To evaluate factors that may decompensate a strabismus or lead to diplopia after refractive surgery.
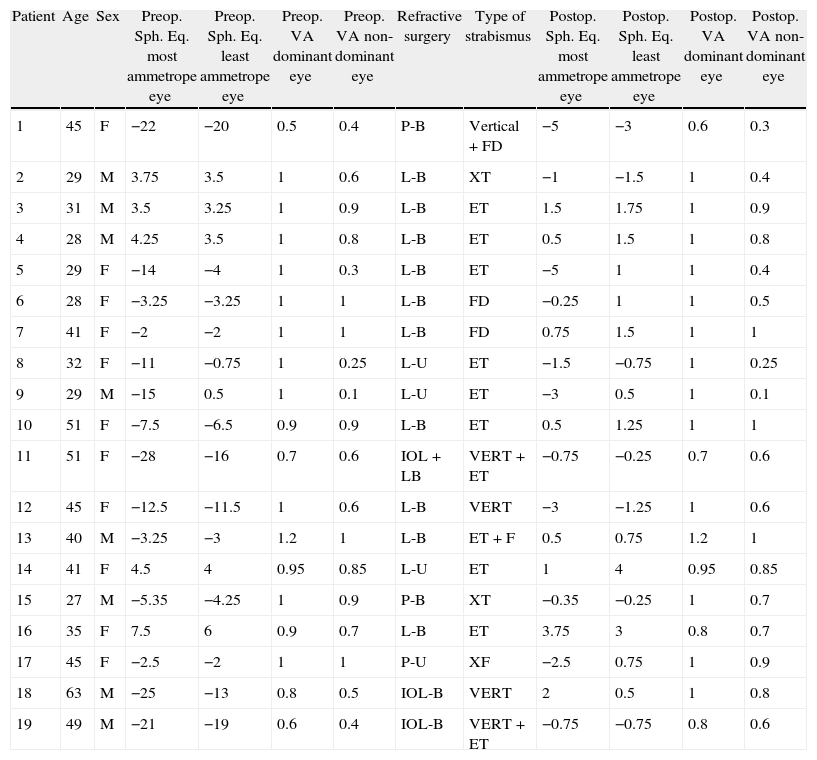
MethodsRetrospective study of 19 patients, who presented with binocular decompensation after refractive surgery. Mean age at surgery was 38.89SD 10.26 (27–63) years. Fourteen patients were myopic, 5 hyperopic, and 5 of them had a marked anisometropia. The photo-refractive keratectomy procedure was used in 3 cases, laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis (LASIK) in 13, posterior chamber-IOL+LASIK in one of them, and bilateral IOL in 2 cases.
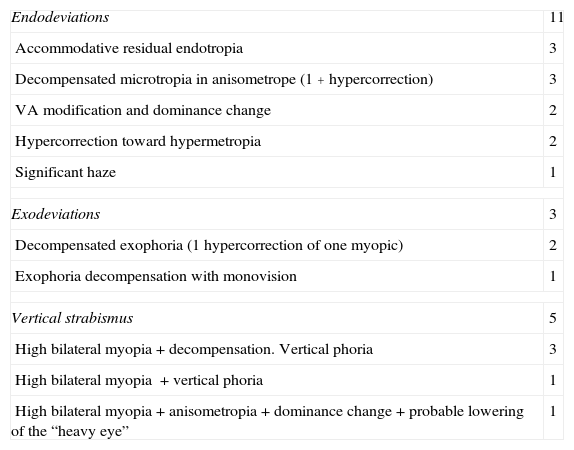
ResultsThere was 0.12% prevalence of strabismus. All of our patients had a binocular pathology previous to the refractive surgery. After surgery, 11 patients had an esophoria or esotropia, 3 exophoria or exotropia, 2 vertical deviations, and 3 horizontal and vertical deviations. Several factors often worked simultaneously in the same patient, such as: residual accommodation, refractive overcorrection (hyperopia), visual instability or anisoacuity, high myopia and phoria decompensation, elimination of suppression, dominance change, and a presbyopic age.
ConclusionsAll of our patients had a previous binocular pathology. Binocularity may decompensate by several factors but mostly by myopic overcorrection, accommodation and visual factors, particularly in patients close to or in presbyopic age, in anisometropia and high myopia.
Analizar los factores que pueden incidir en la descompensación del estrabismo o aparición de diplopía en pacientes sometidos a cirugía refractiva.
MétodosEstudio retrospectivo de 19 pacientes remitidos por presentar descompensación de la motilidad ocular y/o de la visión binocular tras cirugía refractiva. La edad media era 38,89 DS±10,26 años (rango 27 a 63). Catorce pacientes eran miopes, cinco hipermétropes. Cinco de ellos presentaban anisometropía intensa. En tres casos la técnica refractiva fue fotoqueratectomía refractiva, en trece de tipo Lasik, en uno LIO+Lasik y en dos LIO bilateral.
ResultadosLa prevalencia de diplopía poscirugía refractiva fue 0,12% (5 de los 19 procedían de nuestro centro, sobre una base de datos de 4.135 pacientes sometidos a cirugia refractiva, al realizar el estudio). Todos tenían patología binocular previa a la cirugía. Tras esta, once presentaban endoforia o endotropía, tres exoforia o exotropía, dos desviaciones verticales y tres horizontal y vertical. Las causas de descompensación fueron: factor acomodativo residual, hipercorrección refractiva en sentido hipermetrópico, inestabilidad visual, anisoagudeza, descompensación de una foria en el estrabismo del miope magno, pérdida de supresión, cambio de dominancia y presbicia. Frecuentemente varios factores actuaron simultáneamente.
ConclusionesLa aparición de diplopía o estrabismo poscirugía refractiva es poco frecuente. Varios factores pueden incidir en la descompensación, fundamentalmente la hipercorrección miópica y los factores acomodativos y visuales, especialmente en edad présbita, en fuertes anisométropes y miopes magnos.