Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is the most frequent type of acute leukemia in adults. Despite recent advances in the characterization of pathogenesis of AML, the cure rates are under 40%, being leukemia relapse the most common cause of treatment failure. Leukemia relapse occurs due to clonal evolution or clonal escape. In this study, we aimed to analyze the clinical and biological factors influencing outcomes in patients with AML relapse.
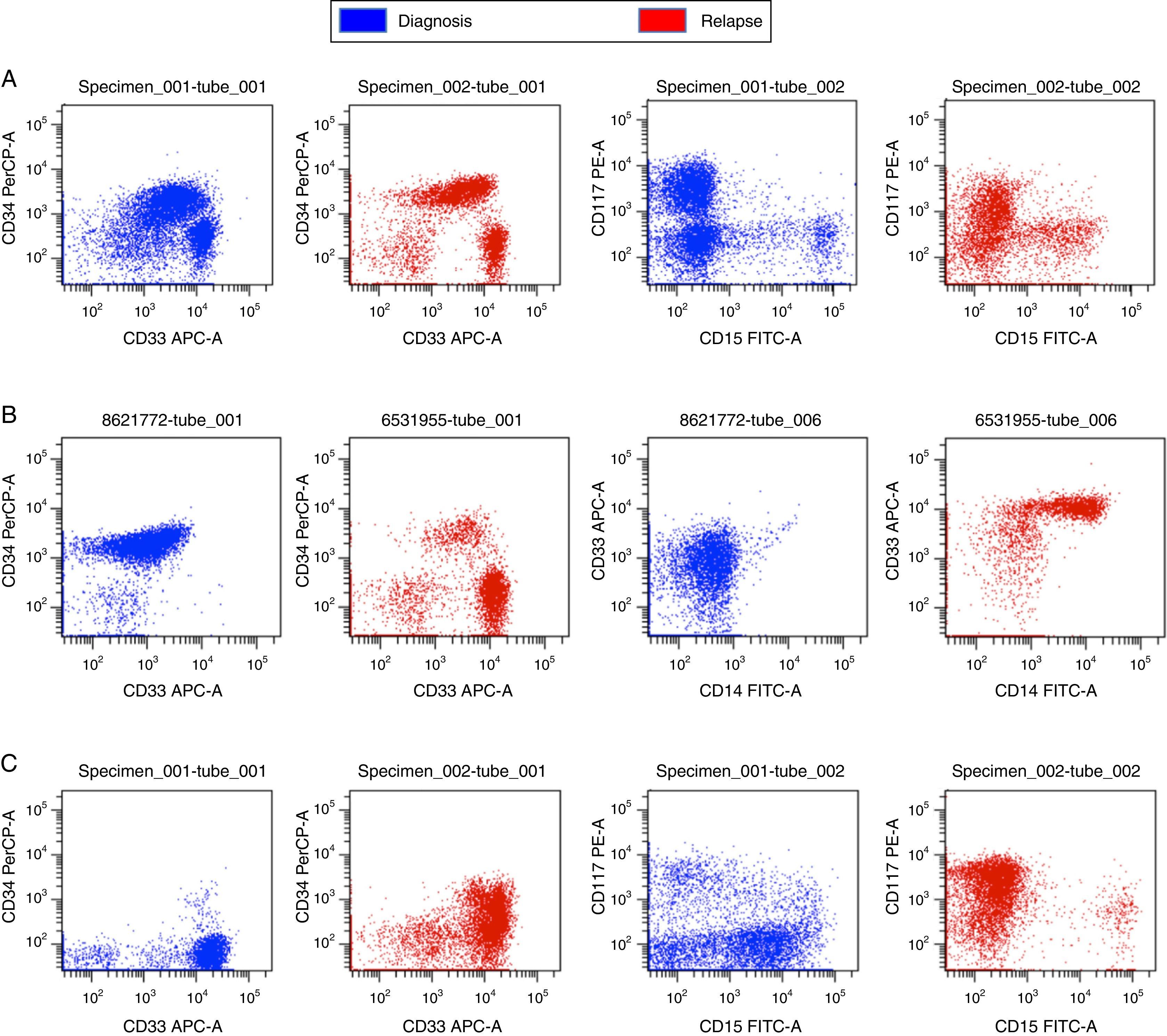
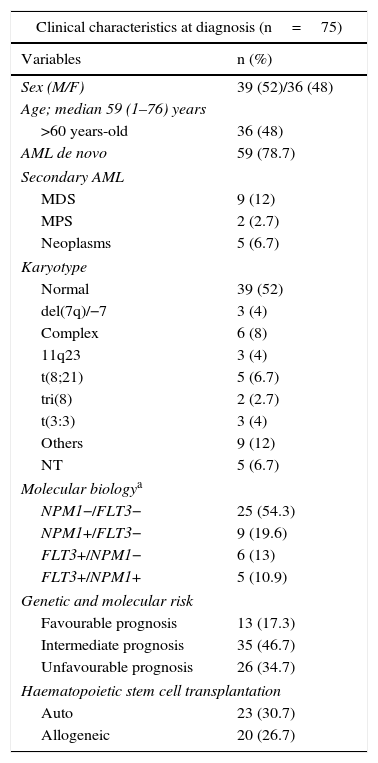
Patients and methodsWe included a total of 75 AML patients who experienced leukemia relapse after achieving complete remission. We performed complete immunophenotyping and conventional karyotyping in bone marrow aspirates obtained at diagnosis and at leukemia relapse.
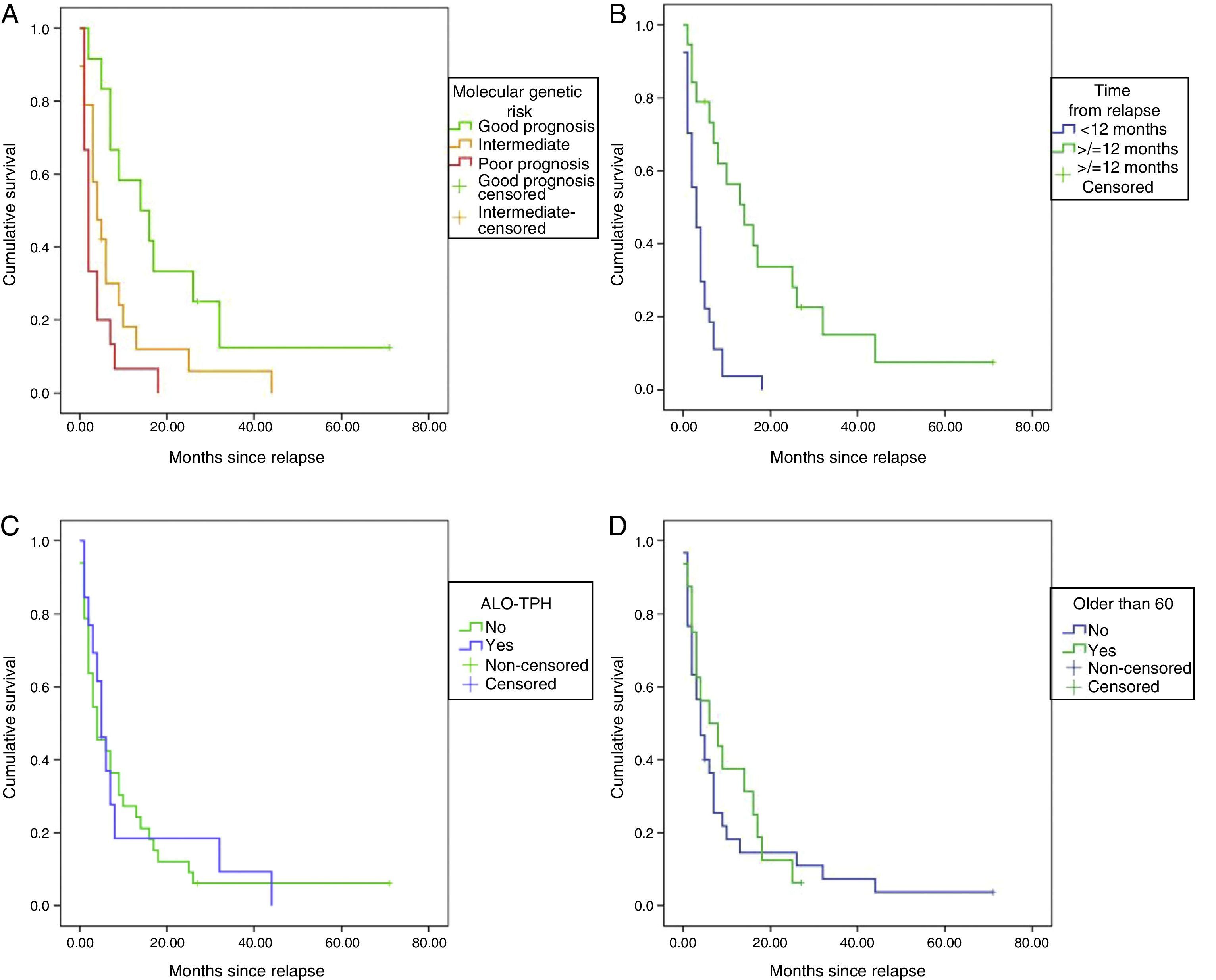
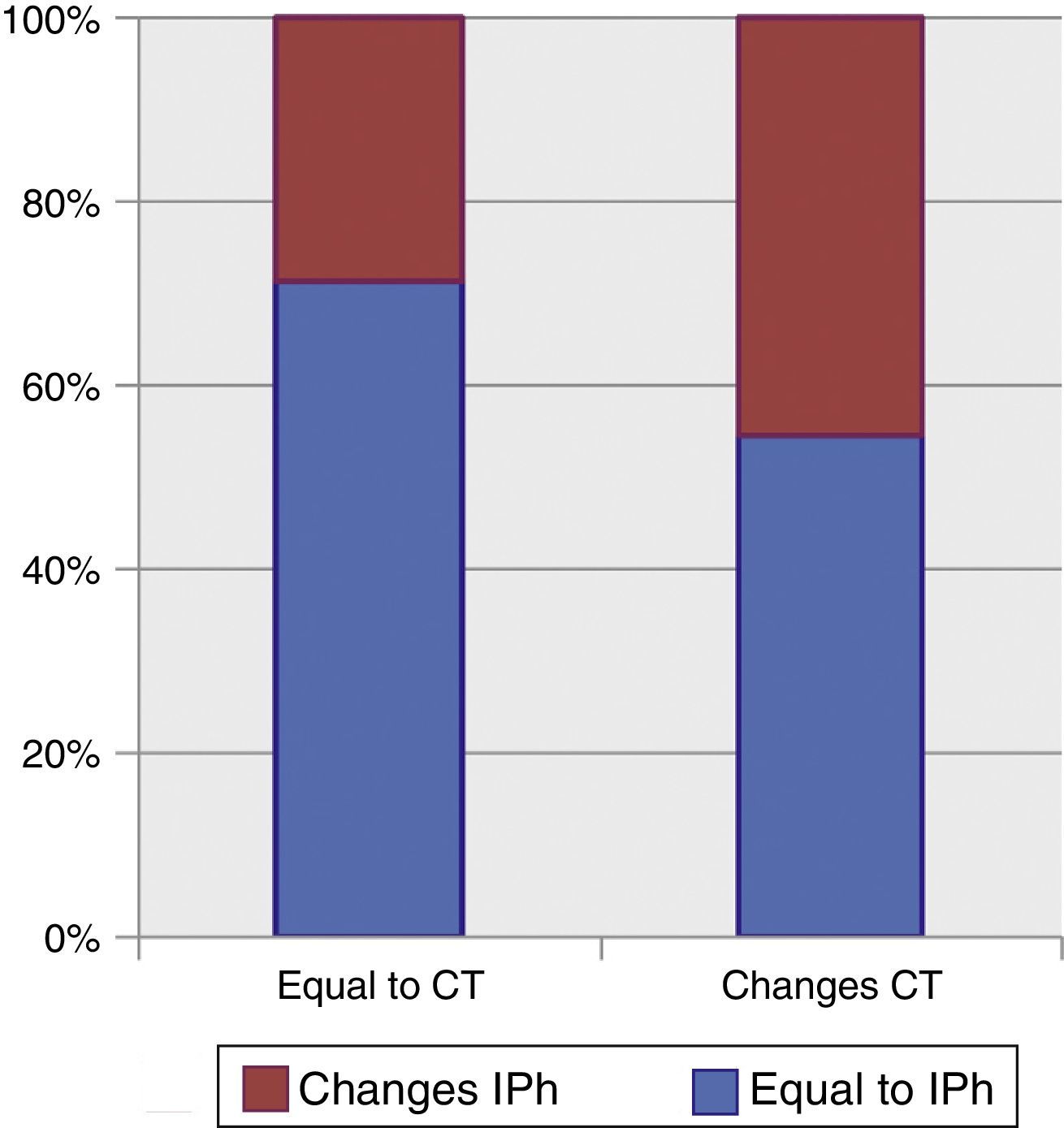
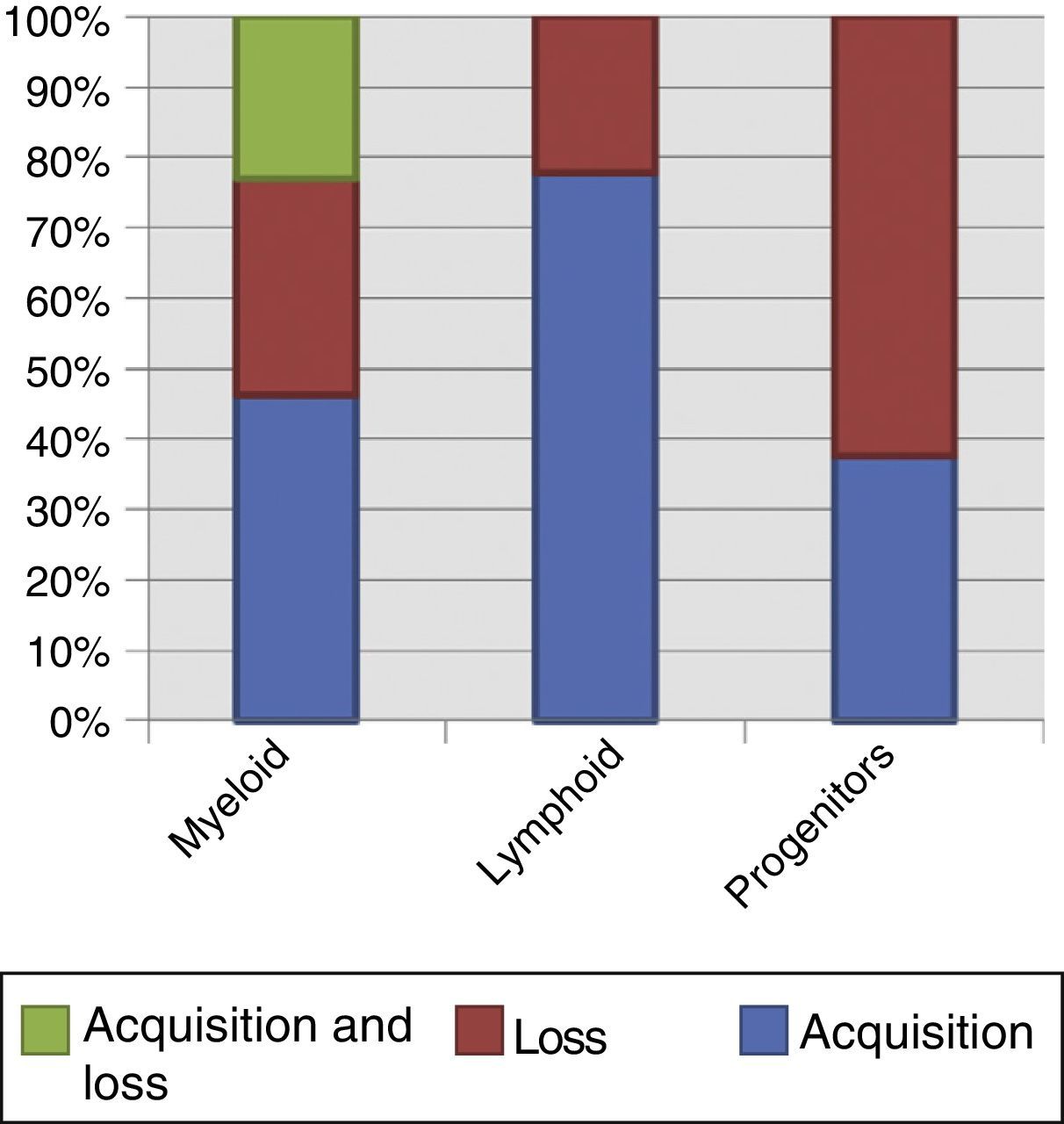
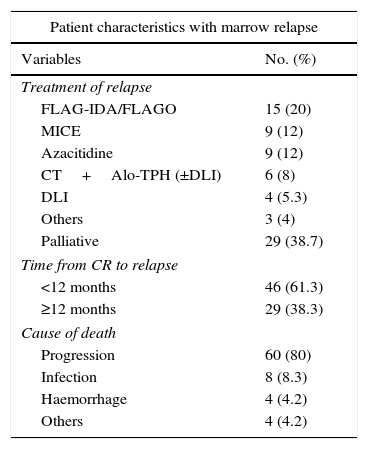
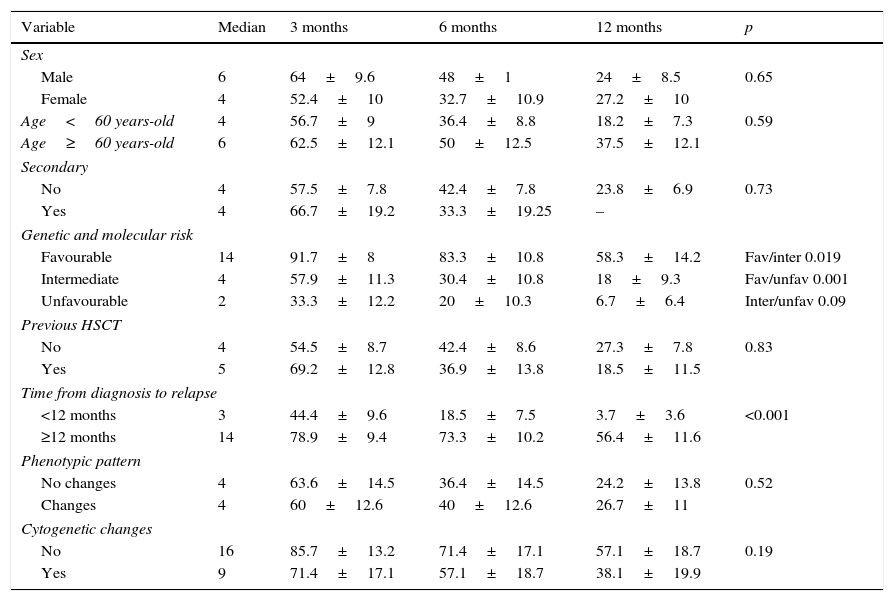
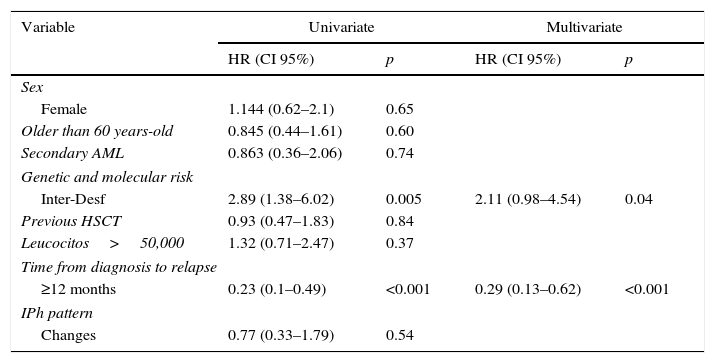
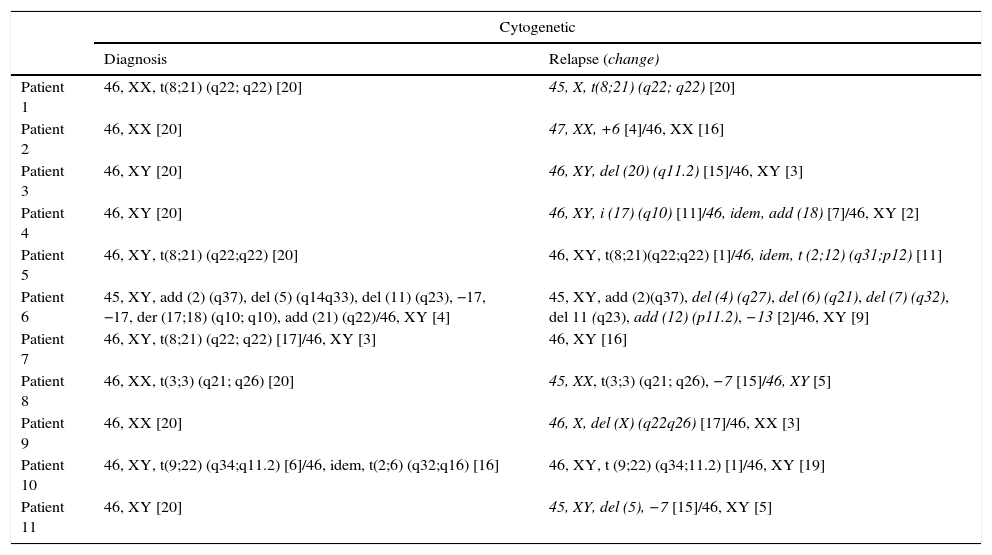
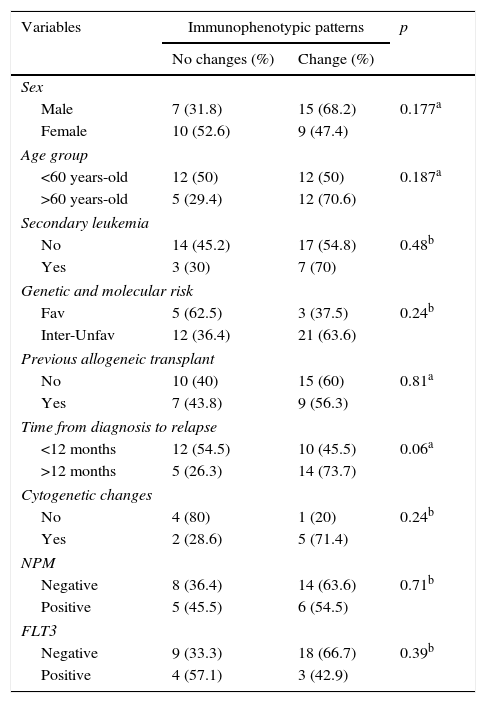
ResultsOverall survival (OS) of the series was 3.7±2.3%, leukemia progression being the most common cause of death. Patients relapsing before 12 months and those with adverse cytogenetic-molecular risk had statistically significant worse outcomes. A percentage of 52.5 of patients showed phenotypic changes and 50% cytogenetic changes at relapse. We did not find significant clinical factors predicting clonal evolution. The presence of clonal evolution at relapse did not have a significant impact on outcome.
ConclusionsPatients with relapsed AML have a dismal prognosis, especially those with early relapse and adverse cytogenetic-molecular risk. Clonal evolution with phenotypic and cytogenetic changes occurred in half of the patients without predictive clinical factors or impact on outcome.
La leucemia aguda mieloblástica (LAM) constituye la leucemia más frecuente en adultos. A pesar de los avances en el conocimiento de su patogenia, las tasas de curación no superan el 40%, siendo la recaída de la enfermedad la causa más frecuente de fallo de tratamiento. La recaída ocurre por fenómenos de evolución clonal. En este estudio analizamos los factores pronósticos clínicos y biológicos en pacientes adultos con LAM en recaída.
Pacientes y métodosAnalizamos un total de 75 pacientes que presentaron recaída leucémica tras haber alcanzado la remisión completa. Se realizó un estudio inmunofenotípico mediante citometría de flujo y estudio citogenético mediante cariotipo convencional en muestras de médula ósea obtenidas en el momento del diagnóstico y de la recaída.
ResultadosLa supervivencia global (SG) de la serie fue del 3,7%±2,3, siendo la principal causa de muerte la progresión leucémica (83,3%). Los pacientes con recaídas precoces –antes de 12 meses– y aquellos con riesgo citogenético-molecular adverso presentaron SG significativamente inferiores. En el momento de la recaída el 52,5% de los pacientes mostraron cambios fenotípicos, y el 50%, cambios citogenéticos, sin observarse factores clínicos predictivos de dicha evolución clonal. La evolución clonal fenotípica o citogenética no mostró ningún impacto significativo en la SG.
ConclusionesLos pacientes con recaída de LAM presentan un pronóstico infausto, especialmente aquellos con recidiva precoz y riesgo citogenético-molecular adverso. La evolución clonal fenotípica y/o citogenética ocurre en la mitad de los casos sin factores clínicos predictivos ni impacto pronóstico.