To assess visual outcomes of retreatment after laser in situ keratomileusis (LASIK) by lifting the flap or performing photorefractive keratectomy (PRK) on the flap, as well as to establish whether there was an increased risk of epithelial ingrowth (EIG) when LASIK and lifting of the flap are separated by a long time interval and to determine the incidence of corneal haze after PRK.
MethodsRetrospective study of 4077 patients (5468 eyes) who underwent LASIK and subsequent retreatment were reviewed in order to study their visual results and identify cases of EIG and corneal haze.
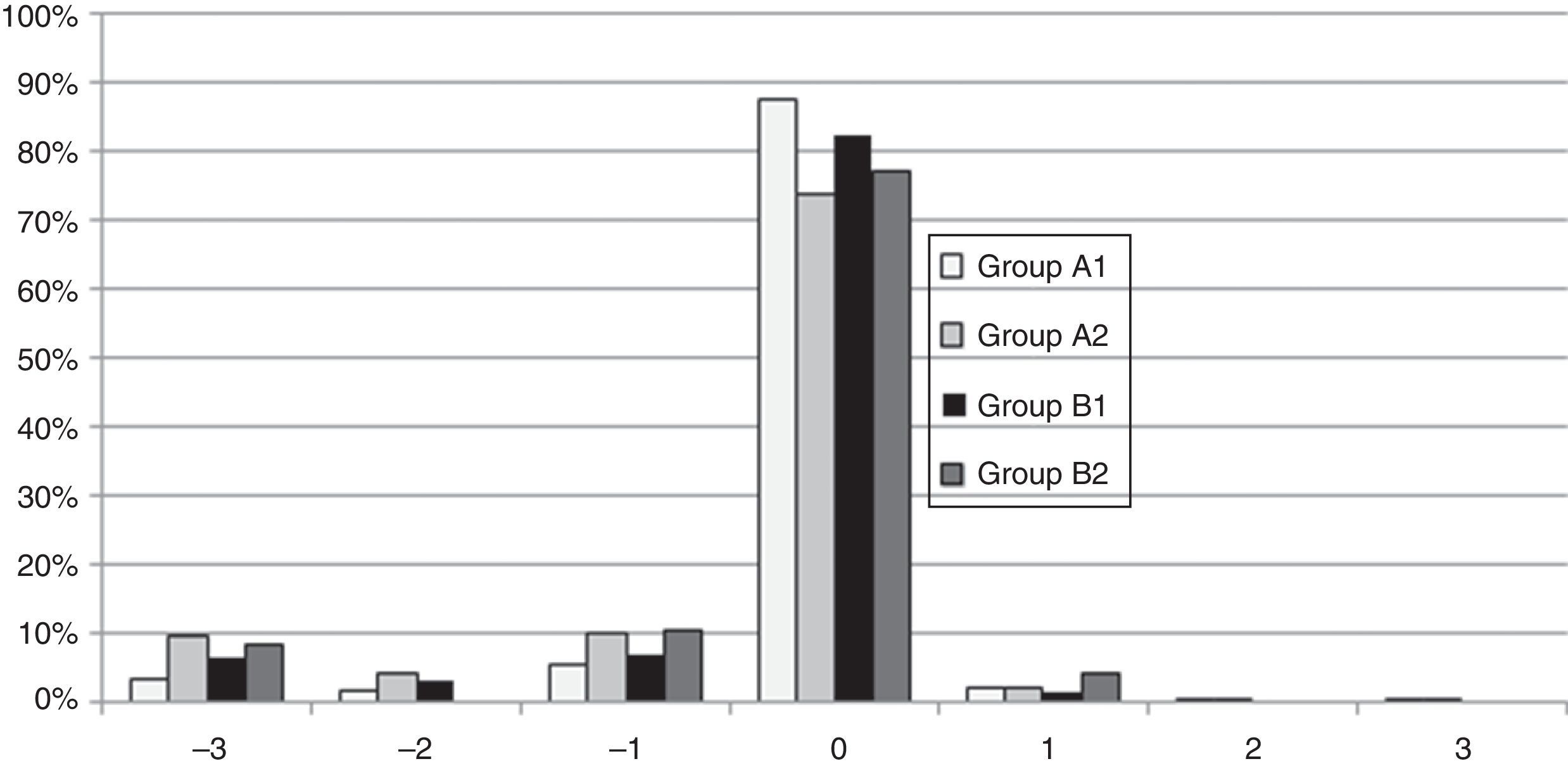
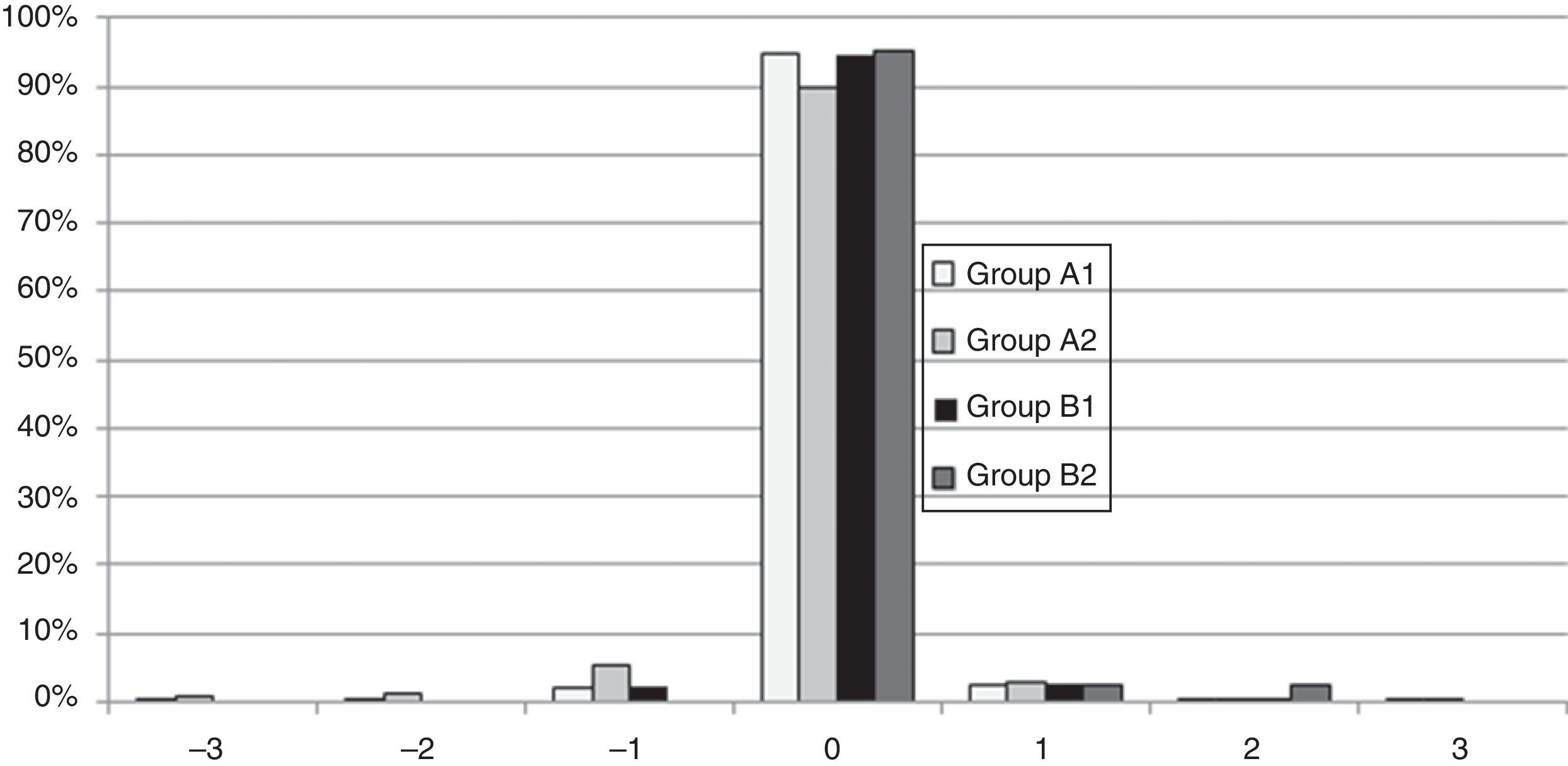
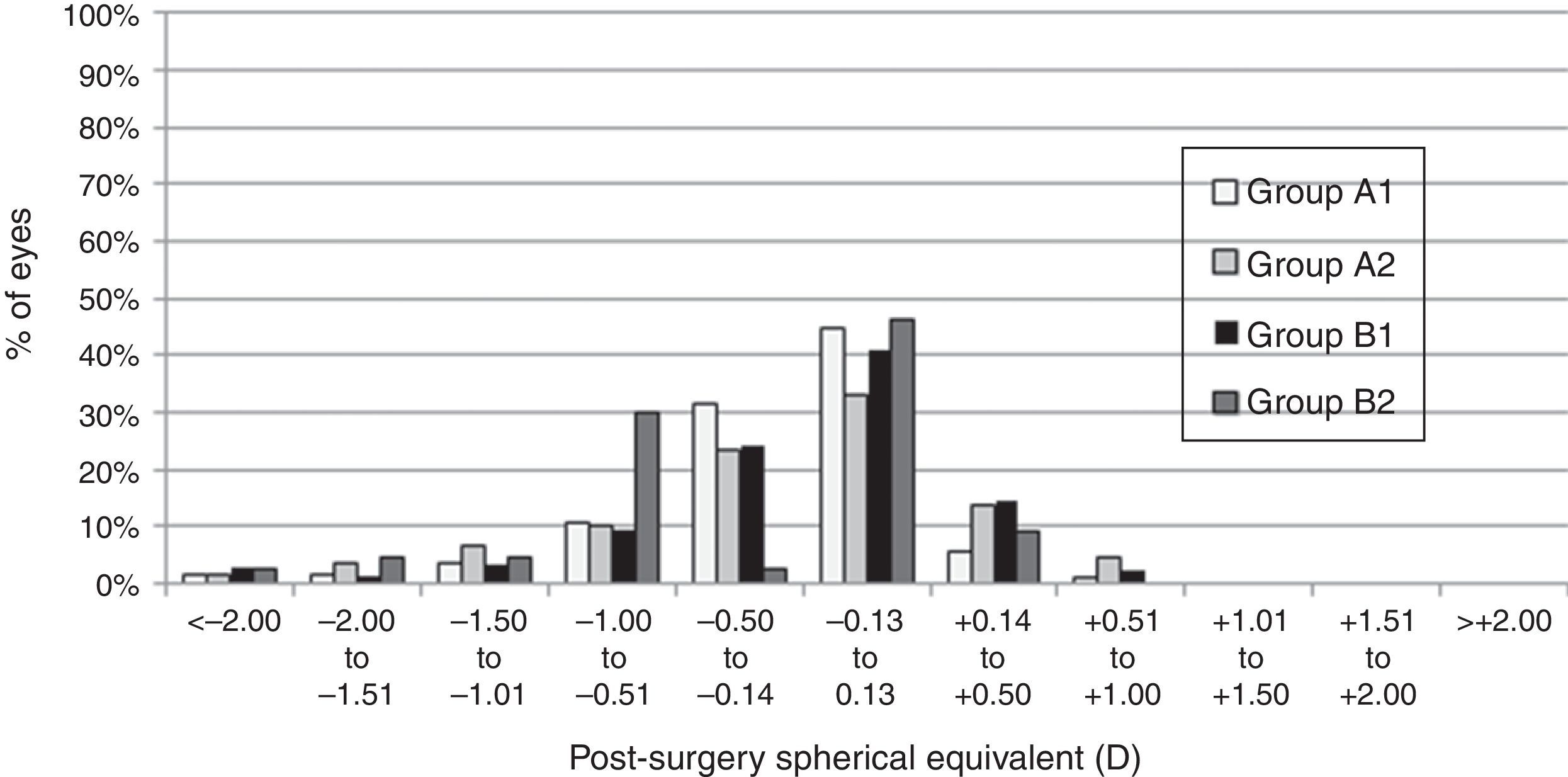
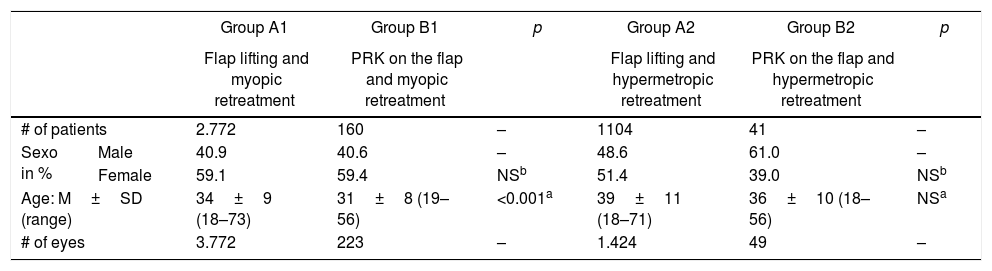
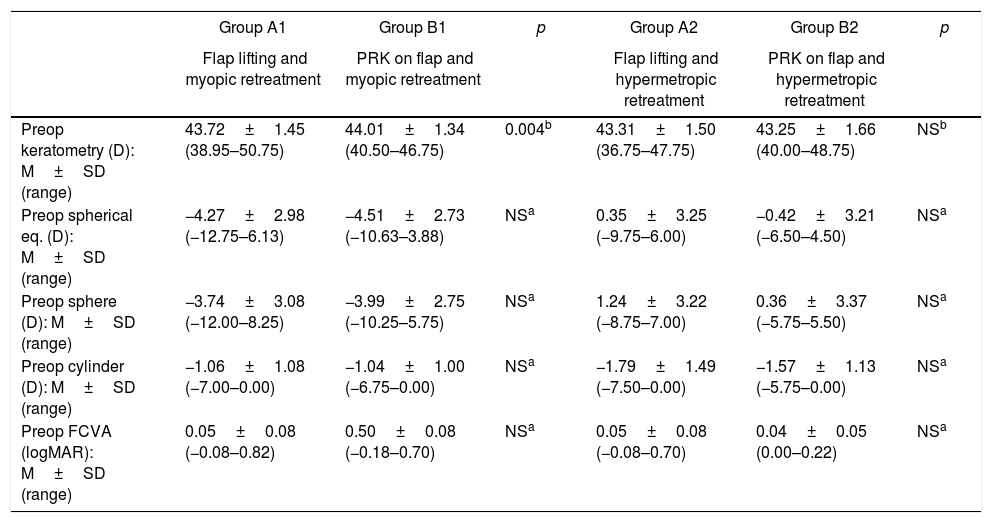
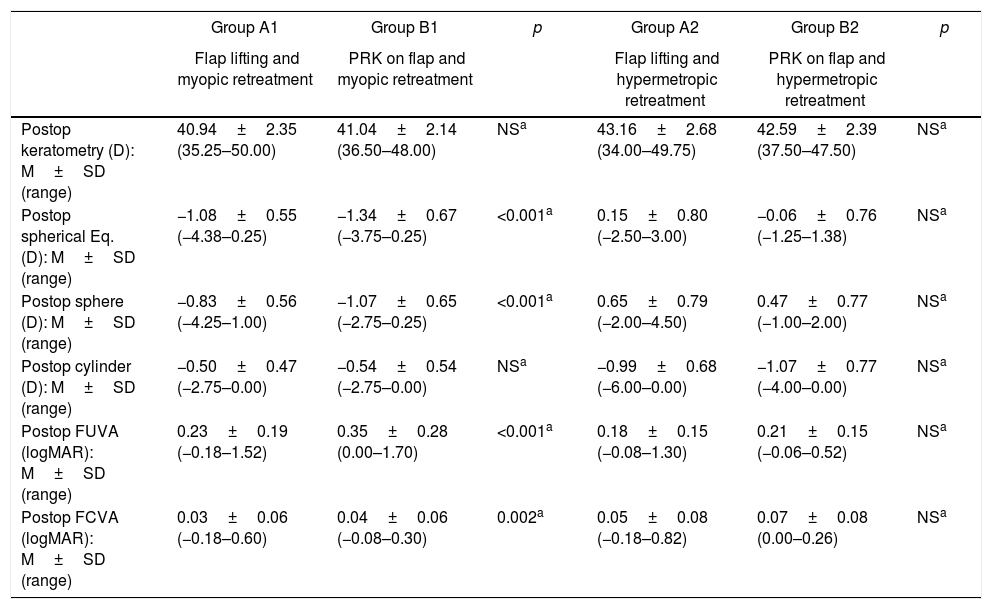
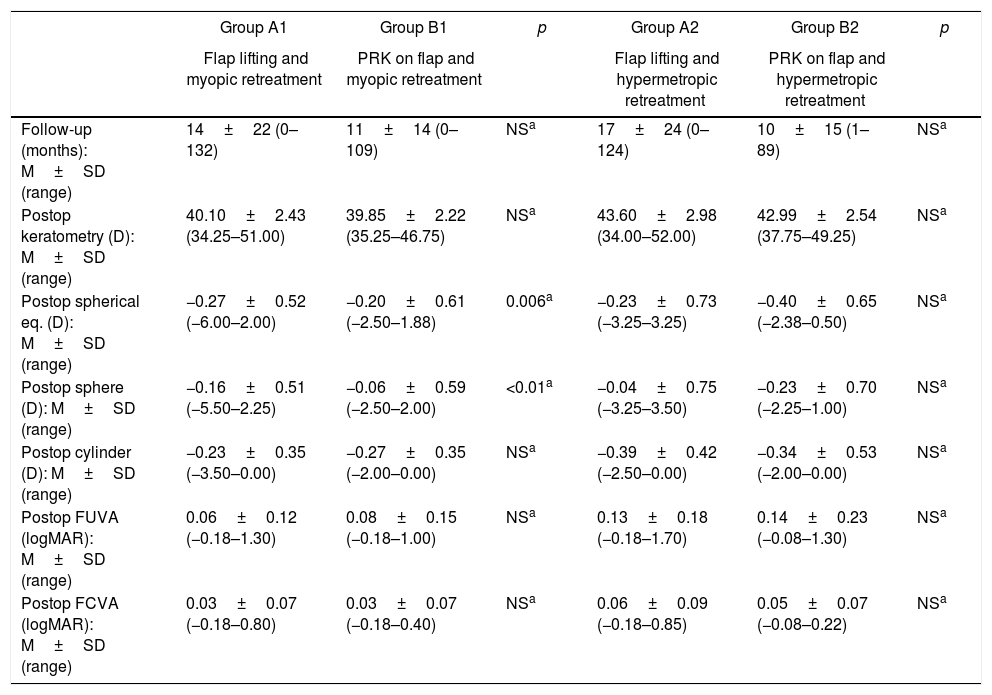
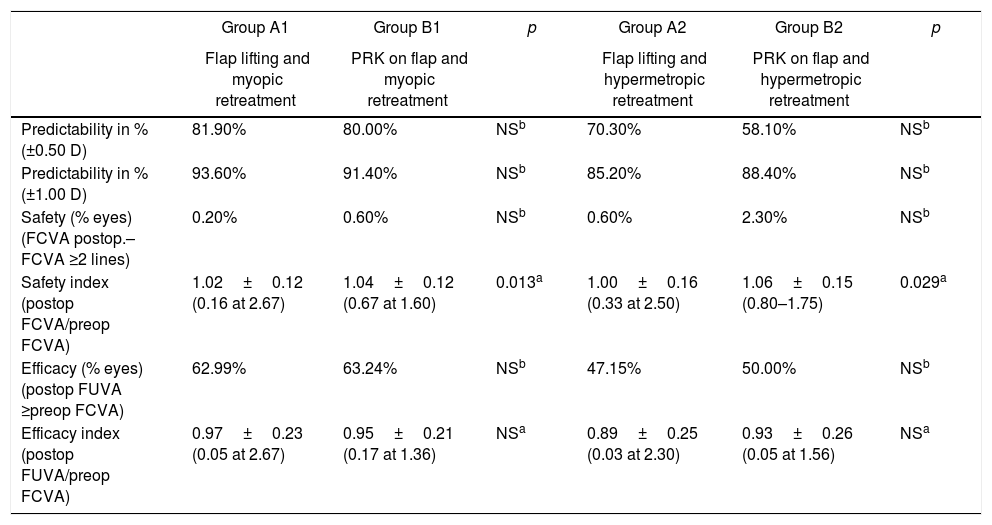
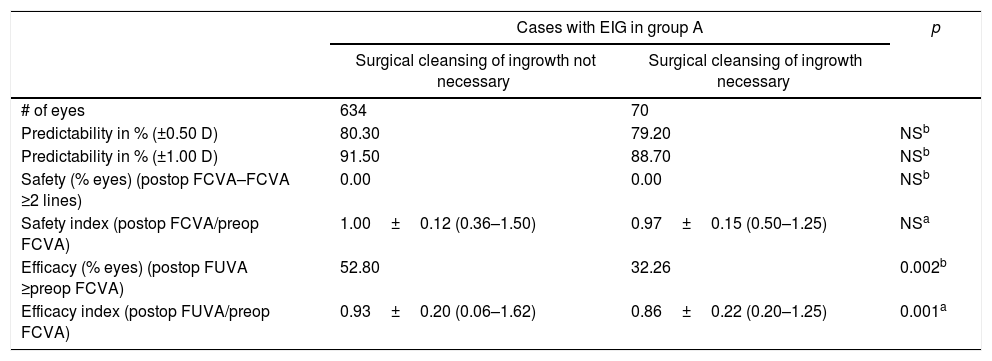
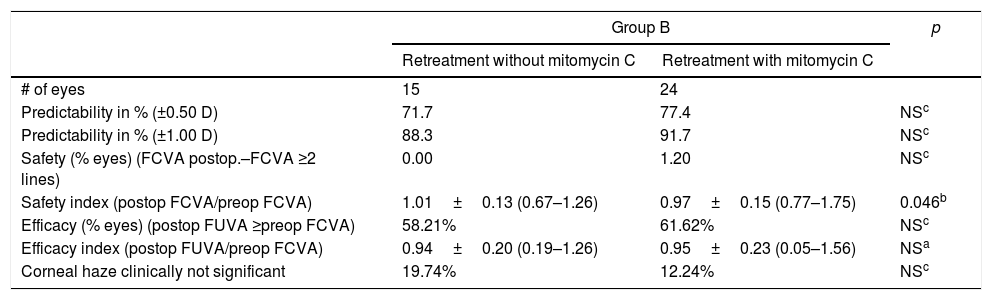
ResultsEnhancements included 5196 eyes from 3876 patients that were retreated by lifting the flap, and 272 eyes from 201 patients that were retreated by PRK on the flap. No statistically significant differences were found between the retreatments in terms of predictability, efficacy, and safety. A total of 704 cases of EIG were found after lifting the flap, for which surgical cleansing was necessary in 70. Surgical cleansing decreased the efficacy index when compared with patients with EIG who did not need cleansing (p=0.01). Differences in terms of safety and predictability were not statistically significant. The incidence of corneal haze after ablation of the surface of the previous flap was 14.34%, although none of these cases were clinically relevant.
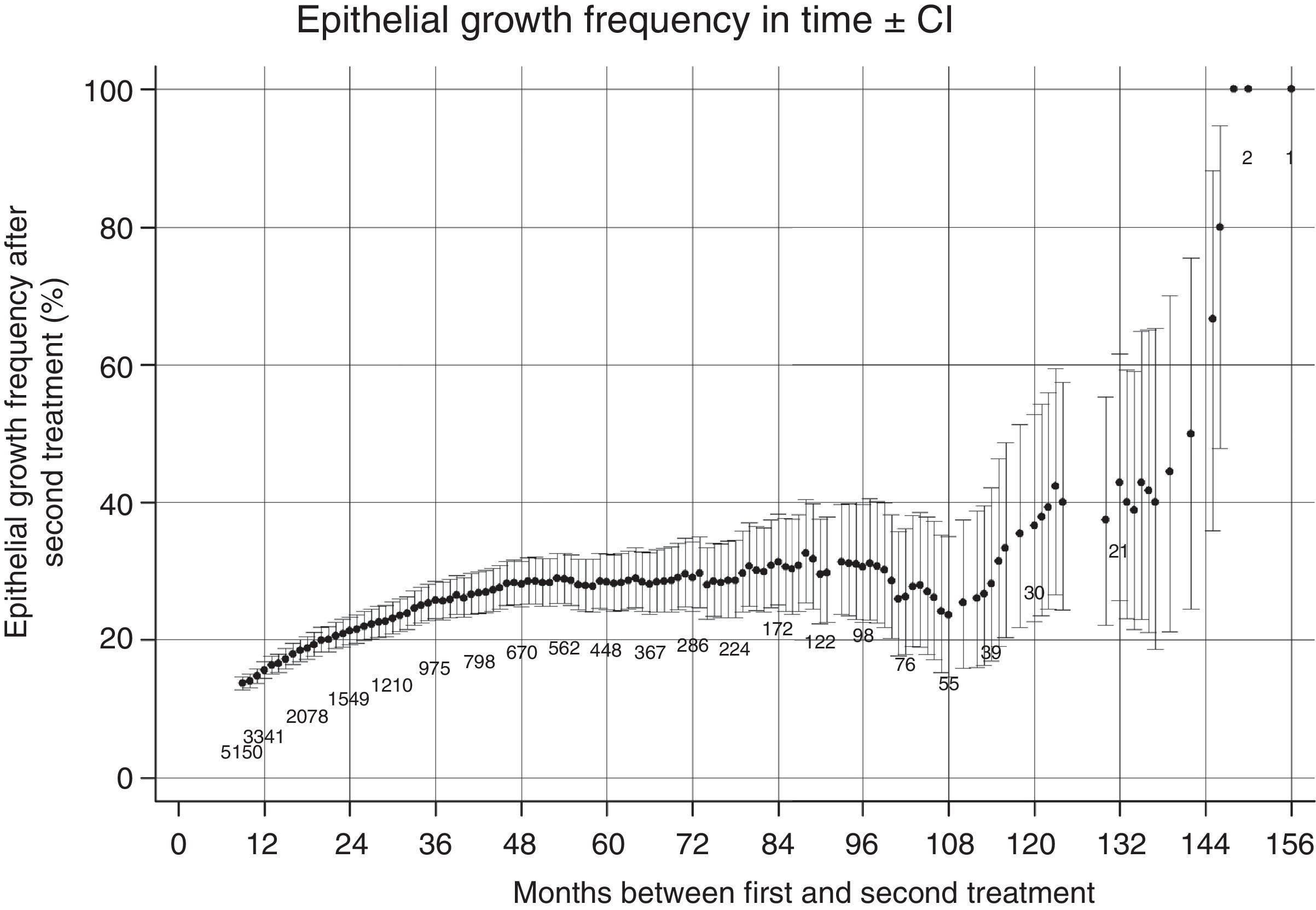
ConclusionsVisual outcomes were similar between patients who were retreated by lifting the flap and those who underwent PRK. The incidence of EIG when the flap was lifted was 13.55%. The incidence of EIG increases with the time elapsed between the primary procedure and retreatment.
Describir los resultados visuales del retratamiento tras láser in situ queratomileusis (Lasik) levantando el lentículo previamente o realizando queratectomía fotorrefractiva (PRK) sobre él, establecer si el riesgo de crecimiento epitelial de la interfase (CEI) es mayor cuanto más tiempo ha pasado entre el Lasik inicial y el retratamiento por levantamiento y determinar la incidencia de la opacidad corneal (haze) tras PRK.
MétodosEstudio retrospectivo de 4.077 pacientes (5.468 ojos) tratados mediante Lasik y retratamiento para estudiar los resultados visuales e identificar los casos de CEI y haze corneal.
ResultadosSe estudiaron 5.196 ojos de 3.876 pacientes retratados de miopía levantando el lentículo y 272 ojos de 201 pacientes retratados mediante PRK en el lentículo. No se encontraron diferencias estadísticamente significativas entre los retratamientos en predictibilidad, eficacia y seguridad. Se encontró un total de 704 casos de CEI tras levantar el lentículo; se necesitó limpieza quirúrgica en 70. La limpieza quirúrgica disminuyó el índice de eficacia al compararlo con el de los pacientes con CEI que no precisaron limpieza (p=0,01). Las diferencias en términos de seguridad y predictibilidad no fueron estadísticamente significativas. La incidencia de haze corneal tras la ablación de superficie sobre el lentículo previo fue del 14,34%, aunque ninguno de estos casos fue clínicamente relevante.
ConclusionesLos resultados visuales son similares entre los pacientes retratados mediante levantamiento del lentículo o mediante PRK. La incidencia de CEI levantando lentículo fue del 13,55%. La incidencia de CEI aumenta a medida que aumenta el tiempo entre el procedimiento primario y el retratamiento.