Accumulating studies have pointed out that gut-blood and blood-brain barrier dysfunctions due to the alterations in permeability may play a role in the pathophysiology of neurodevelopmental disorders. Tight junctions are crucial components of these barriers and some peptides including claudin-5, occludin, zonulin and tricellulin are important components of these structures. This study aimed to investigate the relationship between these molecules and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children and adolescents.
MethodsA total of 57 children with ADHD and 60 controls aged between 6 and 12 years were included in the study. The severity of ADHD symptoms was assessed through a parent-rated questionnaire, and Conner's Continuous Performance Test was administered to the study group. Serum levels of biochemical variables were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits. Biochemical parameter levels and scale scores were compared using Mann-Whitney U or Student's t tests. In addition, a multivariate analysis of covariance (MANCOVA) and a one-way analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) was performed on the outcome variables. Finally, a hierarchical regression model was conducted on the study group.
ResultsSerum claudin-5 and tricellulin levels were significantly lower in the ADHD group compared to the control group. The difference between the groups in terms of serum claudin-5 and tricellulin levels remained significant after controlling for confounding factors such as age, gender and autistic characteristics. There was no significant difference between the groups in terms of serum zonulin and occludin levels.
ConclusionThese results reveal that claudin-5 and tricellulin levels vary in patients with ADHD. Alterations in these peptides may affect the brain by leading to a dysregulation in intestinal or blood-brain barrier permeability. The causal relationship between these peptides and ADHD requires further investigation.
Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by inattention, hyperactivity/impulsivity which impairs the functionality of the individual.1 Although it has been suggested that genetic, neurobiological and environmental factors contribute to the etiopathogenesis of ADHD, its etiopathology remains poorly understood.2 Studies focusing on the biological variations in ADHD report several structural3 functional4 and molecular5 differences between ADHD and non-ADHD subjects.
The intestinal barrier (IB) and the blood-brain barrier (BBB) permeability are of interest and have been investigated in recent studies to demonstrate their possible impact on the etiopathogenesis of several psychiatric disorders (i.e. autism spectrum disorder, schizophrenia, depression).6 Similarly, the relationship between ADHD and IB and BBB has been studied in previous studies demonstrating alterations in tight junction proteins such as zonulin and claudin-5.7–9 It has been suggested that pathways between the gut and the central nervous system play a role in the regulation of mood and cognition. Increased intestinal permeability, also called "leaky gut" in this context, is receiving increasing attention in the pathophysiology of mental disorders including ADHD.10,11 It has been suggested that it may play a role in the etiology of ADHD by causing neuroinflammation in the central nervous system as a result of increased intestinal permeability.12
Several molecules have been described to indicate the permeability of IB and BBB in recent studies. Among these molecules, zonulin, claudin-5, tricellulin and occludin are peptides that have been previously investigated in several diseases including psychiatric disorders.12–14 Zonulin is a regulator of intestinal permeability and a physiological modulator of intercellular tight junctions. In addition to its effect on the intestines, zonulin also regulates BBB permeability.15 Studies to date have reported associations between zonulin and psychiatric disorders such as ASD, BPD and schizophrenia.14,16,17 however, only four studies have explored the relationship between ADHD and zonulin reporting inconsistent results. Özyurt et al. and Çakir et al. reported higher zonulin levels in ADHD subjects compared to the control group. In the former study, a positive relationship was shown between zonulin levels and hyperactivity and social dysfunctions in children with ADHD.12 In the latter one, a positive correlation was found between Conner's parent rating score and zonulin level.8 However, two other studies reported no significant difference in zonulin levels between ADHD and control groups.9,18
Occludin and claudins are known to be important molecules for the continuation and functionality of the BBB and intestinal barrier. The tight junctions are formed by these molecules.19 Claudin-5 is one of the most important components of endothelial tight junctions in the BBB and if claudin-5 dysfunction occurs, the brain is more frequently exposed to harmful environmental factors.20 Studies have detected that claudin 5 may be associated with psychiatric disorders such as obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), bipolar disorder (BPD), schizophrenia and ADHD.9,14,17,21 In the literature, there is only one study examining the relationship between ADHD and claudin-5. In that study, higher claudin-5 levels were found in the ADHD group compared to the control group and the authors stated that a significant increase in serum claudin-5 levels may have emerged as a secondary compensation mechanism for increased BBB permeability, and this condition may be related to a neuroinflammation of the several zones of the brain.9 While claudin-5 plays a more prominent role in the BBB, occludin, another important molecule that forms the basis of tight junctions, takes an active role in both the BBB and the intestinal barrier.22 Studies have reported that dysfunctions in occludin may be associated with schizophrenia and autism.13,22 To date, there are only two studies investigating the relationship between ADHD and occludin. Çakir et al. found higher occludin levels in the ADHD group.8 In the second study, no significant difference was found between the groups in terms of occludin levels. In this study, the serum levels of occludin showed a positive correlation with the subtest of detectability in the Conner's Performance Test.18
Tricellulin is a regulator of the structure of all tight junctions -including three-cellular tight junctions (tTJ)- by changing the structure of tight junction fibrils. tTJ is considered to be the weakest point of the tight junction network.23 Many studies have provided evidence for the close relationship between tricellulin and intestinal permeability. Studies demonstrated tricellular disruptions in intestinal diseases such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease which have been associated with increased intestinal permeability.24,25 A postmortem study exploring the relationship between psychiatric disorders and tricellulin found decreased tricellulin levels in the cortex, and increased tricellulin levels in the intestines of individuals with ASD.13 To our knowledge, the relationship between tricellulin and ADHD has not been investigated previously.
The previous literature provides insufficient data on the potential roles of these molecules in tight junctions in the BBB and intestinal barrier, and their relationship with ADHD. To the best of our knowledge, our study will be the first to investigate the relationship between tricellulin and ADHD. The hypotheses of this study are that the serum levels of the mentioned molecules would differ in children with ADHD compared to the unaffected control group, and they would be associated with ADHD severity.
Material and methodsSubjectsThe study group was composed of children and adolescents diagnosed with ADHD between the ages of 6 and 12, recruited among the subjects who were admitted to the Child and Adolescent Psychiatry Outpatient Clinic. The participants of the study group were recruited among the patients admitted to our clinic between 01/07/2020 and 01/05/2021 consecutively. One hundred patients who were eligible for the study were admitted to our clinic, 35 of them did not accept participating in the study, and 8 were not eligible because of having at least one of the exclusion criteria. In total 57 subjects were recruited for the study. The following exclusion criteria were applied for the study group: Having a chronic physical, metabolic, genetic, respiratory, neurological, or acute/chronic gastrointestinal system disease; having a history of severe head trauma or organic brain injury; having diagnoses of any psychiatric disorders except ADHD according to DSM-5 diagnostic criteria; and previous use of ADHD and/or any other psychiatric medication. The control group consisted of children and adolescents (n = 60) who applied to the Pediatric Cardiology Outpatient Clinic and volunteered for themselves and their parents. Many children apply to the cardiology clinics for very benign reasons (i.e. consultation for a check for eligibility for a sportive activity and innocent heart murmur). Patients who were not diagnosed with any cardiologic disorder after cardiologic evaluation (except innocent heart murmur) were referred to us. Subsequently, psychiatric evaluation of the patients was performed and those with no current or previous psychiatric diagnosis and no psychiatric medication use were included in the control group. Participants with a previous psychiatric diagnosis were not included in the control group. Other exclusion criteria were the same as the ADHD group exclusion criteria mentioned above. Verbal and informed written consent was obtained from the parents of the participants.
Diagnostic and symptom assessmentDuring the examinations of the children, Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia for School-Aged Children, Present and Lifetime Version (K-SADS-PL) was applied by an experienced clinician and ADHD was diagnosed based on DSM-5 diagnostic criteria.1,26 After the examination, the sociodemographic data form was filled out by the clinician for all participants. Parents of the participants in the study group filled out Conner's Parent Rating Scale-Short Form to determine the severity of ADHD symptoms. Since the previous data indicate a possible relationship between ASD and molecules related to BBB and intestinal permeability,13,16 we aimed to control the effect of ASD symptoms. Therefore, the parents filled out the Turkish Version of the Autism Spectrum Screening Questionnaire (ASSQ) for the purpose of screening autistic characteristics in children.27,28 Parents of the participants in the control group filled out the Child Behavior Checklist for 4–18 age (CBCL/4–18) to test the severity of psychiatric disorders and those who demonstrated over threshold levels of psychiatric symptoms of any psychiatric disorder were excluded from the study. The reliability and validity of CBCL/4–18 were previously established for the Turkish population.29 Conner's Continuous Performance Test was applied to all children in the study group by an expert psychologist to assess the performance of the participants in the areas of inattention, impulsivity, sustained attention and vigilance.30
Blood samplesVenous blood samples of the participants in the study and control groups were drawn from the antecubital vein between 08:00 and 10:00 in the morning after 8 h of fasting due to the possibility of a relationship between satiety level and molecules we have investigated in our study.31 Blood samples were centrifuged and serum samples were kept frozen at −80 °C until the study day. Serum levels of claudin-5 (E-EL-H1630-Elabscience, Wuhan, China), occludin (E-EL-H1073-Elabscience, Wuhan, China), zonulin (E-EL-H5560-Elabscience, Wuhan, China), and tricellulin (MBS2706976-MyBioSource, San Diego, California, USA) were measured using commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits following the protocols of the manufacturers. In spectrophotometric measurements, all biochemical parameter results were calculated as “ng/ml” according to the absorbance-concentration calibration graphs using the Bio-rad Microplate absorbance reader xMark (Bio-rad Laboratories, California, USA) system.
Statistical analysisStatistical analyses were performed using SPSS 20.0 statistical software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). The normality distributions of all variables were checked using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. Age, biochemical parameter levels and scale scores of the study and control group were compared using Mann-Whitney U or Student's t-tests according to the distribution characteristics. In addition, a multivariate analysis of covariance (MANCOVA) was performed to reduce the risk of type I errors related to the multiple-test effect and to control for potential confounding factors such as age, gender, and autistic traits. After determining that there was a significant difference between the study and control groups by performing MANCOVA, a one-way analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) was performed on the outcome variables. After comparison analyses, Pearson or Spearman correlation analyses were utilized in the study group to test the relationships between biochemical parameters and clinical variables. Finally, a hierarchical regression model was conducted on the study group to determine whether Conner's scale scores and CPT scores had incremental predictive validity in predicting the biochemical parameters we investigated. In the first step, we tested the effects of age and gender, then, we added the ASD screening scale total score to the model in the second step. Finally, we tested the effects of Conner's total score and subscale scores and CPT scores in different models in the third step. Non-normally distributed variables (i.e. claudin-5, occludin and zonulin levels) were log-transformed and log-transformed values were used in MANCOVA and ANCOVA. A value of p < 0.05 (two-tailed) was considered to indicate significance.
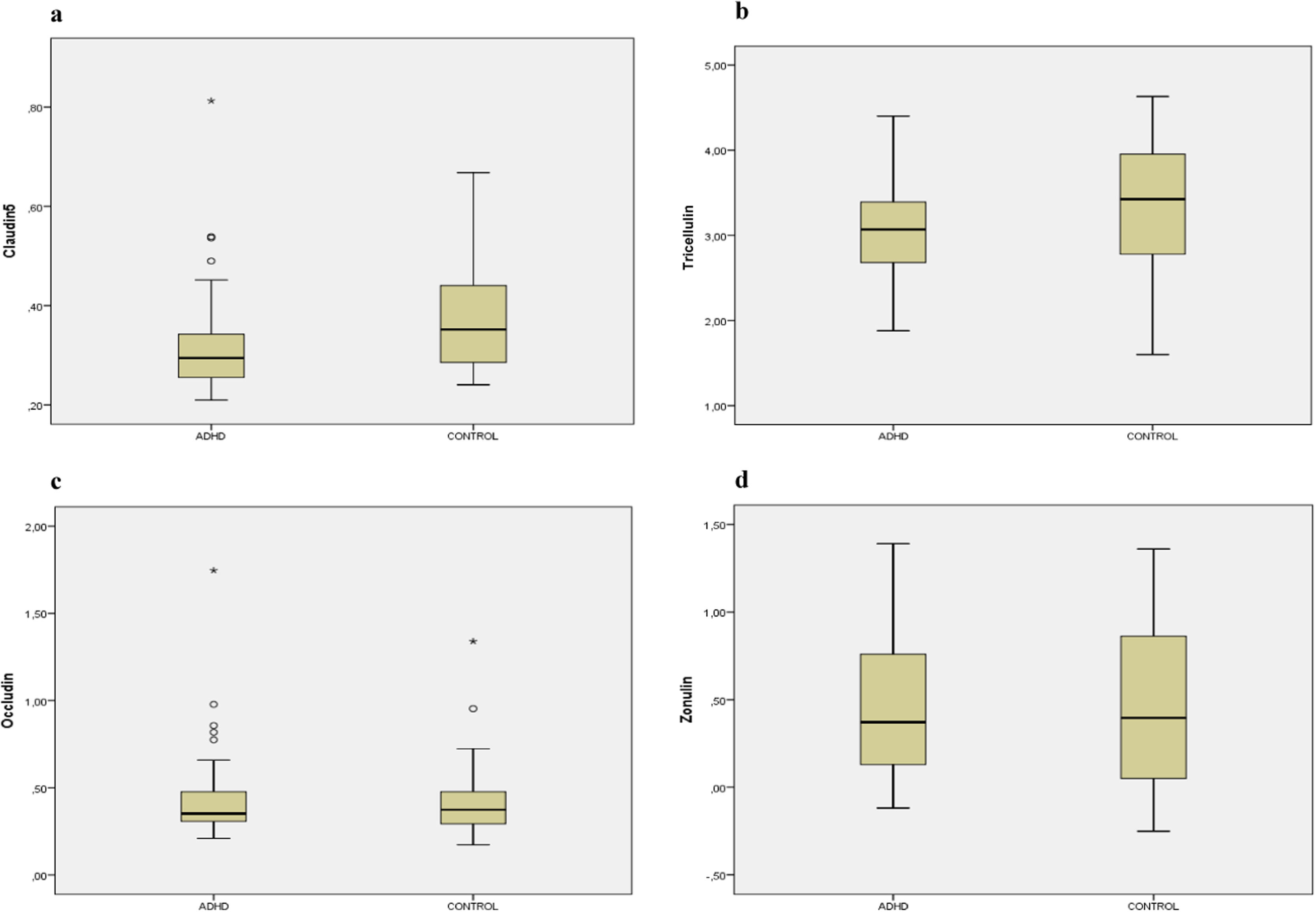
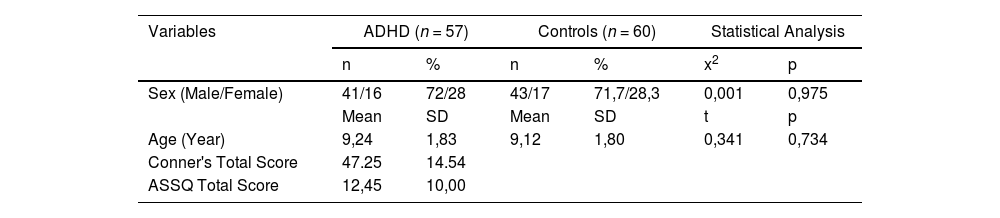
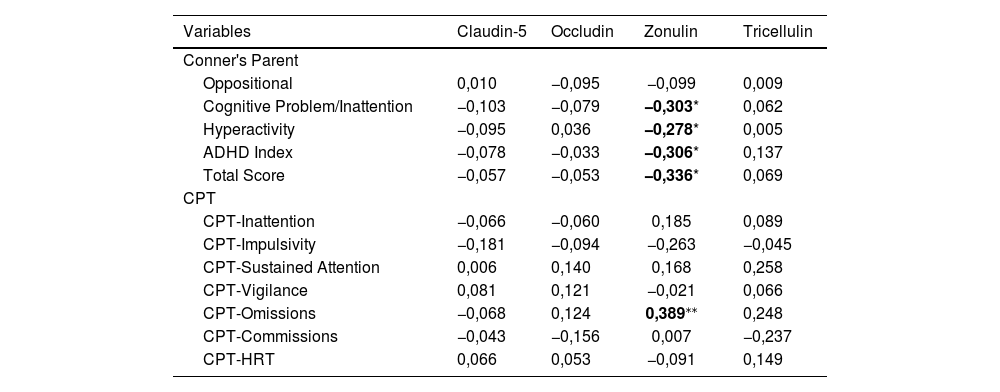
ResultsThe study included 57 participants with ADHD (41 boys, 16 girls) and 60 control participants (43 boys, 17 girls). The mean age did not differ significantly between the study (9.24 ± 1.82 years) and control (9.12 ± 1.80 years) groups. In the ADHD group, the mean Conner's total score was 47.25 ± 14.54 and the mean ASSQ total score was found to be 12.45 ± 10.00. Demographic and clinical characteristics of participants with ADHD and controls are presented in Table 1. Serum claudin-5 and tricellulin levels were found to be significantly lower in the ADHD group compared to the control group. There was no significant difference between ADHD and control groups in terms of zonulin and occludin levels. The MANCOVA test demonstrated that there were significant differences between the groups for the whole sample (Pillai's Trace V = 0,129, F(1115) = 4059, p = 0,004 and ηp2 = 0,129). Separate univariate ANCOVAs were used after being adjusted same confounding factors. The analyses demonstrated significant differences for claudin-5 and tricellulin, but no significant differences for occludin and zonulin between the groups (Table 2; Fig. 1).
Demographic characteristics of ADHD and controls and scale scores of ADHD group.
ADHD: attention deficit hyperactivity disorder; ASSQ; autism spectrum screening questionnaire; SD: standard deviation.
Serum claudin-5, occludin, zonulin and tricellulin levels of ADHD and controls.
| ADHD (n = 57) | Controls (n = 60) | Statistical Analysis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANCOVAc | |||||||
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | z/t | P | F | p | ηp2 | |
| Claudin-5 *(ng/mL) | 2,14 ± 0,71 | 2,47 ± 0,71 | −3702 | P< 0,001a | 10,196 | 0,002 | 0,083 |
| Occludin *(ng/mL) | 3,75 ± 7,17 | 2,99 ± 2,75 | −0,136 | p = 0,892a | 0,264 | 0,608 | 0,002 |
| Zonulin *(ng/mL) | 4,82 ± 5,89 | 5,06 ± 5,53 | −0,076 | p = 0,939a | 0,008 | 0,930 | < 0,001 |
| Tricellulin *(ng/mL) | 3,04 ± 0,56 | 3,34 ± 0,71 | −2552 | p = 0.012b | 6650 | 0,011 | 0,56 |
ADHD: attention deficit hyperactivity disorder; SD: standard deviation.
Box plots representing the distribution of (a) claudin-5, (b) tricellulin, (c) occludin, (d) zonulin levels with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and healty controls. Claudin-5, occludin and zonulin levels were log-transformed prior to analyses. Mann-Whitney U test and Student-t-test was used for comparisons between two groups.
In correlation analyses, a negative correlation was found between zonulin and Conner's total score, and cognitive problem/inattention, hyperactivity, and ADHD index scores among Conner's subscales. A positive correlation was detected between zonulin and CPT omissions. No correlation was found between serum levels of other biochemical variables and ADHD severity (Table 3).
The correlation of serum claudin-5, occludin, zonulin, and tricellulin levels of ADHD group and Conner's Parent Rating Scale scores and CPT scores.
| Variables | Claudin-5 | Occludin | Zonulin | Tricellulin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conner's Parent | ||||
| Oppositional | 0,010 | −0,095 | −0,099 | 0,009 |
| Cognitive Problem/Inattention | −0,103 | −0,079 | −0,303* | 0,062 |
| Hyperactivity | −0,095 | 0,036 | −0,278* | 0,005 |
| ADHD Index | −0,078 | −0,033 | −0,306* | 0,137 |
| Total Score | −0,057 | −0,053 | −0,336* | 0,069 |
| CPT | ||||
| CPT-Inattention | −0,066 | −0,060 | 0,185 | 0,089 |
| CPT-Impulsivity | −0,181 | −0,094 | −0,263 | −0,045 |
| CPT-Sustained Attention | 0,006 | 0,140 | 0,168 | 0,258 |
| CPT-Vigilance | 0,081 | 0,121 | −0,021 | 0,066 |
| CPT-Omissions | −0,068 | 0,124 | 0,389⁎⁎ | 0,248 |
| CPT-Commissions | −0,043 | −0,156 | 0,007 | −0,237 |
| CPT-HRT | 0,066 | 0,053 | −0,091 | 0,149 |
ADHD: attention deficit hyperactivity disorder CPT: Conner's Continuous Performance Test; HRT: hit reaction time.
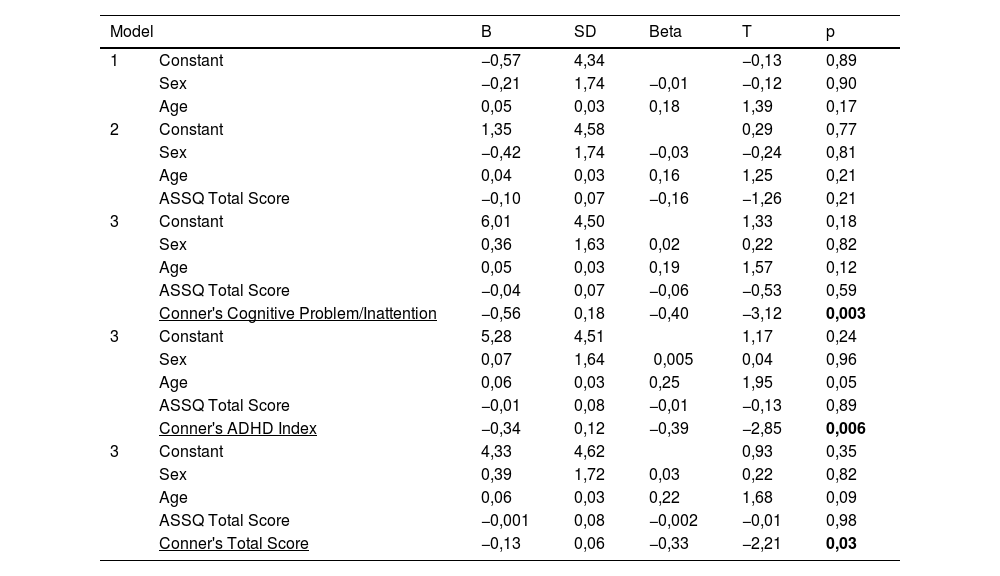
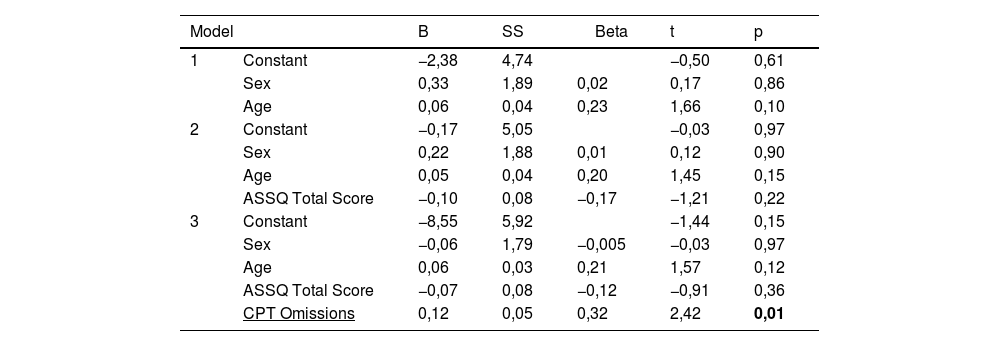
Hierarchical regression analyses demonstrated that serum zonulin level was negatively predicted by Conner's total score, ADHD index and cognitive problem/inattention subscale scores. Omissions score -one of the CPT subscales- positively predicted serum zonulin levels (Tables 4 and 5). Other biochemical parameters were not predicted by any of the ADHD and CPT variables. Conducting regressions among highly correlated variables may cause the inflation effect and this condition may question the reliability of the analysis. To test the inflation effect of the analyses, we have tested the multicollinearity in the regression analysis using the variance inflation factor (VIF). All of the VIF scores of the analyses were lower than 1,5 inferring no inflation effect.
Hierarchical regression analysis of Conner's Parent Rating Scale scores predicting serum zonulin level.
SD: standard deviation; ASSQ: autism spectrum screening questionnaire.
Hierarchical regression analysis of CPT scores predicting serum zonulin level.
CPT: Conner's Continuous Performance Test; ASSQ: autism spectrum screening questionnaire.
In this study, we have investigated the association between ADHD and serum levels of claudin-5, occludin, zonulin and tricellulin in children and adolescents. We found that serum claudin-5 and tricellulin levels were significantly lower in subjects with ADHD compared to the control group. However, there was no significant difference between the groups in terms of serum zonulin and occludin levels. To the best of our knowledge, our study is the first to investigate the relationship between ADHD and tricellulin.
In our study, lower serum claudin-5 levels were found in the ADHD group compared to the control group, and the significant difference continued after controlling for confounding factors such as age, gender, and ASD score. Claudin-5 is one of the important components of endothelial TJs in the BBB acting by inhibiting the passage of pathogenic molecules to the brain.31 In a study with animal models, decreased claudin-5 expression and loss of function in tight junctions in vascular structures were detected in rats exposed to chronic stress. The authors proposed that the loss of function in tight junctions causes an increase in the permeability of the BBB, and as a result, depression-like behaviors develop in rats.32 Several human studies have explored claudin-5 and its effect on psychiatric disorders. For example, recent two studies reported decreased claudin-5 levels in patients with depression and schizophrenia.14,33 Also, an increased IgA response to claudin-5 was found in schizophrenic patients with deficiency syndrome compared to schizophrenic patients without deficiency syndrome and the control group. The authors concluded that the increased IgA response to claudin-5 may cause a deterioration in tight junctions in the BBB, which may have an effect on the pathogenesis of schizophrenia.22 In addition to schizophrenia, studies showed increased claudin-5 levels in psychiatric disorders such as BPD and OCD.17,21 However, only one study investigated the relationship between claudin-5 and ADHD reporting increased serum claudin-5 levels in individuals with ADHD compared to the control group.9 The authors reported that the increased claudin-5 levels in the ADHD group may be due to a compensatory mechanism against claudin-5-related disruption in BBB. However, comorbid diagnoses such as ODD, CD, OCD, anxiety disorders and MDD that may affect the claudin-5 level were not considered in this study. Since these accompanying diagnoses may affect claudin-5 levels, it may be difficult to investigate the possible direct relationship between ADHD and claudin-5. In our study, unlike the mentioned study, K-SADS-PL was applied to the participants while consisting the study group, and participants with comorbid psychiatric disorders were excluded to compose a pure ADHD group. We think that the decrease in claudin-5 level that we have detected in the ADHD group might have resulted in increased permeability of the BBB by disrupting its structure, and this mechanism may be involved in the etiopathogenesis of ADHD. On the other hand, in addition to the brain and intestines, claudin-5 is also present in tissues of organs such as lung, liver, stomach. Non-symptomatic and undetected disorders of these organs may also affect claudin levels.34
Our results showed that serum tricellulin levels were significantly reduced in the ADHD group compared to the control group. In the literature, the relationship between tricellulin and diseases in which changes in intestinal permeability are observed -such as ulcerative colitis and Chron's disease- has been shown. In a study, decreased tricellulin levels were found in patients with ulcerative colitis. In this study, the authors report that IL 13, which is known to be increased in ulcerative colitis, suppresses the level of tricellulin which causes an increase in the permeability of tTJs.24 Another study conducted in 2019 reported that children of mothers with higher gestational IL-13 levels had more frequent and higher levels of inattention, hyperactivity, and behavioral problems and this relationship has been associated with increased neuroinflammation related to high IL-13 levels in this study.35 Considering the data from these studies, the relationship between IL-13 and tricellulin may be one of the mechanisms contributing to the etiopathogenesis of ADHD.
There is only one study in the literature investigating the relationship between tricellulin and psychiatric disorders. In that study, tricellulin levels were found to be increased in the cortex of individuals with ASD compared to the control group in the postmortem examination of the subjects. The authors of this study interpreted this increase as a compensatory mechanism for the deterioration in impaired BBB. In the same study, intestinal tricellulin levels were found to be lower in the ASD group as a result of intestinal biopsies taken from individuals diagnosed with ASD, which was proposed to play a role in the etiopathogenesis of ASD.13 There is no study in the literature investigating the relationship between ADHD and tricellulin. Our study is the first to investigate this relationship. In line with the data obtained from the studies carried out so far, it is known that tricellulin has an important role in the intestinal barrier. Moreover, it has been reported that tTJs, in which tricellulin plays an important role, are the weak point of the all tight junction network.23 Decreased tricellulin levels may disrupt the structure of the intestinal barrier and thereby increase intestinal permeability. Studies have shown that increased intestinal permeability and neuroinflammation affect brain function, which is associated with higher psychiatric symptoms.15 The low levels of tricellullin we detected may indicate a disruption of the intestinal barrier and hence increased permeability. These mechanisms may also contribute to the etiopathogenesis of ADHD.
"Leaky/permeable gut syndrome" resulting from disruptions in zonulin has been associated with the pathogenesis of diseases such as celiac disease, irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease, and it has been reported that zonulin may be a biomarker of increased intestinal permeability.15,36 Previous research indicates higher serum zonulin levels in children with ASD compared to the control group,16,37 however, inconsistent findings were also reported in patients with MDD.38,39 There are two studies in the literature investigating the relationship between ADHD and zonulin. While Özyurt et al. reported higher zonulin levels,12 Aydoğan Avşar et al. reported no significant difference between children with ADHD and the control group.9 In our study, no significant difference was found between the groups in terms of serum zonulin levels, which is consistent with the previous study. In addition to this finding, we found that there was a negative correlation between serum zonulin levels and cognitive problem/inattention, hyperactivity and ADHD index in Conner's ADHD scale. Furthermore, regression analyses demonstrated that serum zonulin levels were negatively predicted by Conner's total score, ADHD index and cognitive problem/inattention subscale scores in the ADHD group. In a study conducted on patients with MDD, it was reported that more epithelial destruction would increase intestinal permeability and that zonulin expression might decrease as a result of this excessive destruction.38 This study supports our finding and we also think that the negative correlation between zonulin and the aforementioned scale scores that we found in the ADHD group, may be due to excessive zonulin destruction.
We found that there was a positive correlation between the omissions score -which defines the score indicating the missing targets in the CPT test- and serum zonulin levels, and the omissions score predicted the zonulin level positively in the regression analysis. In a recent study, it was reported that CPT results may be clinically useful, but should not be used solely for diagnosis due to low sensitivity and CPT scores may be helpful as a component in a multivariate continuous approach.40 We think that the positive relationships between zonulin and omission scores in CPT -which is contradictive of our other findings- might be due to the low sensitivity of CPT. More studies are needed to better understand the relationship between zonulin and ADHD and to clarify its role in the etiopathogenesis of ADHD.
Occludin, part of the integral membrane protein family, is an important element of the tight junction that can weaken the tight junction barrier and increase intestinal permeability.41 Increased IgM and IgA response to occludin was demonstrated in patients with schizophrenia22,42 and it has been stated that these increased Ig responses may result in a disruption in the occludin mechanism -and therefore in the structure of the TJs- which may conclude in an increased intestinal permeability. In addition, Fiorentino et al. reported that while there was no significant difference in the cortex occludin levels of the subjects with ASD and controls, they reported decreased occludin levels in the intestines of subjects with ASD.13 To date, there are two studies in the literature investigating the relationship between ADHD and occludin. In the first one, significantly higher levels of occludin were found in the ADHD group.8 In the second study, no significant difference was found between the groups in terms of occludin levels.18 In our study, similar to the previous study, no significant difference was found between the ADHD group and the control group in terms of serum occludin levels. The relationship between occludin and psychiatric disorders is not fully known yet. Our findings did not support the possible role of occludin in ADHD and further studies investigating the link between occludin and ADHD are needed.
Some limitations should be considered when interpreting our results. First of all, the sample size of our study was relatively small. Future studies with larger samples will make a larger contribution to this field. In addition, the parameters we investigated were analyzed only in the serum samples of the patients. Body fluids indicating the direct effect of the molecule (i.e. cerebrospinal fluid) would provide more reliable data. We collected the blood of the participants in the morning (i.e. between 8.00 a.m. and 10.00 a.m.) after 8 h of fasting to avoid the confounding effect of diet and diurnal rhythm. However, this condition may cause another limitation since zonulin levels can fluctuate throughout the day.25 Another limitation of our study is that the control group was composed of patients admitted to pediatric cardiology department. Selecting control group among normal population would give more sensitive results. In addition, the food allergy and microbiome of the subjects may influence the gut-blood barriers and should be considered in future studies.43 Also, this is a cross-sectional study and because of the nature of cross-sectional studies, we could not provide data about the developmental process of the disorder. Because the developmental process of many disorders may vary in children and adolescents, focusing on a specific age group may give more robust data in the field.
ConclusionIn conclusion, although we cannot infer a causal relationship between the biomarkers and ADHD because of the cross-sectional design of the study, our results suggests that changes in claudin-5 and tricellulin molecules may play a role in the etiopathogenesis of ADHD. Alterations in these molecules can alter the intestinal barrier or BBB permeability, leading to a detrimental effect on the CNS. Future studies with larger populations will increase our knowledge of whether decreased claudin-5 and tricellulin levels occur as a cause or consequence of the pathophysiological processes that lead to ADHD, and whether they are among potential mechanisms of ADHD.
This study was accepted as an oral presentation at the 31st European Congress of Psychiatry and will be presented on March 27, 2023.
Funding for this study was provided by a grant from the Necmettin Erbakan University Scientific Research Projects Unit within the scope of project number 201518024.