Levator aponeurosis advancement is a technique used to treat aponeurotic ptosis, which can be performed via anterior (transcutaneous) or posterior (transconjunctival) approach, each with specific advantages. This study aims to evaluate and compare pre- and postoperative eyelid aperture outcomes for both techniques and analyze the rate of over- and undercorrections, contributing to a better understanding of their efficacy and limitations.
Materials and methodsWe conducted a retrospective study on 62 eyelids with aponeurotic ptosis and good levator function. A total of 32 anterior and 30 posterior approaches were performed, assessing marginal reflex distance 1 (MRD1), eyelid aperture (EA), and their pre- and postoperative variations, along with the rate of over- and undercorrections relative to ideal values.
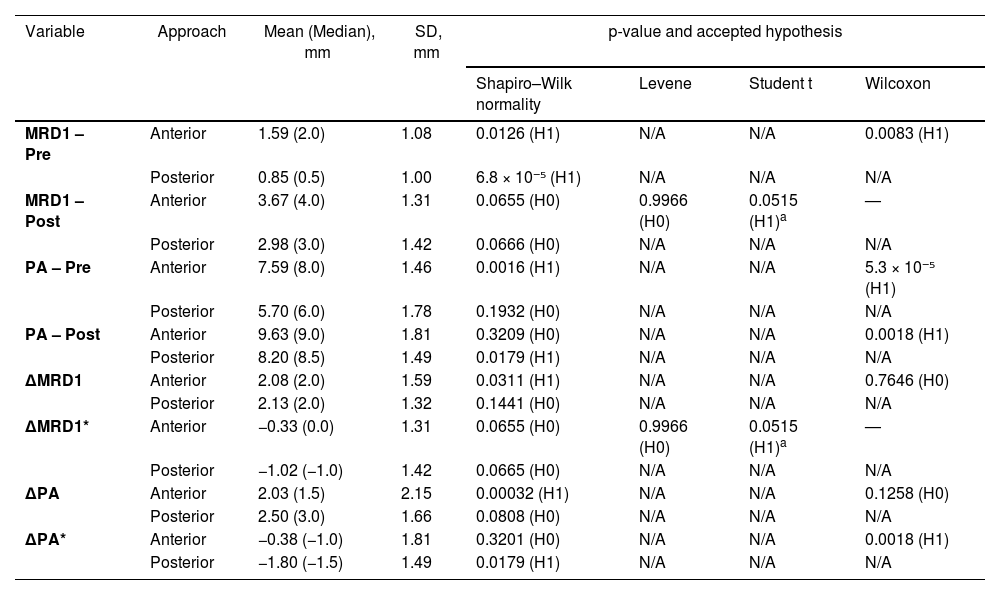
ResultsMRD1: Preoperative values for the anterior approach were 1.59 ± 1.08 mm, and 0.85 ± 1.00 mm for the posterior approach. Improvements were 2.08 ± 1.59 mm for the anterior approach and 2.13 ± 1.32 mm for the posterior one (p > 0.05).
EA: Improvements were 2.03 ± 2.15 mm for the anterior approach and 2.50 ± 1.66 mm for the posterior one (p > 0.05).
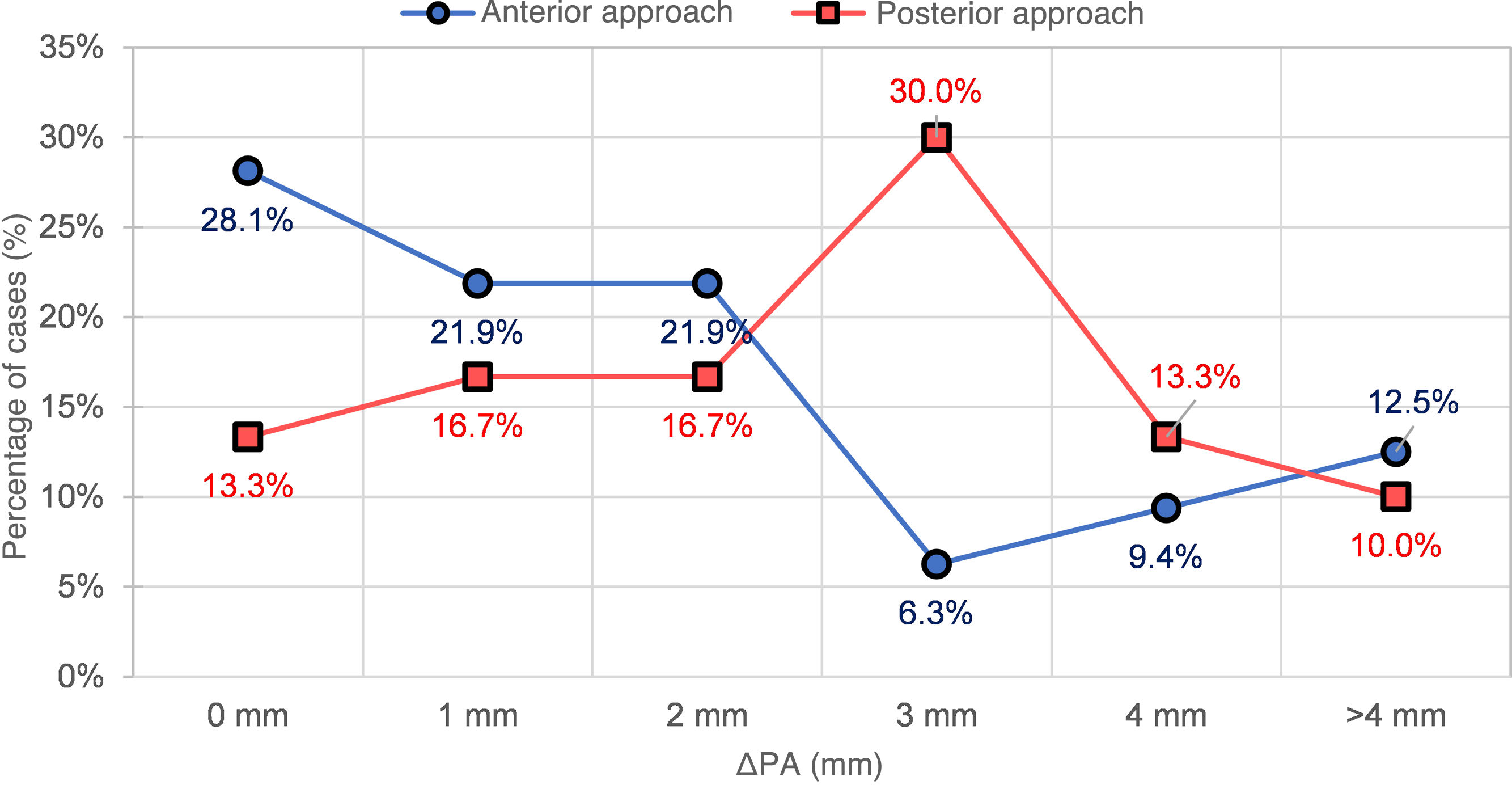
Ideal MRD1 correction (4 mm) was achieved in 31.3% of anterior cases vs 20.0% of posterior cases (p ≈ 0.05).
Ideal EA correction (10 mm) was achieved in 18.8% of anterior cases vs 3.3% of posterior cases (p < 0.05).
ConclusionsBoth approaches are effective, but the anterior approach demonstrates higher rates of ideal corrections and fewer undercorrections. The posterior approach was used in lower preoperative MRD1 cases, which may have influenced the results. Selection should be based on the patient’s specific characteristics and needs.
La reinserción de la aponeurosis elevadora es utilizada para tratar ptosis de origen aponeurótico, mediante abordaje anterior (transcutáneo) o posterior (transconjuntival), cada uno con ventajas según el caso. El presente estudio tiene como objetivo evaluar y comparar la apertura palpebral preoperatoria y postoperatoria obtenida con ambas técnicas, y analizar la incidencia de hipercorrecciones e hipocorrecciones, contribuyendo al entendimiento de la efectividad y limitaciones de cada técnica.
Materiales y métodosEstudio retrospectivo de 62 párpados con ptosis palpebral aponeurótica y buena función elevadora. Se realizaron 32 abordajes anteriores y 30 posteriores, evaluando la distancia reflejo-margen 1 (DMR1), apertura palpebral (AP) y sus variaciones preoperatorias y postoperatorias, además determinando hipercorrecciones o hipocorrecciones con respecto a valores ideales.
ResultadosDMR1: el preoperatorio del abordaje anterior fue 1,59 ± 1,08 mm, versus 0,85 ± 1,00 mm del posterior. El abordaje anterior tuvo mejoría de 2,08 ± 1,59 mm, versus 2,13 ± 1,32 mm del posterior (p > 0,05).
AP: el abordaje anterior tuvo mejoría de 2,03 ± 2,15 mm versus 2,50 ± 1,66 mm del posterior (p > 0,05).
Corrección ideal de DMR1 (4 mm): lograda en el 31,3% de los abordajes anteriores, versus 20,0% de los posteriores (p ≈ 0,05).
Corrección ideal de AP (10 mm): lograda en el 18,8% de los abordajes anteriores, versus 3,3% de los posteriores (p < 0,05).
ConclusionesAmbos abordajes son efectivos, pero el anterior muestra mayor tasa de correcciones ideales y menos hipocorrecciones. El abordaje posterior se usó en ptosis con DMR1 preoperatorias menores, lo cual pudo haber influenciado en los resultados. La elección debe basarse en las características y necesidades específicas del paciente.