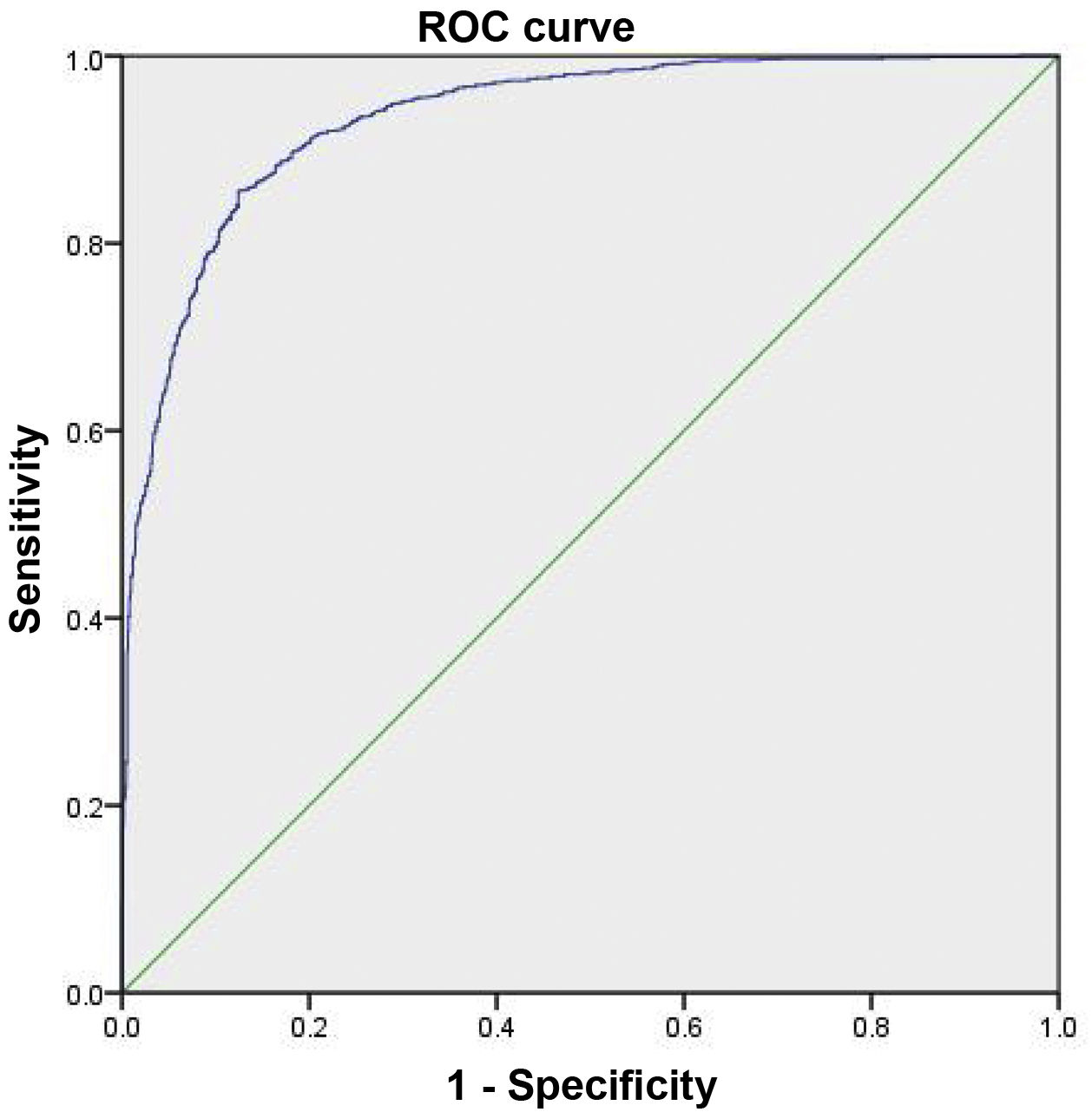
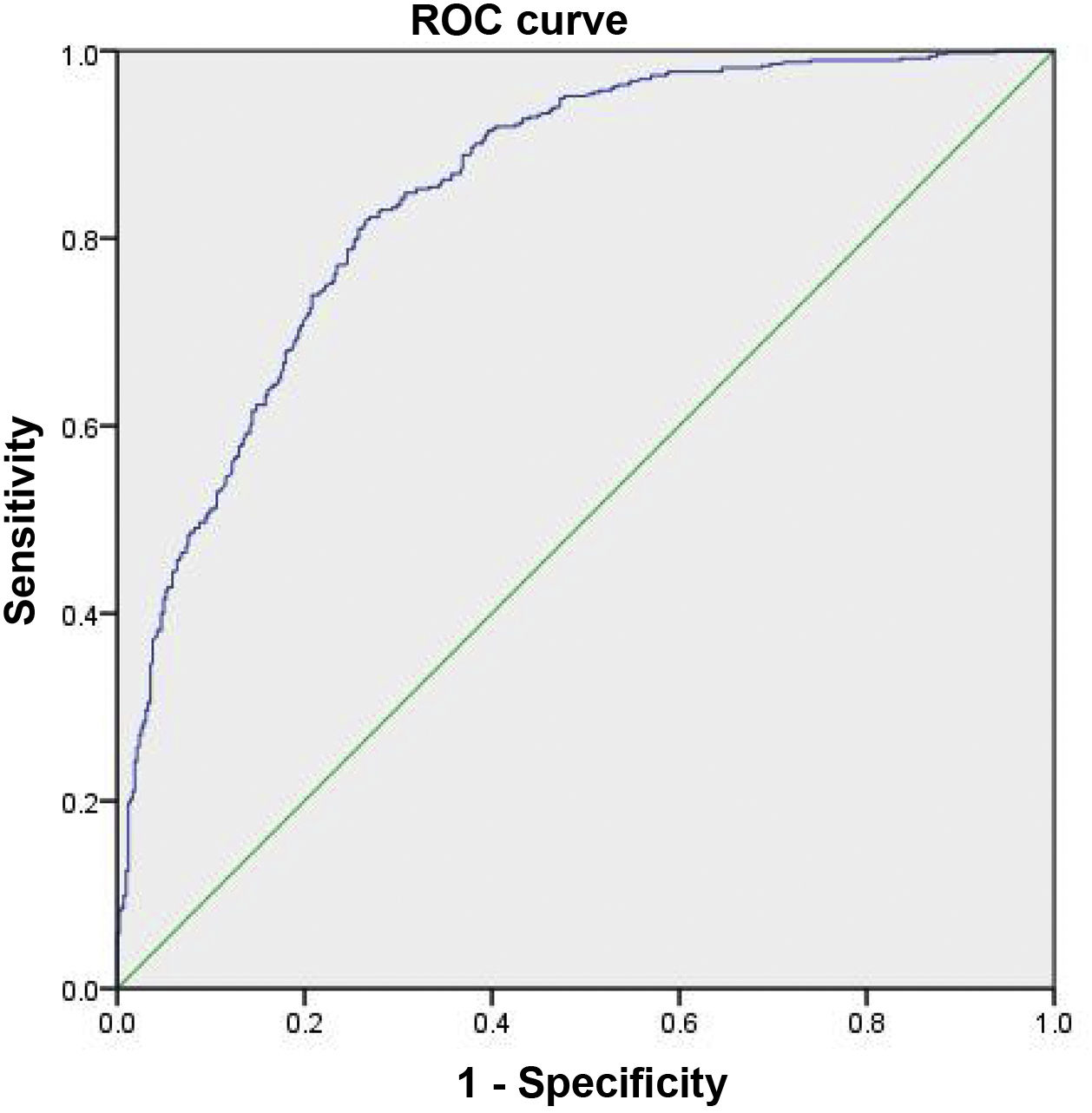
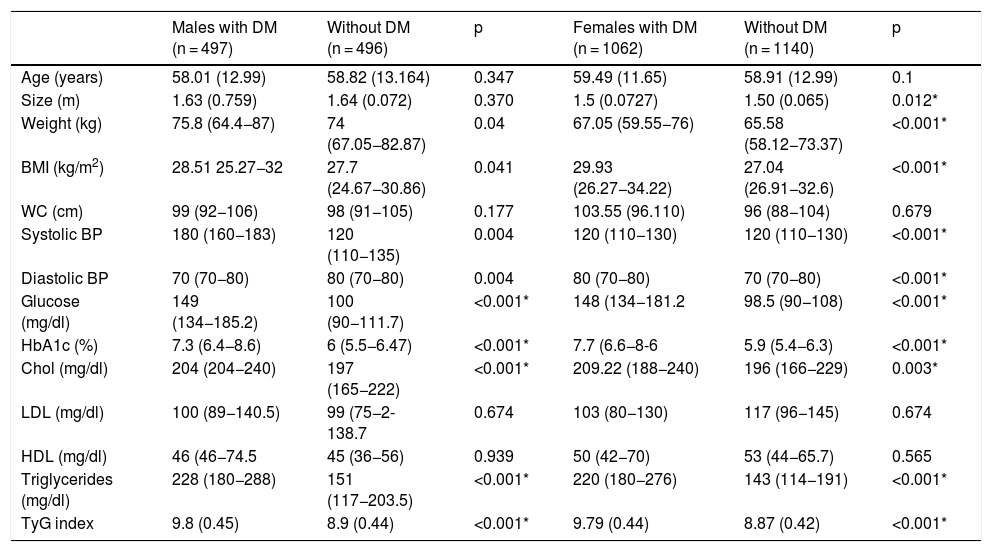
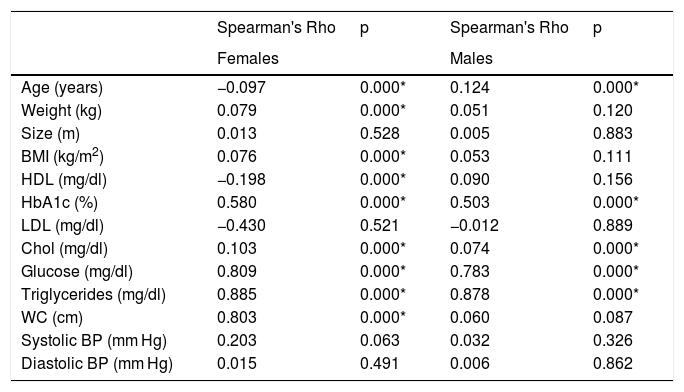
ResultsThe value of the TyG index was significantly higher for patients who develop DM2. Values of AUC = 0.934, 95% CI: 0.924–0.924. Obtaining a cut-off point of 9.45 in women; in men: DM2 AUC = 0.824, 95% CI: 0.824–0.873, and cut-off point 9.12.
ConclusionsThe TyG index is a good marker in the prediction of DM2. The CHAID determination is a useful tool in the prediction of DM2.
En México la diabetes mellitus tipo 2 (DM2) presenta niveles epidemiológicos con una tasa de prevalencia de 9,12% y con los índices de sobrepeso y obesidad mas altos a nIvel mundial. Para superar esta sitiación se debe crear estrategias enfocadas a la identificación de sujetos en riesgo. El índice Triglicérido y glucosa (TyG), fue creado para la detección de la resisitencia a la insulina, recientemente se ha empleado en la predicción de diabetes mellitus. El objetivo del presente estudio fue determinar el poder predictivo del índice TyG en una cohorte de la Ciudad de México.
MétodosSe seleccionarosn 3.195 pacientes de una cohorte de pacientes del área crónico degenerativos del los Centros de Salud de los Servicios de Salud Pública de la Ciudad de México. Se evaluó la capacidad del índice TyG en la predicción de diabetes calculado como: ln (triglicéridos en ayunas [mg/dl] × glucosa en ayunas [mg/dl]/2). despues de un seguimiento de al menos 4,5 años. Se determinó una prueba Chi-squared automated interaction detector analysis, que fue corroborada por una prueba ROC.
ResultadosEl valor del índice de TyG fue significativamente mayor para los pacientes que desarrollar DM2. Los valores de AUC = 0,934, intervalo de confianza (IC) 95% = 0,924–0,924. Obteniendo un punto de corte de 9.45, en mujeres; en hombres: DM AUC = 0.824, IC95% = 0,824–0,873 punto de corte 9.12.
ConclusionesEl índice TyG es un buen marcador en la predicción de DM2 respaldado por la aplicación del algoritmo CHAID como herramienta útil para la predicción de DM2.