To analyze the effect of an intervention with a Mediterranean diet supplemented with either extra virgin olive oil or nuts, on the fatty liver index (FLI), compared to a low-fat control diet.
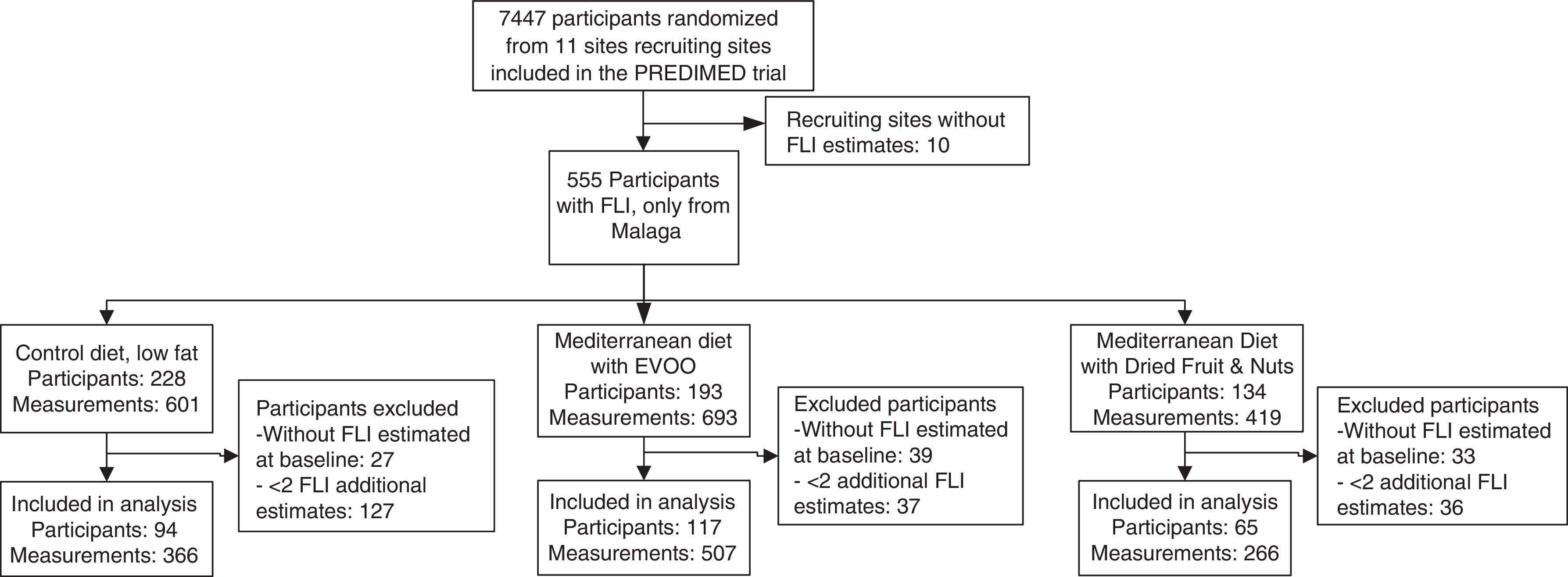
MethodsParticipants of the PREDIMED-Malaga trial, free from cardiovascular disease at baseline, but with a high risk to develop it, were included in this study. Anthropometric measurements were assessed and blood samples were taken to calculate participants’ FLI at study baseline and after one, 3, 5 and 6 years. Mixed linear models were used to explore the fixed effects of the 3 intervention groups on the FLI as well as their interaction with time.
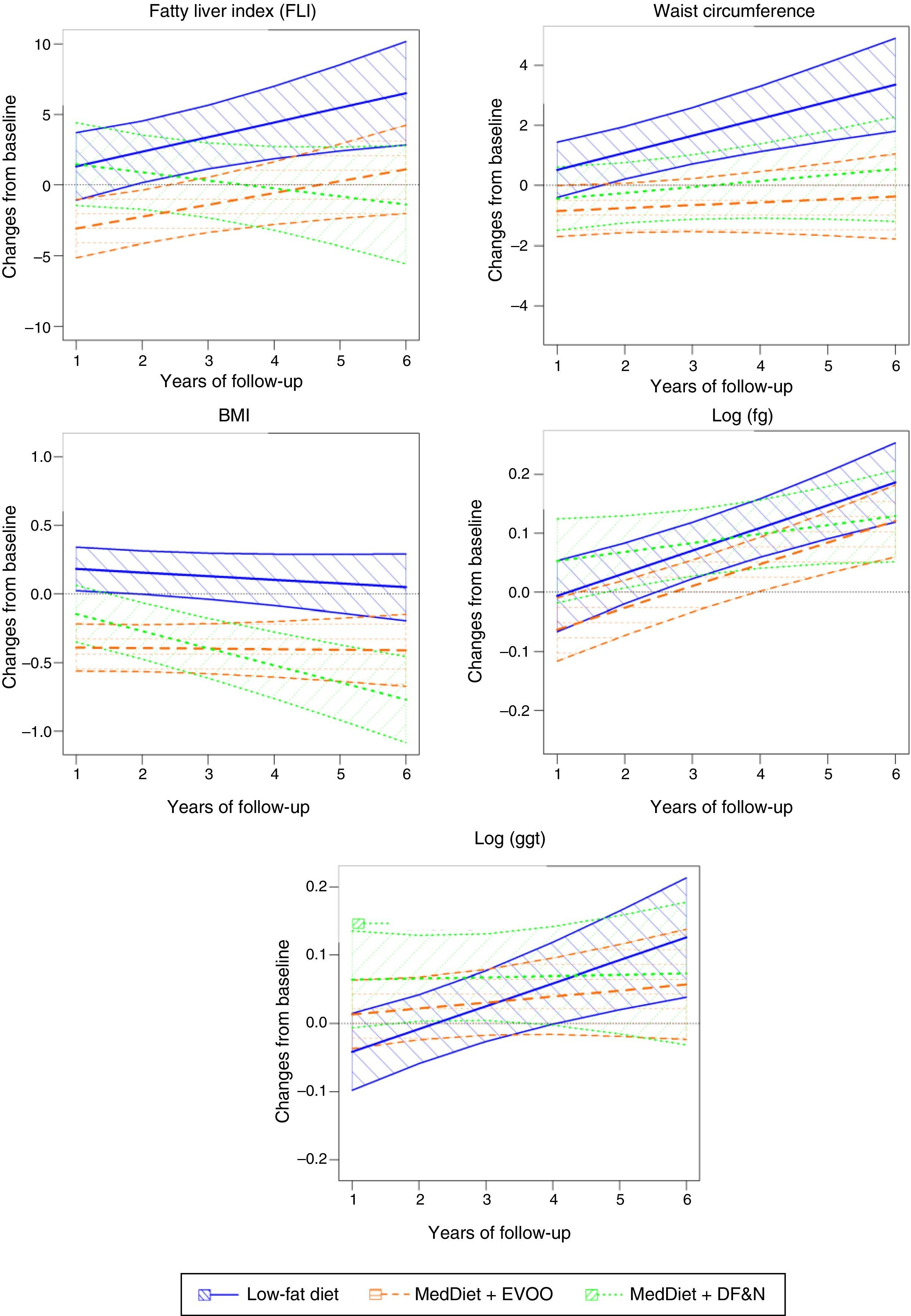
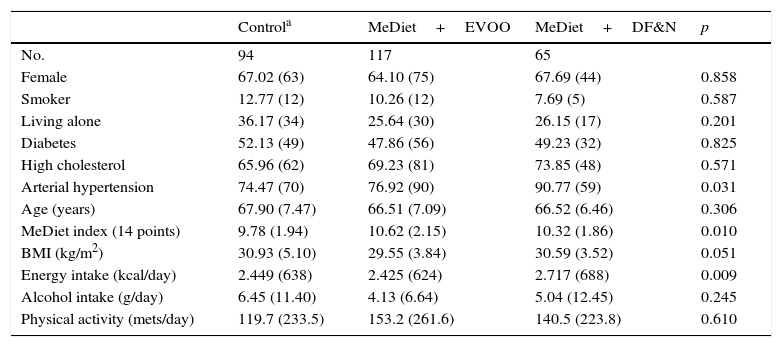
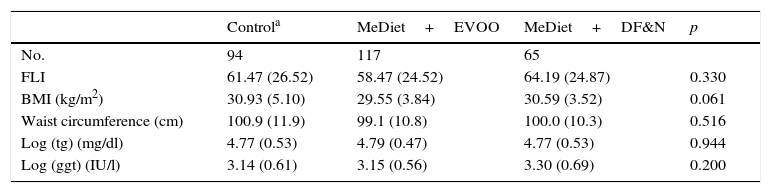
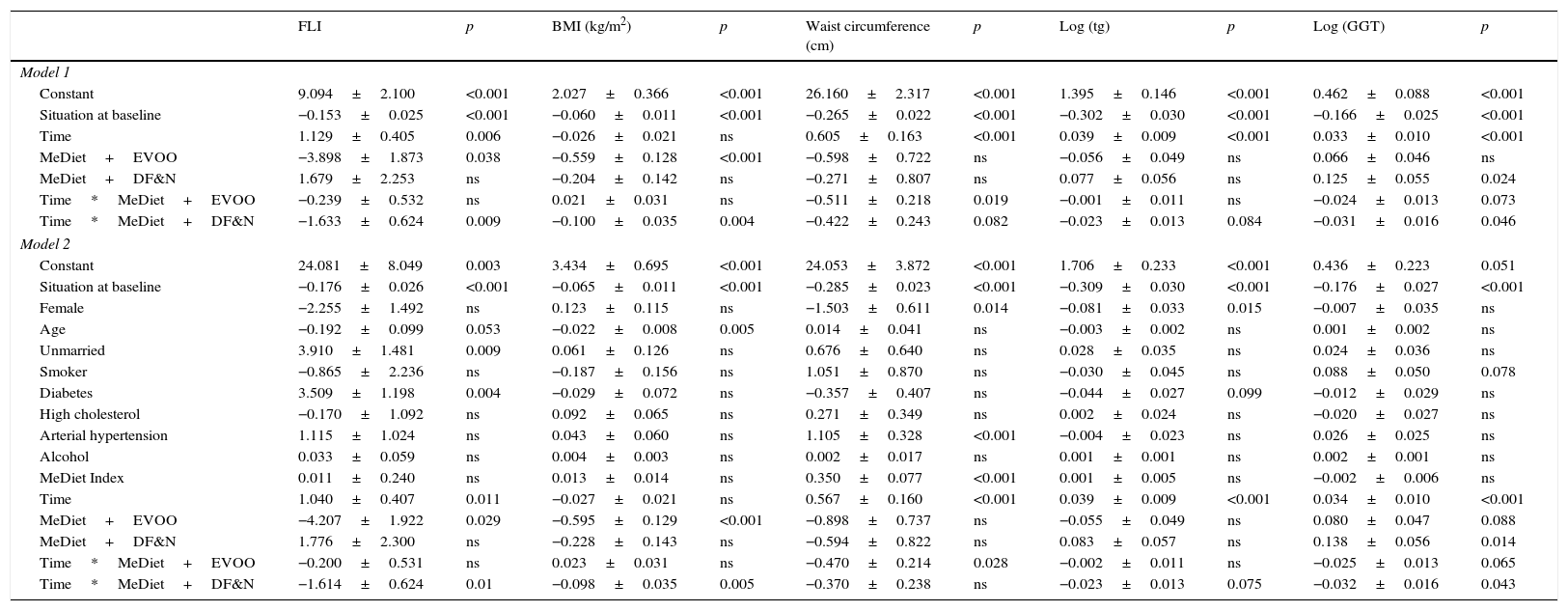
ResultsA total of 276 participants were included in the study. Average participant age was 67 years, with 66% of participants being women. The baseline prevalence of NAFL was 57%. The change in the FLI of the control group increased significantly over time (1.13±0.41; p=0.006). In the MedDiet+EVOO group, the time trend of the change in the FLI was similar to that of the control group, although it was seen to be lower (−3.90±1.9; p=0.038). In the MedDiet+Nuts group, the trend was significantly lower than that of the control group (−1.63±0.62; p=0.009). In the MedDiet+Nuts group, the trend of changes in participants’ BMI was 0.100 points lower per year compared to the control group (p=0.004). In the control group, the change in waist circumference increased significantly over time (0.61±0.16cm/year; p<0.001) in contrast to the MedDiet+EVOO group, in which this variable remained stable (−0.51±0.22; p=0.019).
ConclusionsA dietary intervention consisting of a Mediterranean diet could delay or slow down the natural progression of NAFL, thus, being beneficial for its prevention and treatment. However, further studies supporting these conclusions have yet to be carried out.
Analizar el efecto sobre el fatty liver index («índice de hígado graso») de la intervención con dieta mediterránea enriquecida con aceite de oliva virgen extra o frutos secos frente a un grupo control con una dieta baja en grasas.
MetodologíaParticipantes del ensayo PREDIMED-Málaga, libres de enfermedad cardiovascular al inicio, pero con alto riesgo de desarrollarla. Al inicio, al año y a los 3, 5 y 6 años se les realizó mediciones antropométricas y toma de muestras de sangre para calcular el FLI. Se usaron modelos lineales mixtos para explorar los efectos fijos de los 3 grupos de intervención sobre el FLI, y sus interacciones con el tiempo.
ResultadosCumplían los criterios de participación en el estudio 276 participantes. La edad media fue de 67 años, con un 66% de mujeres. La prevalencia basal de HGNA estimado fue del 57%. El cambio temporal del FLI en el grupo control aumentó con el tiempo (1,13±0,4; p=0,006). En el grupo DietMed+AOVE la evolución fue similar a la de este, aunque por debajo (−3,90±1,9; p=0,038), y en DietMed+FS fue significativamente menor (−1,63±0,62; p=0,009). En el DietMed+FS la evolución del cambio del IMC fue 0,100 puntos menor al año en comparación con el grupo control (p=0,004). En el grupo de control, el cambio del perímetro de cintura aumentó significativamente con el tiempo (0,61±0,16cm/año; p<0,001) en contraste con DietMed+AOVE(−0,51±0,22; p=0,019).
ConclusionesLa intervención dietética con dieta mediterránea podría retrasar o enlentecer la progresión natural del HGNA, siendo beneficiosa para la prevención y el tratamiento del mismo. No obstante, se necesitan estudios que ayuden a corroborar las conclusiones obtenidas.