Recently, an inverse relationship between the blood concentration of lipoprotein(a) (Lp(a)) and triglycerides (TG) has been demonstrated. The larger the VLDL particle size, the greater the presence of VLDL rich in apoliprotein E and in subjects with the apoE2/E2 genotype, the lower Lp(a) concentration. The mechanism of this inverse association is unknown. The objective of this analysis was to evaluate the Lp(a)-TG association in patients treated at the Lipid Units included in the registry of the Spanish Society of Atherosclerosis (SEA) by comparing the different dyslipidemias.
Patients and methodsFive thousand two hundred and seventy-five subjects ≥18 years of age registered in the registry before March 31, 2023, with Lp(a) concentration data and complete lipid profile information without treatment were included.
ResultsThe mean age was 53.0 ± 14.0 years, with 48% women. The 9.5% of subjects (n = 502) had diabetes and the 22.4% (n = 1184) were obese. The median TG level was 130 mg/dL (IQR 88.0–210) and Lp(a) 55.0 nmol/L (IQR 17.9–156). Lp(a) concentration showed a negative association with TG concentration when TG values exceeded 300 mg/dL. Subjects with TG > 1000 mg/dL showed the lowest level of Lp(a), 17.9 nmol/L, and subjects with TG < 300 mg/dL had a mean Lp(a) concentration of 60.1 nmol/L. In subjects without diabetes or obesity, the inverse association of Lp(a)-TG was especially important (p < 0.001). The median Lp(a) was 58.3 nmol/L in those with TG < 300 mg/dL and 22.0 nmol/L if TG > 1000 mg/dL. No association was found between TG and Lp(a) in subjects with diabetes and obesity, nor in subjects with familial hypercholesterolemia. In subjects with multifactorial combined hyperlipemia with TG < 300 mg/dL, Lp(a) was 64.6 nmol/L; in the range of 300–399 mg/dL of TG, Lp(a) decreased to 38. 8 nmol/L, and up to 22.3 nmol/L when TG > 1000 mg/dL.
ConclusionsOur results show an inverse Lp(a)-TG relationship in TG concentrations >300 mg/dL in subjects without diabetes, obesity and without familial hypercholesterolemia. Our results suggest that, in those hypertriglyceridemias due to hepatic overproduction of VLDL, the formation of Lp(a) is reduced, unlike those in which the peripheral catabolism of TG-rich lipoproteins is reduced.
Recientemente se ha demostrado una relación inversa entre la concentración en sangre de la lipoproteína(a) (Lp(a)) y los triglicéridos (TG). A mayor tamaño de partículas VLDL, mayor presencia de VLDL ricas en apoliproteína E y en sujetos con genotipo apoE2/E2, Lp(a) más baja. El mecanismo de esta asociación inversa es desconocido. El objetivo de este análisis fue evaluar la asociación Lp(a)-TG en los pacientes atendidos en las Unidades de Lípidos incluidos en el registro de la Sociedad Española de Arteriosclerosis (SEA) comparando las diferentes dislipidemias.
Pacientes y métodosSe incluyeron 5.275 sujetos ≥18 años registrados en el registro antes del 31 de marzo de 2023, con datos de concentración de Lp(a) e información completa del perfil lipídico sin tratamiento.
ResultadosLa media de edad fue de 53,0 ± 14,0 años, con un 48% de mujeres. El 9,5% (n = 502) tenían diabetes y 1184 sujetos (22,4%) presentaban obesidad. La mediana de TG fue de 130 mg/dL (IQR 88,0-210) y de Lp(a) 55,0 nmol/L (IQR 17,9 -156). La concentración de Lp(a) mostró una asociación negativa con la concentración de TG cuando los valores de TG superaban los 300 mg/dL. Los sujetos con TG > 1000 mg/dL mostraron el menor nivel de Lp(a) 17,9 nmol/L y los sujetos con TG < 300 mg/dL, presentaron una concentración media de Lp(a) de 60,1 nmol/L.
En sujetos sin diabetes ni obesidad, la asociación inversa de Lp(a)-TG fue especialmente importante (p < 0,001). La mediana de Lp(a) fue de 58,3 nmol/L en aquellos con TG < 300 mg/dL y 22,0 nmol/L si TG > 1000 mg/dL. No se encontró asociación entre TG y Lp(a) en sujetos con diabetes y obesidad, ni en sujetos con hipercolesterolemia familiar. En los sujetos con hiperlipemia combinada multifactorial con TG < 300 mg/dL, la Lp(a) fue 64,6 nmol/L, en el rango de 300-399 mg/dL de TG, la Lp(a) desciende hasta 38,8 nmol/L, y hasta 22,3 nmol/L si TG > 1000 mg/dL.
ConclusionesNuestros resultados muestran una relación inversa Lp(a)-TG en concentraciones de TG > 300 mg/dL en sujetos sin diabetes, ni obesidad y sin hipercolesterolemia familiar. Nuestros resultados sugieren que, en aquellas hipertrigliceridemias por sobreproducción hepática de VLDL, se reducen la formación de Lp(a), a diferencia de aquellas en las que el catabolismo periférico de las lipoproteínas ricas en TG está reducido.
Lipoprotein(a) (Lp[a]) is synthesised in the liver and consists of a particle similar to low density lipoprotein (LDL), in which apolipoprotein B-100 (apo B) covalently binds by means of a disulphide bond to a specific Lp(a) protein, apo A.1
Apo A has evolved from the plasminogen gene by duplication and remodelling. It consists of a repeating number of amino acid sequences called “kringles” and an inactive protease domain.2,3 Despite its similarity to the LDL particle, how Lp(a) is catabolised remains unknown, although it has been seen to be independent of LDL metabolism.4,5 The concentration of Lp(a) varies greatly between subjects (due in part to race and gender). It depends primarily on genetic factors and approximately 25% of the population is known to have elevated Lp(a) levels (>50 mg/dL).6 A higher concentration of Lp(a) has been noted in heterozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia (FH) in users in comparison to the general population; nevertheless, the cause of this increase is still unclear.7–9 Furthermore, homozygous FH patients carrying two null alleles in the LDL receptor (LDLR) gene have twice the Lp(a) concentration of their non-FH relatives.10
High plasma concentrations of this particle are associated with atheromatous cardiovascular (CV) disease and aortic stenosis, possibly as a result of the proinflammatory and proatherogenic properties of Lp(a).11,12 On the other hand, elevated triglyceride (TG) levels are independently associated with increased CV morbidity and mortality, in particular when they correspond to small, dense LDL particles, and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) is decreased.13,14
TG synthesis is an important factor in Lp(a) synthesis in hepatocytes15 and it has been reported that there is an association between blood concentrations of Lp(a) and TG.16 Furthermore, Lp(a) concentrations differ according to APOE genotype, 17 whereas apo E levels in very low-density particles (VLDL) exhibit a direct correlation with Lp(a).18 An inverse Lp(a)-TG correspondence has recently been demonstrated. Subjects with larger VLDL particle size have lower Lp(a) concentration, and subjects with apo E-rich VLDL and those with the apo E2/E2 genotype had lower Lp(a) values. Thus, larger VLDL and apo E-enriched VLDL would be inversely implicated in plasma Lp(a) concentrations.19 The issue as to whether the inverse relationship between TG and Lp(a) depends on the cause of hypertriglyceridemia has yet to be ascertained.
The objective of this analysis is to probe the differences in association between Lp(a)-TG in individuals managed at the Lipids Units of the Spanish Society of Atherosclerosis (SEA) registry by comparing the different dyslipidaemias.
Patients and methodsStudy variablesAmong other data, the registry included personal health history, physical examination (blood pressure, weight, height, body mass index [BMI]), biochemical parameters, and the presence of CV disease.
Details included in the personal health history were hypertension, defined as systolic blood pressure ≥140 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure ≥90 mmHg or the use of antihypertensive medication, and diabetes mellitus (DM), in terms of fasting plasma glucose values ≥126 mg/dL. Obesity was regarded as BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2. Subjects diagnosed with multifactorial combined hyperlipaemia were defined as those with non-HDL cholesterol (c-non-HDL) ≥160 mg/dL and TG ≥ 150 mg/dL in the absence of the FH mutation. These patients were dichotomised on the basis of four variables: DM, obesity, FH, and multifactorial combined hyperlipaemia.
In order to study the association between Lp(a) and TG, only those subjects with Lp(a) and TG data were selected, excluding the rest.
Biochemical data were obtained from samples taken in fasting conditions and without lipid-lowering therapy or adjusted for the lipid-lowering therapy with which patients were being treated. The following baseline lipid data were collected: total cholesterol (TC), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), HDL-C, TG, apo B, and Lp(a). The presence of CV disease was assessed at the time of inclusion in the registry. LDL-C was calculated using the Friedewald formula when TG were less than 400 mg/dL. Lp(a) concentration was measured in md/dL and nmol/L according to the technique used at each centre and then converted to nmol/L to standardise the results. The formula Lp(a), nmol/L = 2.18 × Lp(a), mg/dL - 3.8320 was applied.20
We conducted this study in accordance with the provisions under the Declaration of Helsinki for the protection of the rights and welfare of persons participating in biomedical research.
Statistical analysisVariables were expressed as mean (standard deviation [SD]) for normally distributed variables, median (interquartile range [IQR]) for non-normally distributed variables, or percentage for qualitative variables. The analysis of Lp(a) concentration was arranged by TG groups (0–99; 100–199; 200–299; 300–399; 400–499; 500–999, and ≥1,000 mg/dL, respectively). Analysis of variance test (ANOVA) was used to examine intergroup differences. All data analyses were performed with the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) version 21 (IBM Armonk [New York], USA).
ResultsClinical characteristicsA total of 5,275 subjects from the SEA’s Registry of Dyslipidaemias were included in the study. The most important clinical characteristics of the study population, as well as the concentration of the lipid parameters established are presented in Table 1.
Clinical characteristics and lipid concentrations in the entire population of the Dyslipidaemia Registry.
| Mean (SD)/percentage (n) | Entire population of the Dyslipidaemia Registry | |
|---|---|---|
| n | Mean (SD)/% | |
| Sex, females, n (%) | 5.275 | 48 (100) |
| Age (years) | 5.275 | 53.0 ± 14.0 |
| Weight (kg) | 5.275 | 74.7 ± 25.7 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 5.275 | 27.4 ± 21.8 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 5.275 | 1.293 (24.5) |
| DM2, n (%) | 5.275 | 502 (9.5) |
| History of smoking (smoker), n (%) | 5.275 | 1.224 (23.2) |
| History of CV disease, n (%) | 5.275 | 1.293 (24.5) |
| Untreated TC (mg/dL) | 5.275 | 301.0 (262.0–350.0) |
| Untreated TG (mg/dL) | 5.275 | 130.0 (88.0–210.0) |
| Untreated HDL-C (mg/dL) | 5.275 | 53.00 (43.00–64.00) |
| Untreated LDL-C (mg/dL) | 5.275 | 206.4 (165.2–256.9) |
| Untreated non-HDL-C (mg/dL) | 5.275 | 245.0 (207.0–294.0) |
| Lp(a) (nmol/L) | 5.275 | 55.0 (17.9–155.7) |
BMI: Body mass index; CV: Cardiovascular; DM: Diabetes mellitus type 2; non-HDL-C: Non-HDL cholesterol; HDL-C: Cholesterol bound to high-density lipoproteins; LDL-C: Cholesterol bound to low-density lipoproteins; TC: Total cholesterol; SD: standard deviation; Lp(a): lipoprotein (a); TG: triglycerides.
Continuous data expressed as the mean (SD); categorical data expressed as percentages (number); quantitative data expressed with intervals (median-IQR).
The mean age at the time of inclusion in the registry was 53.0 ± 14.0 years; 48% were female, and the mean BMI was 27.4 ± 21.8 kg/m2. A total of 9.5% (n = 502) had DM and 1184 (22.4%) were obese. The mean TG concentration was 130.0 mg/dL (IQR 88.0–210.0) and Lp(a) was 55.0 nmol/L (IQR 17.9–155.7).
Association between triglycerides and lipoprotein(a)To examine the association between TG concentration and Lp(a), subjects were classified by ranges of 100 mg/dL of TG and Lp(a) was presented in the form of a graph (Fig. 1). The latter displayed a negative correlation with respect to TG. Those subjects with the highest concentration of TG (>1,000 mg/dL) displayed the lowest level of Lp(a) (17.9 nmol/L) and vice versa, those in whom TG values were below the level of 300 mg/dL, the mean amount of Lp(a) was 60.1 nmol/L. When examining the ranges of 0–99, 100–199, and 200–299 mg/dL, Lp(a) concentrations were 59.4, 63.7, and 57.2 nmol/L, respectively. A gradual decrease in the amount of Lp(a) is seen as TG concentrations increase and is especially striking at levels exceeding 300 mg/dL.
The effect of the mechanism of hypertriglyceridemia on the relationship between triglycerides and lipoprotein(a)To study the effect of hypertriglyceridemia on the concentration of Lp(a), the patients included in the registry were divided into four groups, according to the following criteria: with and without DM, with and without obesity, with and without the HF mutation, and with multifactorial combined hyperlipidaemia. The individuals without DM and without obesity exhibited the inverse relationship between Lp(a) and TG that was particularly important (Fig. 2). The higher the TG concentration, the lower the Lp(a) concentration was, revealing a mean of 58.3 nmol/L in those with a TG concentration of less than 300 mg/dL in subjects who had neither obesity nor DM. As evidenced in the entire population, the association becomes even more marked starting at TG values of >300 mg/dL, with values of 43.2, 32.4, 27.2, and 22.0 nmol/L, as TG levels increase in the non-diabetic, non-obese subjects. In contrast, users with both DM and obesity failed to exhibit said association (Fig. 2).
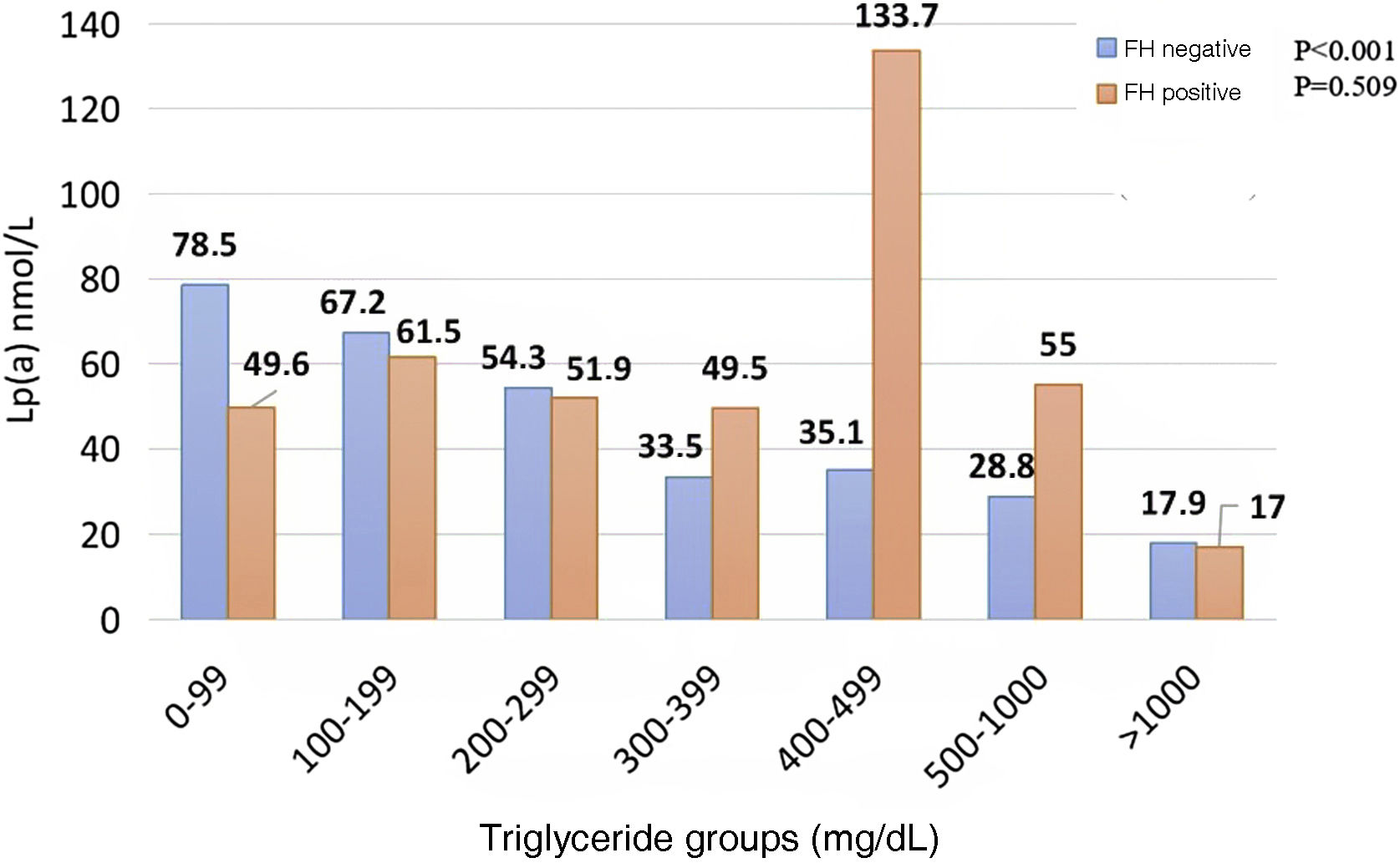
When comparing subjects who carry a mutation related to HF with those who do not, a linear, decreasing association was noted among those who were negative for the mutation, unlike those who carried the mutation who did not present a correspondence between Lp(a) and TG (Fig. 3).
The effect of TG on Lp(a) in patients defined as having multifactorial hyperlipemia is illustrated in Fig. 4. In this case, the mean values for the 0–99 mg/dL TG group reveals a mean figure of Lp(a) of 64.6 nmol/L, whereas those in the 300–399 mg/dL range had mean amounts of 38.8 nmol/L down to 22.3 nmol/L at higher levels of TG.
DiscussionLp(a) concentration is a well-established CV risk factor, which changes little over the course of a person’s lifetime and in which genetic factors play a major role. Nevertheless, different clinical situations including chronic kidney disease,21 nephrotic syndrome,22 pregnancy,23 or cholestasis24 can also alter it, which has aided our understanding of the mechanisms that control Lp(a) in blood. Our study adds another condition, hypertriglyceridemia, which substantially modifies Lp(a) levels, confirming a recent study19 and indicates, for the first time, that the mechanism of hypertriglyceridemia contributes to explaining the inverse relationship between Lp(a) and TG. In our analysis, the reverse association between Lp(a) and TG differs across the comorbidities studied.
To begin with, the present study confirms that in the population of the Dyslipidaemia Registry, taken as a whole, the negative Lp(a)-TG correlation recently reported19 and previously suggested by the research conducted by Bartens et al.25 that revealed that elevated TG concentrations corresponded inversely with Lp(a) levels. That being said, the potential mechanisms underlying this relationship were not analysed, although it did indicate that an increase in apo E-rich TG remnant particles could affect the synthesis of Lp(a).19
Our research suggests that the inverse correspondence between Lp(a) and TG is not linear and that only when TG concentrations exceed 300 mg/dL is the effect significant and becomes very important in subjects with levels of TG > 1,000 mg/dL who have 75% less Lp(a) in their blood than those with TG < 300 mg/dL.
To study the mechanism of this relationship, we have chosen four conditions that may be associated with hypertriglyceridemia: DM,26 obesity,27 FH with mutations in candidate genes,28 and other multifactorial polygenic hypercholesterolaemia, such as multifactorial combined hyperlipaemia, previously known as familial combined hyperlipaemia.29 In this way, we can substantiate the effect of correspondence in situations with decreased peripheral catabolism of TG-rich particles, such as obesity and DM, where peripheral insulin resistance reduces lipoprotein lipase activity26; conditions in which there is a decrease in hepatic lipoprotein catabolism, such as FH, and those with increased synthesis of TG-rich lipoproteins, such as multifactorial combined hyperlipaemia.30 In the case of this last condition.
By studying individuals both with and without DM, as well as those who are and those who are not obese, the inverse relationship between Lp(a) and TG has been found to be non-significant in the presence of either of these conditions and magnified in the absence of both. As most hypertriglyceridemias with neither obesity nor DM are predominantly a consequence of increased hepatic TG synthesis, we can speculate that those situations with overproduction of VLDL particles somehow inhibit Lp(a) synthesis. Consistent with this hypothesis, in subjects with FH and a proven pathogenic variant, the inverse association is no longer observed. In contrast, it is in users with a diagnosis of multifactorial combined hyperlipaemia, where there is the greatest increase in VLDL synthesis among the most common hyperlipaemias, that the negative association is most pronounced and significant.
This inverse relationship between Lp(a) and TG is not constitutive and irreversible, given that in those who succeed in reducing TG concentration either by diet or drugs, Lp(a) concentration increases.19 By means of some unknown mechanism, statins discretely raise Lp(a) concentration.31 From our results, the effect of statins on TG would account for the increase in Lp(a), at least in part. This aspect has yet to be researched and it would be interesting to be able to do so in the future.
Our data suggest that hyperlipaemia resulting from TG hypersynthesis as demonstrated in subjects without DM, obesity, or a pathogenic FH mutation, where there is an enrichment of VLDL particles, probably decreases Lp(a) formation. This phenomenon would be consistent with that already proven and reported for cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) inhibitors.32 Conversely, in those hypertriglyceridemias that are a consequence of a catabolism disorder, where there is a decrease in TG catabolism such as in DM and obesity, this inverse Lp(a)-TG correlation does not appear to be apparent.
In summary, the inverse Lp(a)-TG association would seem to depend on the aetiology of the hyperlipaemia, where increased synthesis at the hepatic level predominates and corresponds more strongly to this phenomenon.
Authors’ contributionConceptualization: VM-B and FC; Data curation: VM-B, AC, PC, AMB, AV, CM-A, JP, JM-G, AF-A, MS-T, and FC. Analysis: VM-B and FC; Procurement of funding: FC; Research, VM-B, AC, ML, and FC; Methodology: VM-B and FC; Project administration: FC; Resources: FC; Software: VM-B and FC; Drafting – Preparation of the original draft: VM-B and FC; Revision: All the authors. All of the authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
FundingThis study has been paid for with grants from the Spanish Ministry of the Economy and CompetitivityPI 18/01777 PI 19/00694 and CIBERCV, and the government of Aragon B-14. These projects are co-funded by the Instituto de Salud Carlos III (Carlos III Institute of Health) and the European Union Regional Development Fund (ERDF) «A way to make Europe».
Conflict of interestsThe authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
This communication was presented at the XXXIII SEA National Conference – Virtual from 7 to 10 June 2021 and was awarded with the prize for the best communication on the subject/ topic: lipid units, secondary prevention, and treatments.