Surgically site infections (SSIs) are a major problem that limits the benefits of surgical interventions. The cumulative incidence of SSIs in colon surgery and compliance with antibiotic prophylaxis as well as the causes of non-compliance were evaluated.
MethodsMulti-centre prospective surveillance study between 2012 and 2019 in seven hospitals of the Canary Health Service using an active epidemiological surveillance system. SSIs was defined according to the criteria of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
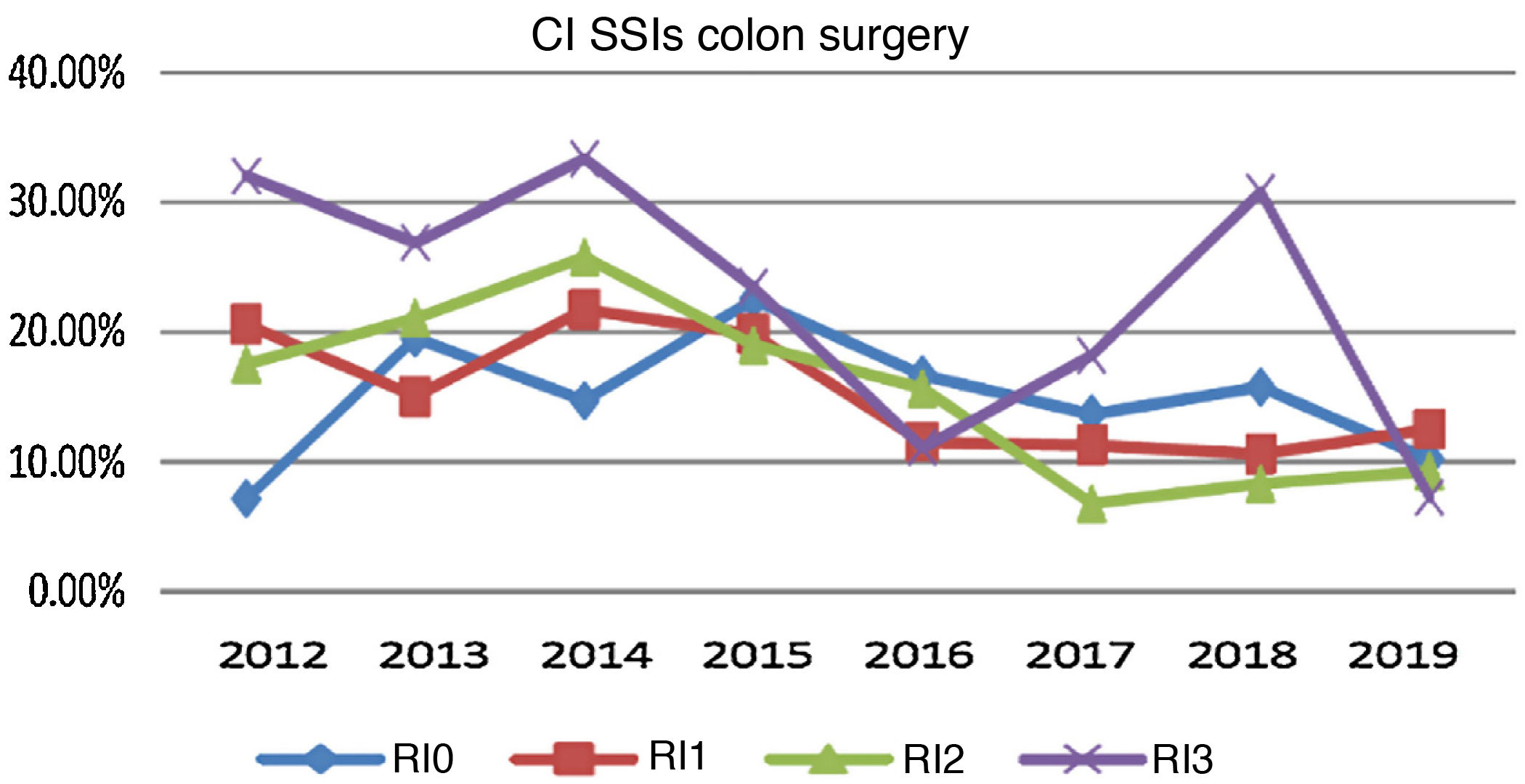
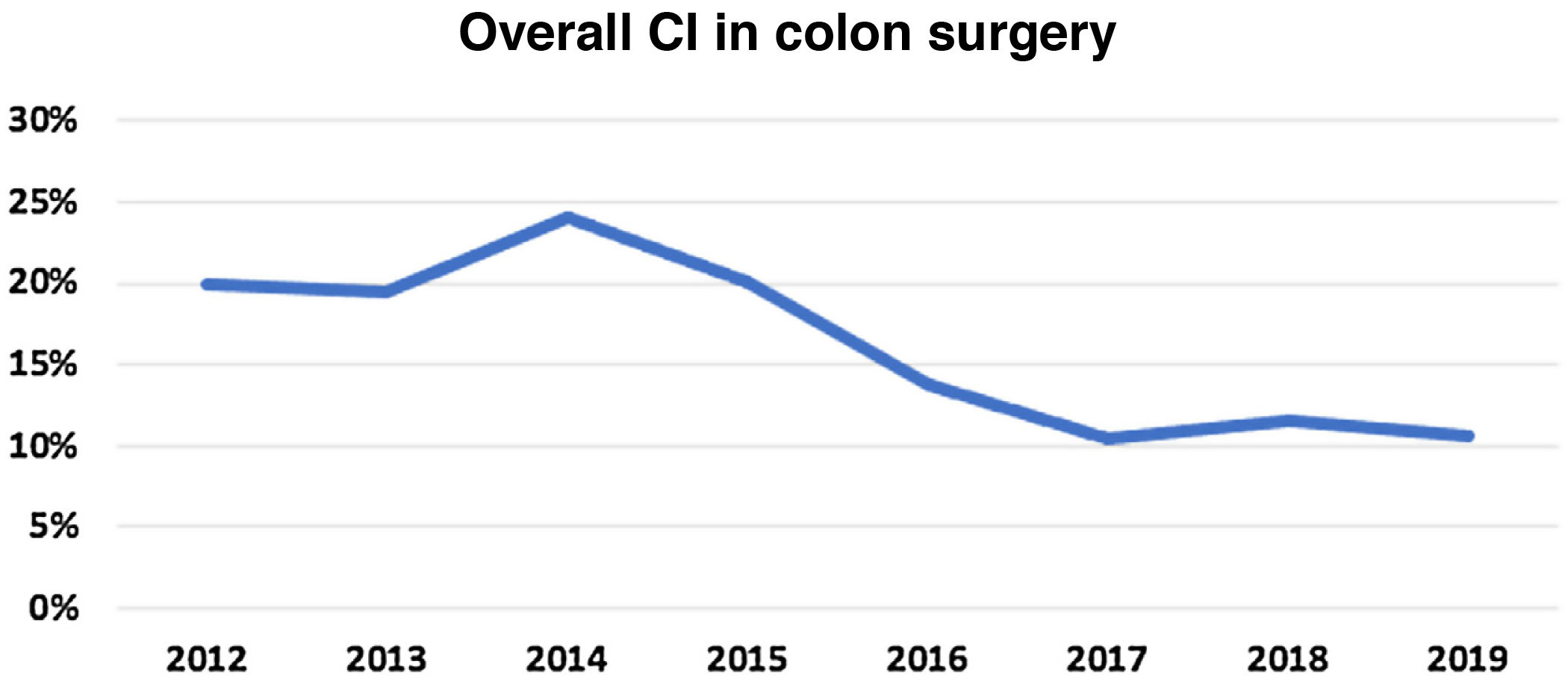
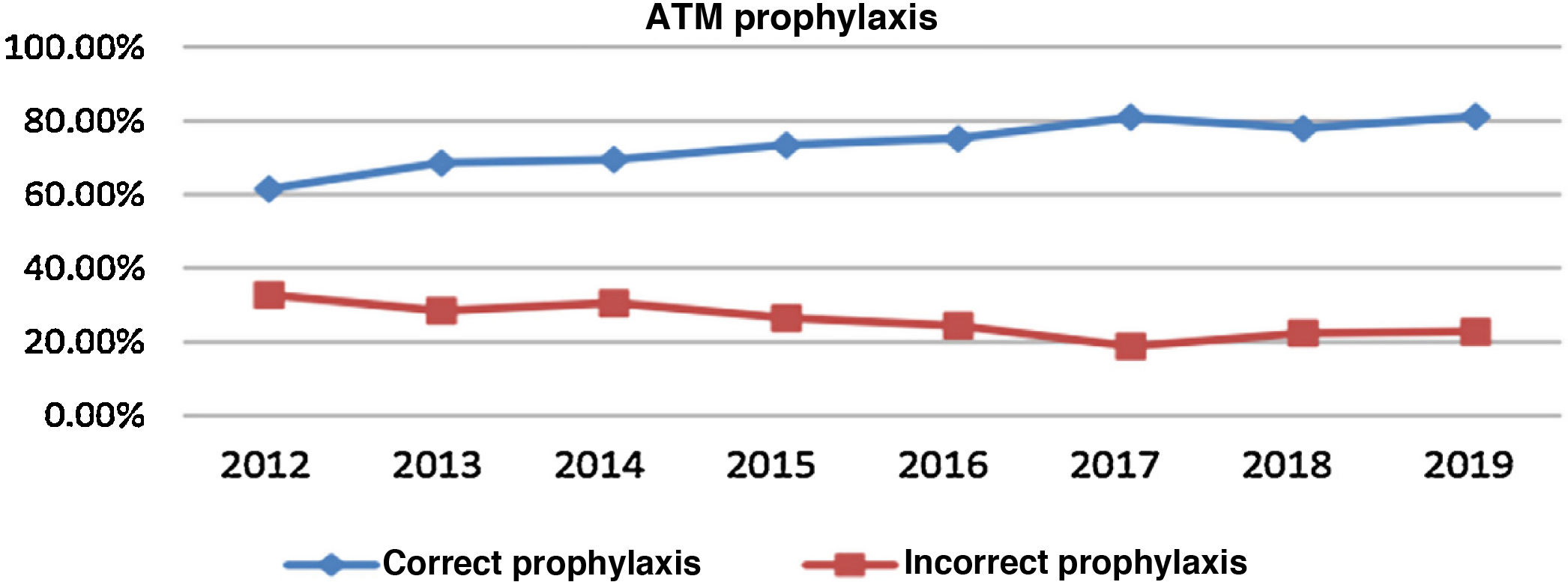
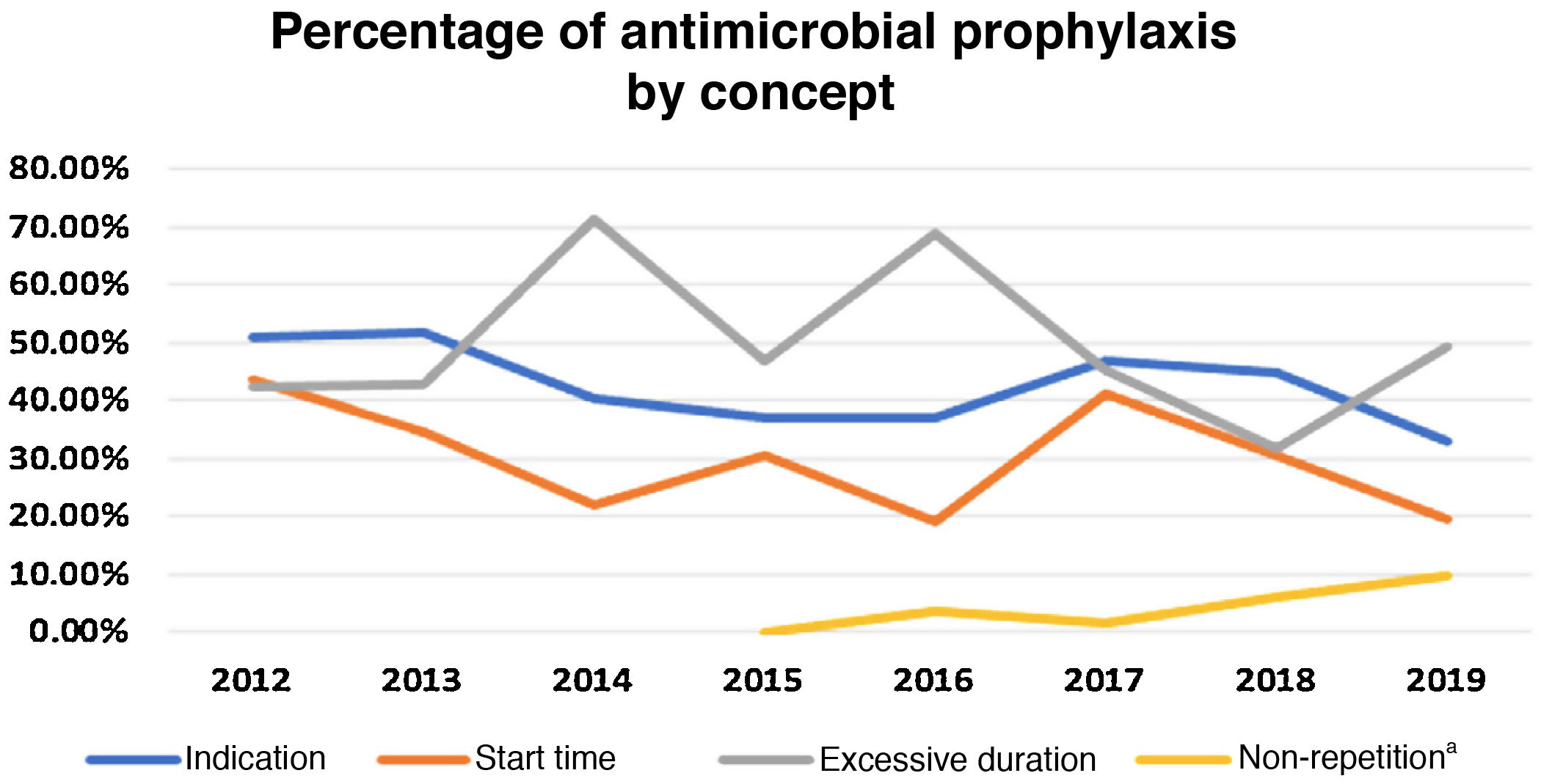
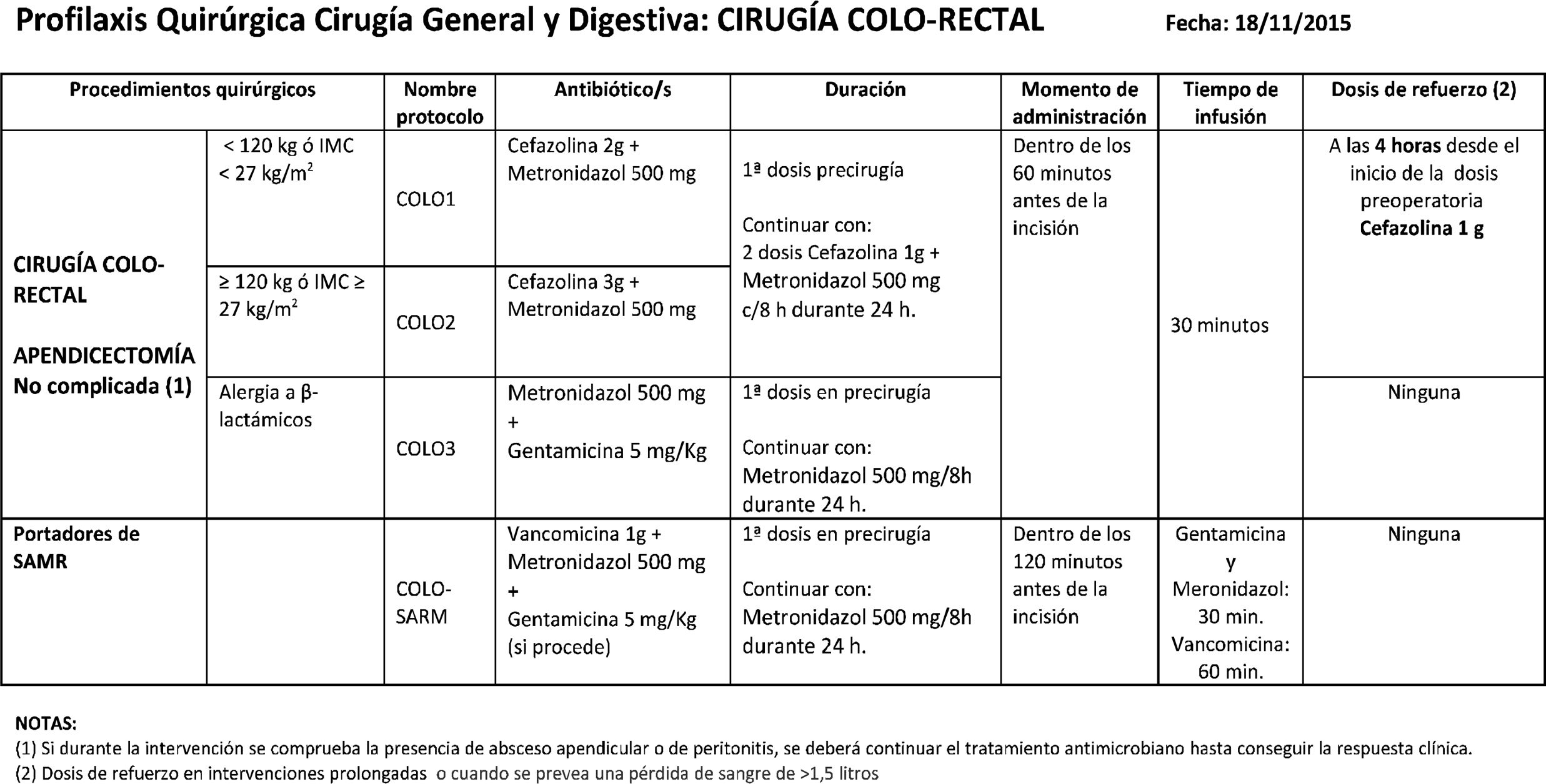
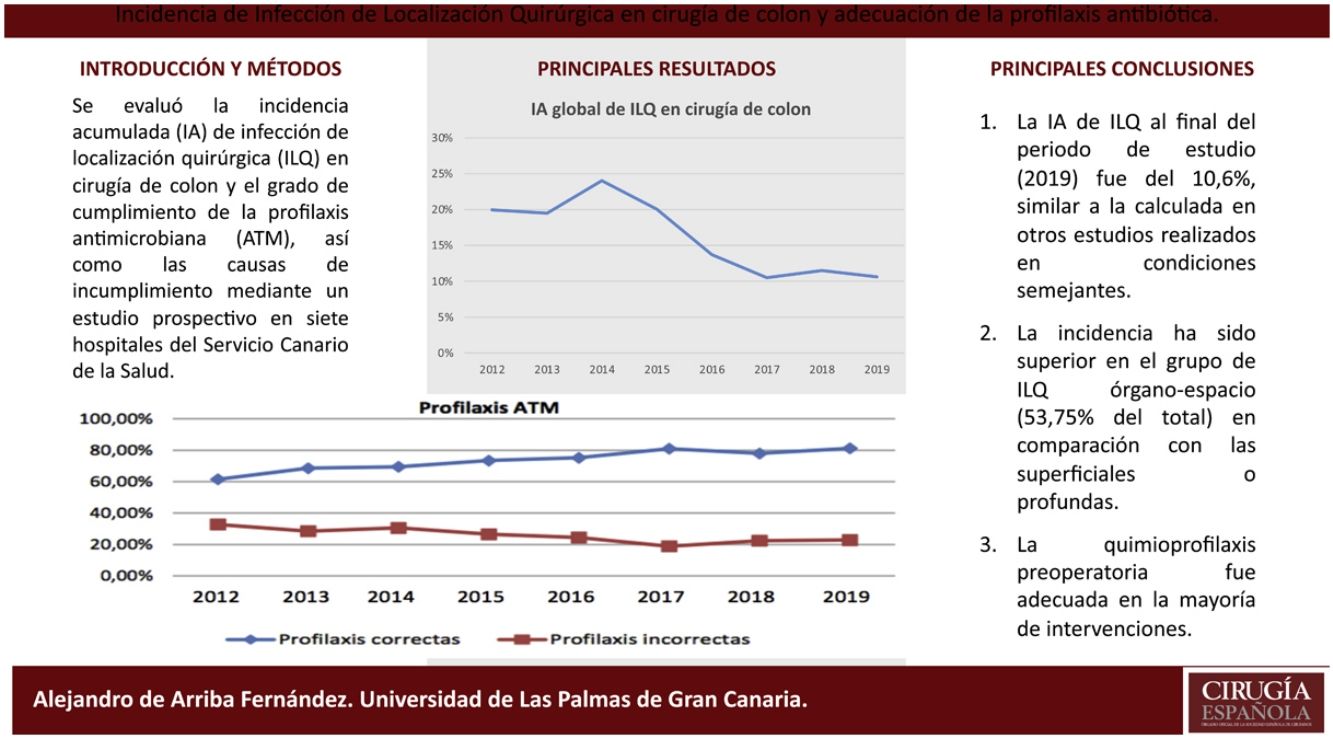
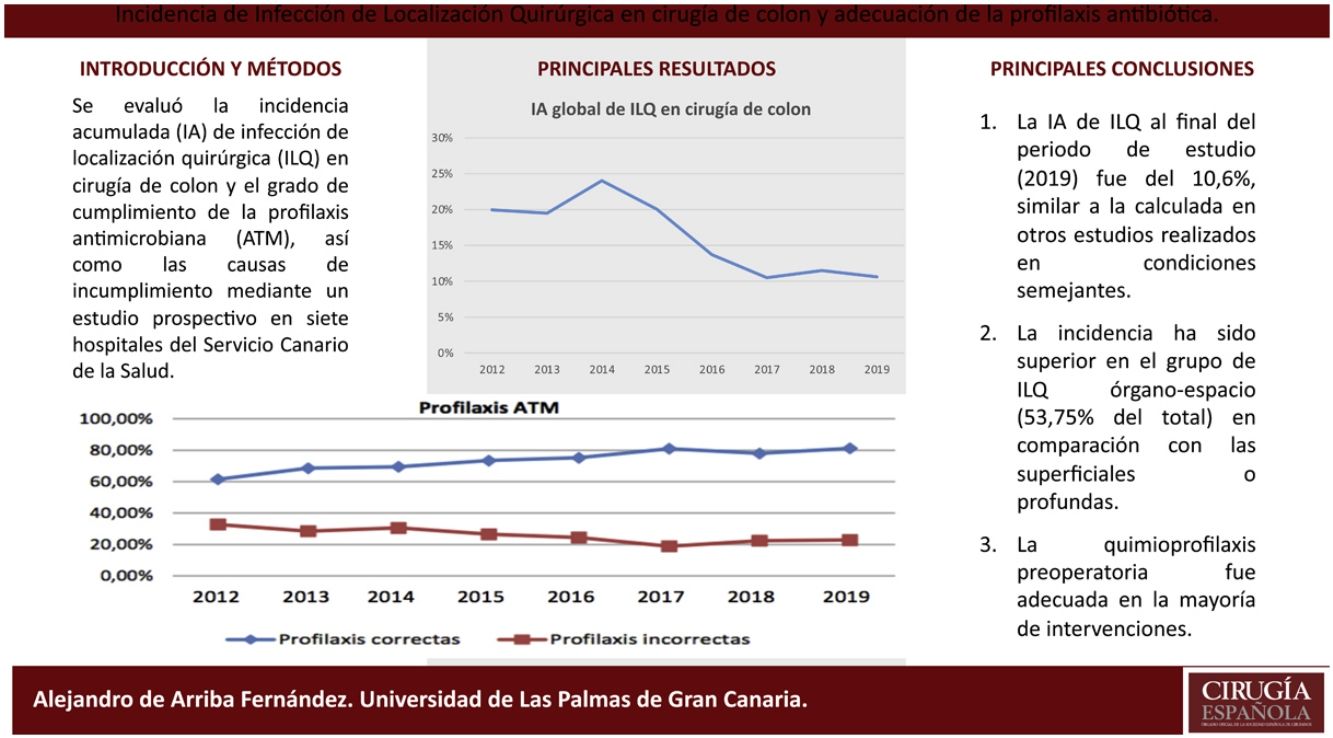
ResultsIn 2019, the cumulative incidence of SSIs was 10.6% (n = 80), which implies maintaining the downward trend since 2012. The appearance of SSIs was more frequent during admission (76%). Surgical prophylaxis was adequate in 81.2%, the main causes of inadequacy being the excessive duration of the antimicrobial prescription (49%) and failure in the indication (33%). The incidence was higher in the group of organ-space infections (53.75% of the total) compared to superficial and deep infections.
ConclutionThe cumulative incidence of SSIs obtained is similar to that calculated in other studies carried out under similar conditions. Preoperative chemoprophylaxis was adequate in most of the interventions.
Las infecciones de localización quirúrgica (ILQ) son un importante problema que limitan los beneficios de las intervenciones quirúrgicas. Se evaluó la incidencia acumulada de ILQ en cirugía de colon y el cumplimiento de la profilaxis antibiótica, así como las causas de su incumplimiento.
MétodosEstudio prospectivo observacional multicéntrico entre los años 2012 y 2019 en siete hospitales del Servicio Canario de Salud mediante un sistema de vigilancia epidemiológica activa. Se definió ILQ de acuerdo con los criterios de los Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
ResultadosEn el año 2019 la incidencia acumulada de ILQ fue del 10,6% (n = 80), lo que supone mantener la tendencia descendente desde el año 2012. La aparición de ILQ fue más frecuente durante el ingreso (76%). La profilaxis quirúrgica fue adecuada en el 81,2%, siendo las principales causas de inadecuación la duración excesiva de la prescripción del antimicrobiano (49%) y los fallos en la indicación (33%). La incidencia ha sido superior en el grupo de ILQ órgano-espacio (53,75% del total) en comparación con las superficiales o profundas.
ConclusiónLa incidencia acumulada de ILQ obtenida es similar a la calculada en otros estudios realizados en condiciones semejantes. La quimioprofilaxis preoperatoria fue adecuada en la mayoría de intervenciones.