To determine quantitative and qualitative differences of aqueous humor proteome in patients with and without glaucoma.
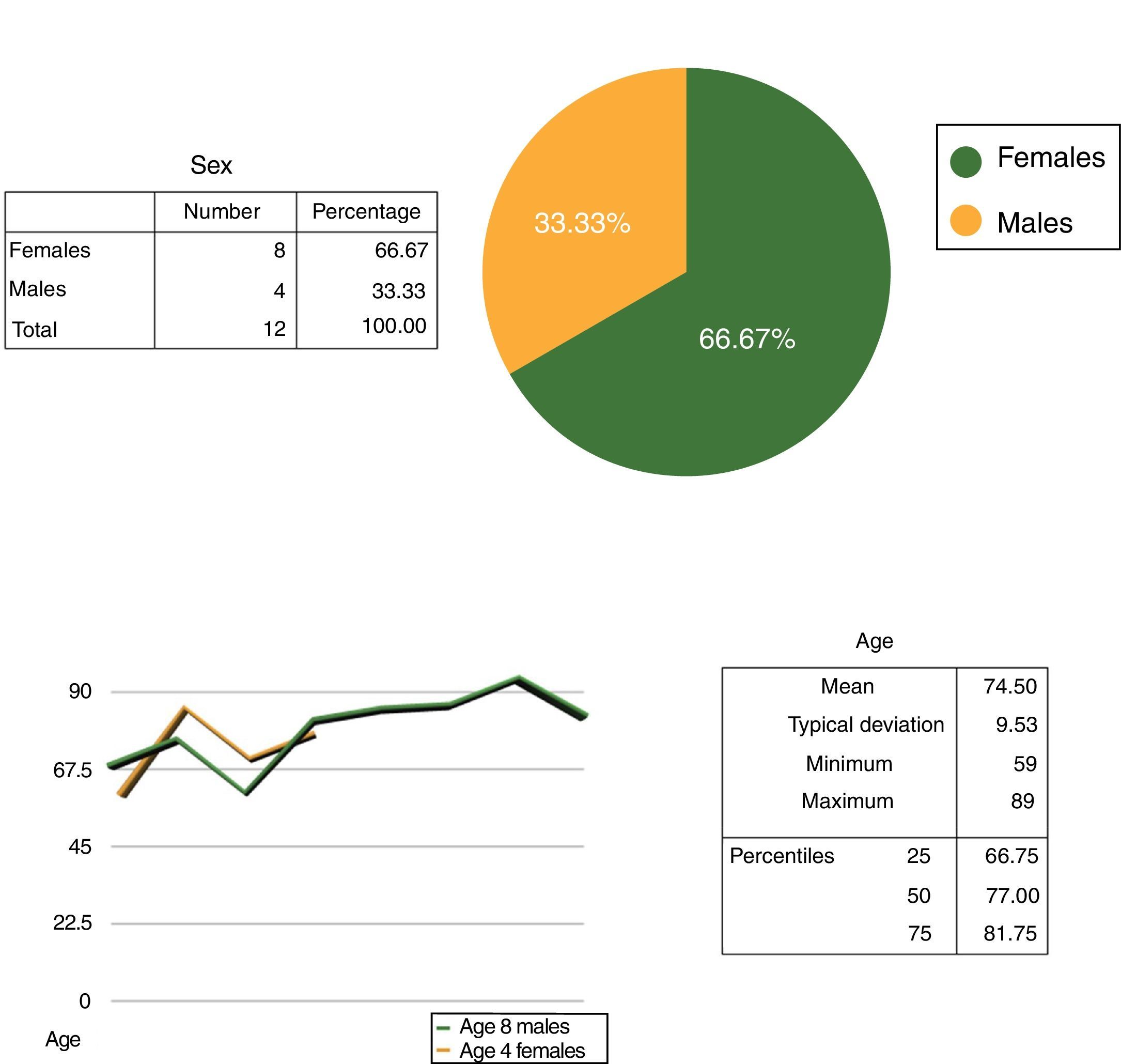
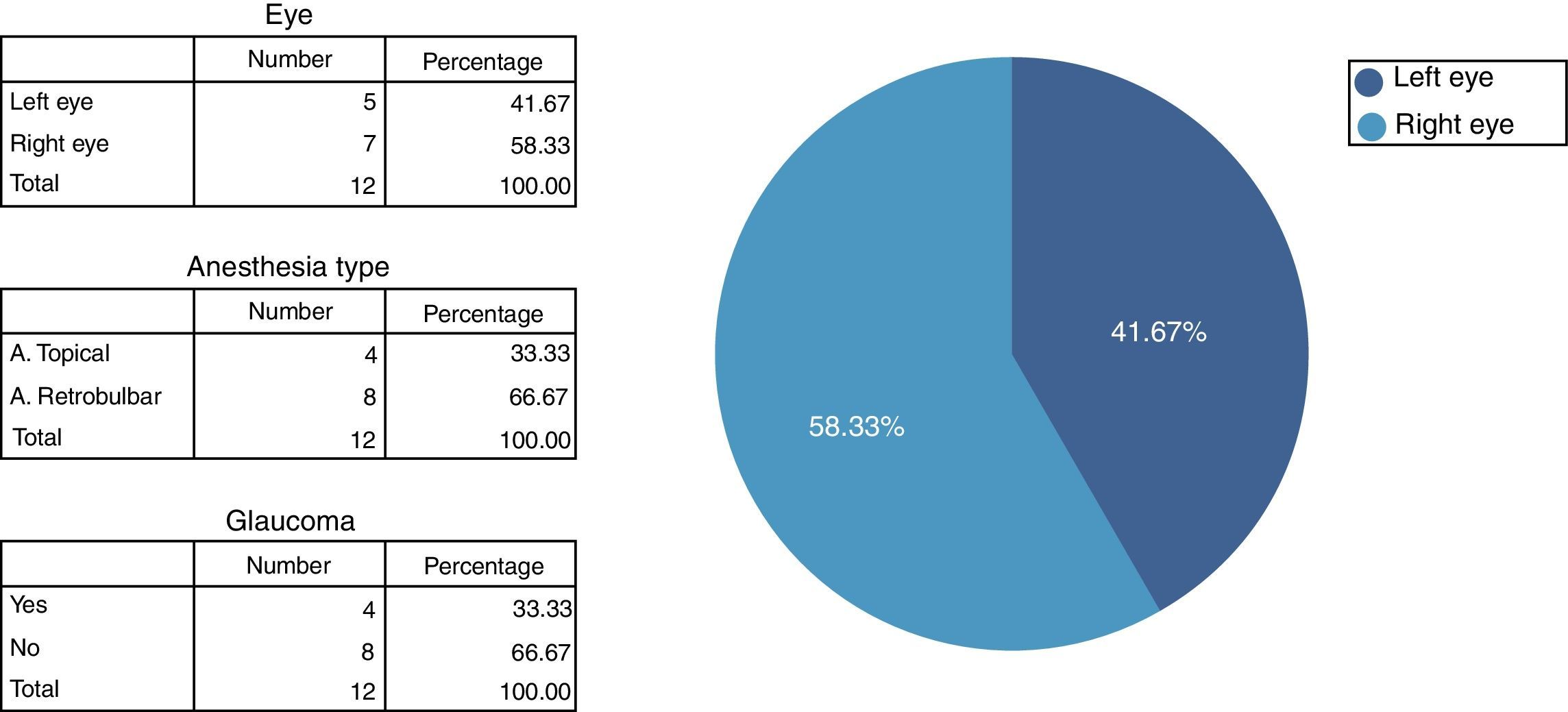
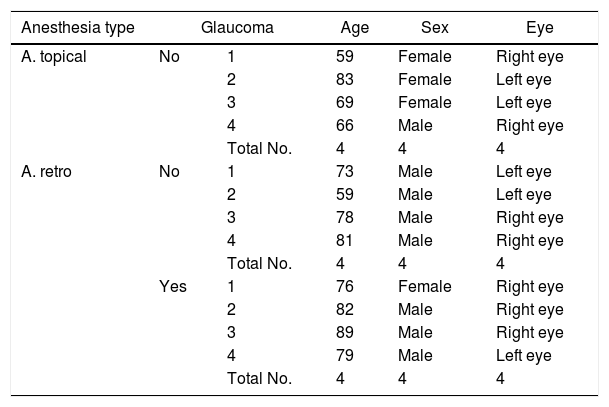
MethodObservational, descriptive and cross-sectional study of 12 patients (8 men; 4 women) with and without glaucoma. There are 3 groups of minority proteins with serum equimolar contribution of each of the patients. Specimens were obtained during cataract surgery from patients without glaucoma (performed with retrobulbar anesthesia [cataract retrobulbar patient – CRP; n=4] or topical [cataract topical patient – CTP; n=4]), or from patients with glaucoma (performed with retrobulbar anesthesia [glaucoma retrobulbar patient – GRP; n=4]). The humor proteome samples were frozen at −80°C until processing by trypsin digestion to obtain tryptic peptides, and then performing liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS) to obtain the proteome and its differential expression between groups. Statistical analysis was performed using the SPSS v.17 program.
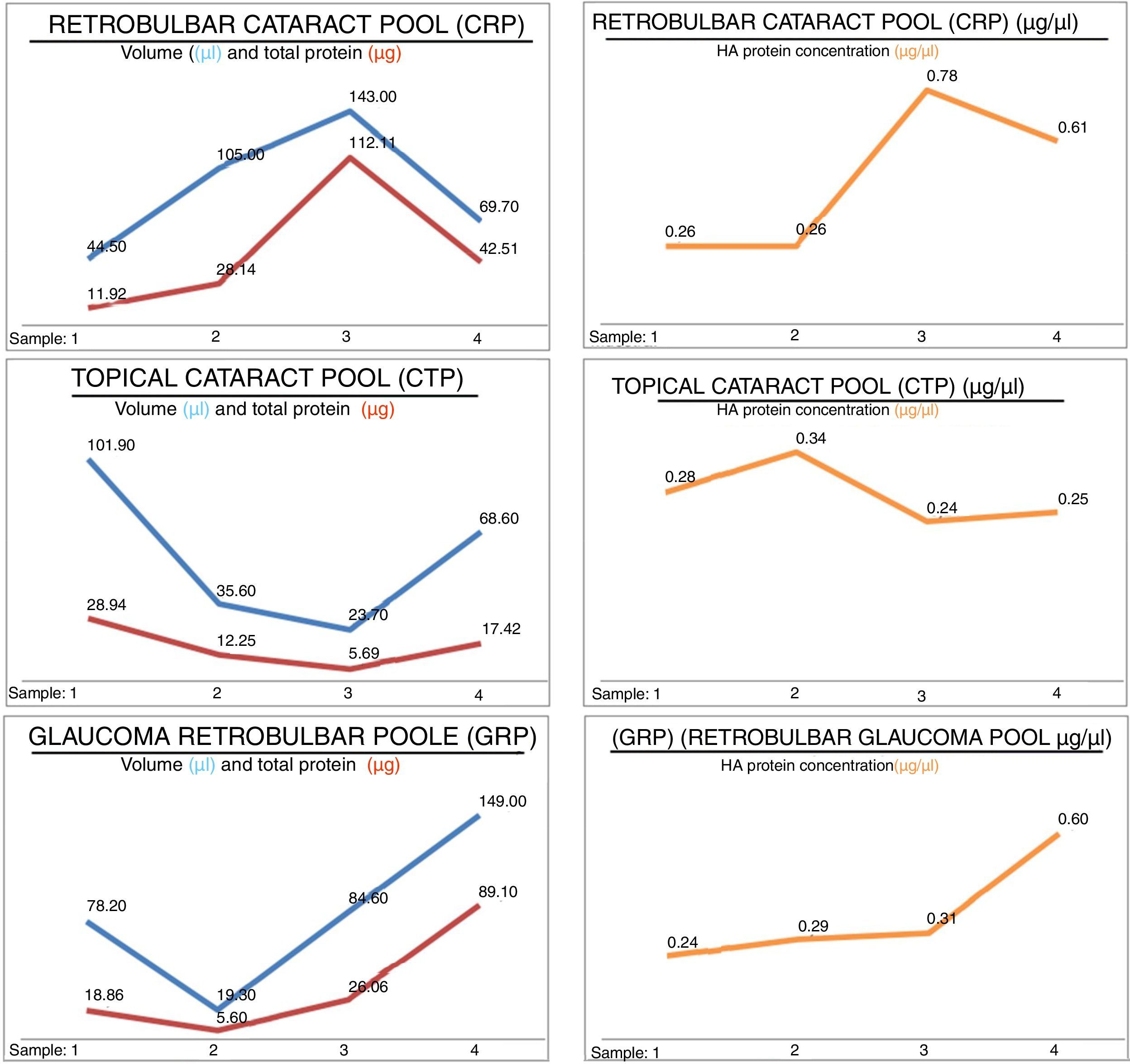
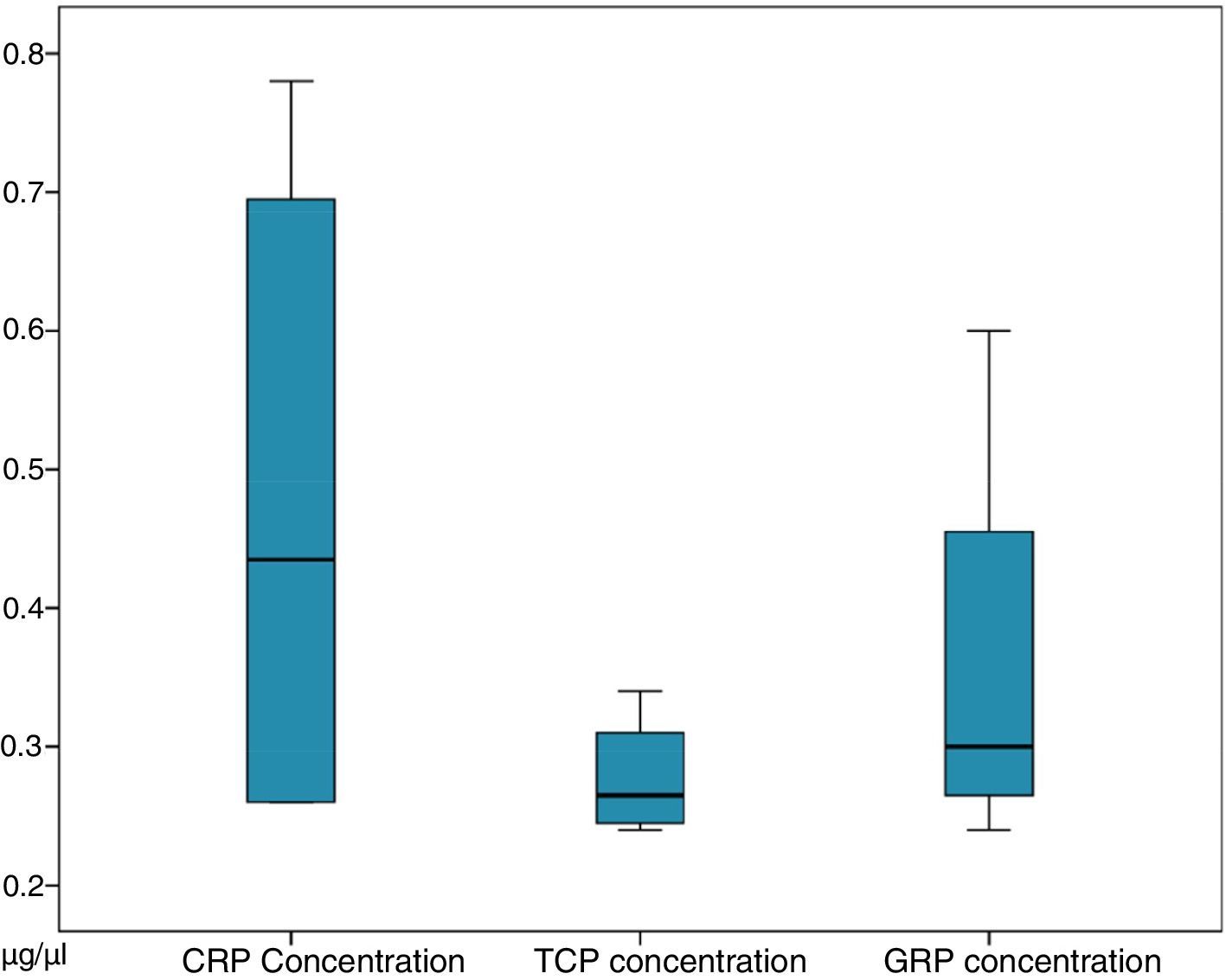
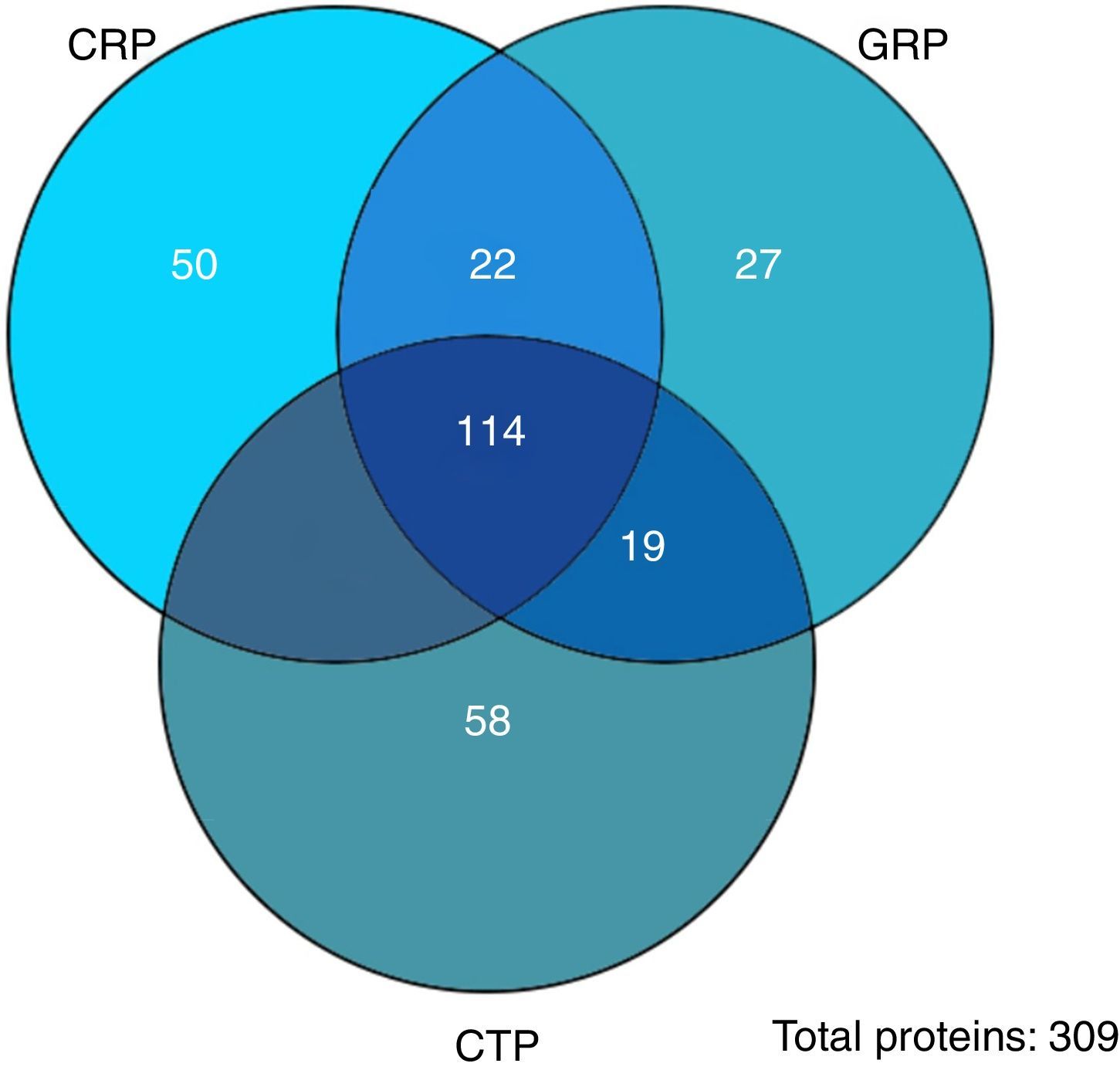
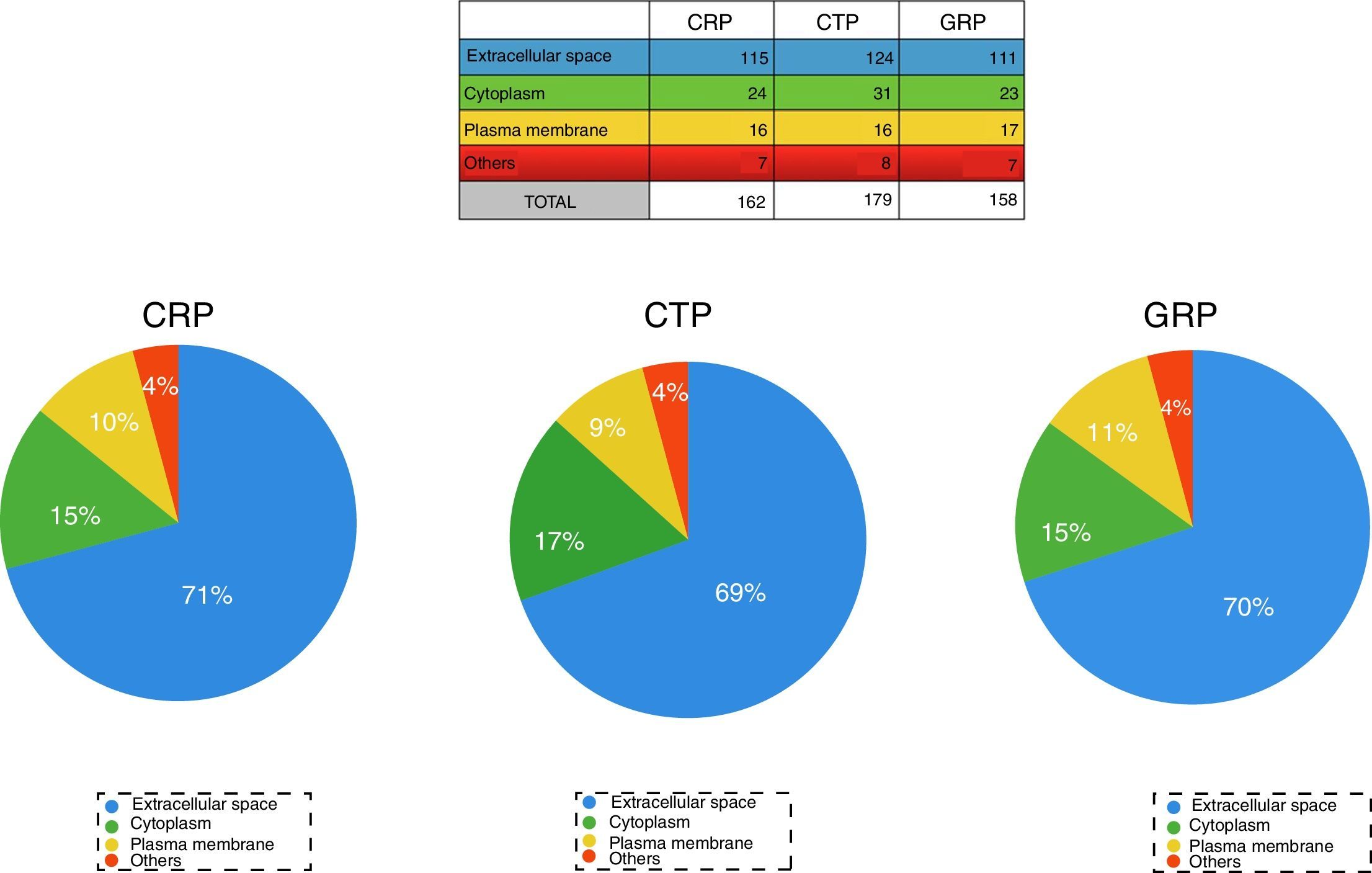
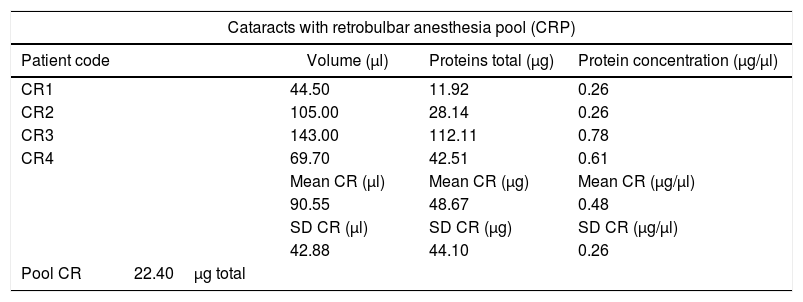
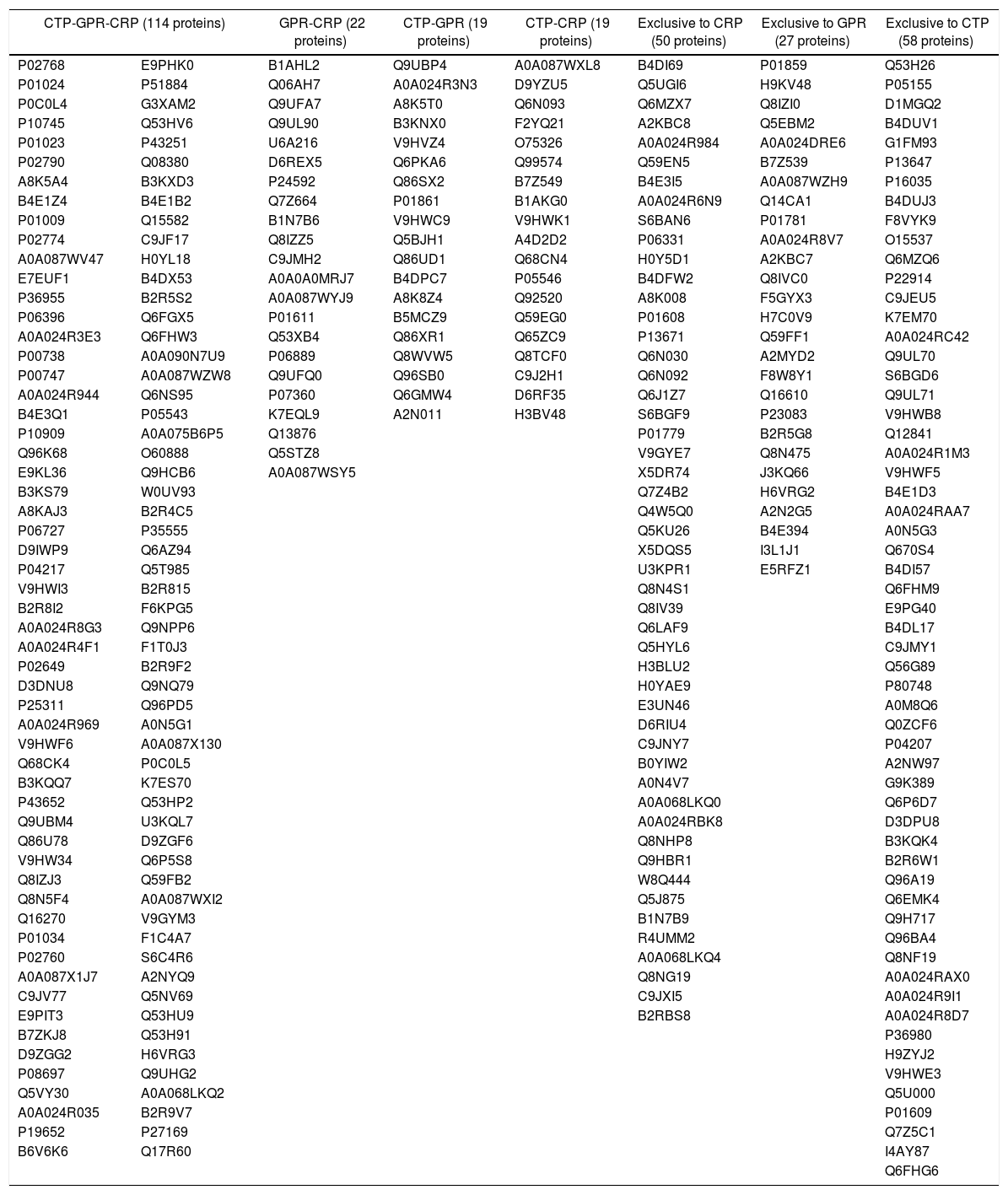
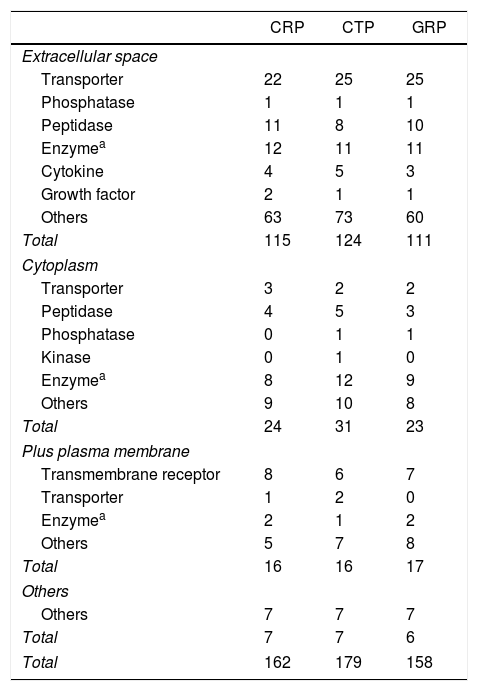
ResultsThe study included 12 patients, aged (mean±standard deviation) 74.50±9.53 years. Concentrations obtained: 0.48±0.25μg/μl for CRP, 0.28±0.04μg/μl for CTP, and 0.35±0.16μg/μl for GRP. A total of 309 proteins were identified, of which 205, 210, and 182 were in CRP, CTP, and GRP, respectively. A total of 114 proteins were common to all three groups, 50 were exclusive to CRP, 58 to CTP, and 27 to GRP.
ConclusionsIn this pilot study, a quantitative difference was found in the protein expression of humor among patients with glaucoma, there being 27 proteins unique to patients with glaucomatous disease.
Determinación cuantitativa y cualitativa del proteoma en humor acuoso de pacientes con y sin glaucoma.
MétodoEstudio observacional, descriptivo y transversal, de 12 pacientes (8 hombres; 4 mujeres) con y sin glaucoma. Se constituyen 3 grupos de proteínas minoritarias con aportación sérica equimolar de cada uno de los pacientes. Las muestras se han obtenido durante la cirugía de cataratas, de pacientes sin glaucoma (realizada con anestesia retrobulbar [cataract retrobulbar patient –CRP–; n=4] o tópica [cataract topical patient –CTP–; n=4]), o de pacientes con glaucoma (realizada con anestesia retrobulbar [glaucoma retrobulbar patient –GRP–; n=4]). Las muestras de humor acuoso se congelaron a -80°C hasta su procesamiento mediante digestión con tripsina para obtener péptidos trípticos y realizar cromatografía líquida acoplada a espectrometría de masas en tándem (LC-MS/MS), para obtener el proteoma y su expresión diferencial entre grupos. El análisis estadístico se realizó mediante el programa SPSS v.17.
ResultadosDoce pacientes, con edad (media±desviación estándar) de 74,50±9,53 años. Concentraciones proteicas obtenidas; 0,48±0,25μg/μl para CRP, 0,28±0,04μg/μl para CTP y 0,35±0,16μg/μl para GRP. Identificadas 309 proteínas, de estas 205, 210 y 182 se encuentran en CRP, CTP y GRP, respectivamente. Comunes a los tres grupos 114. Exclusivas 50 de CRP, 58 de CTP y 27 de GRP.
ConclusionesEn nuestro estudio piloto, encontramos diferencia cuantitativa en la expresión proteica del humor acuoso entre pacientes con y sin glaucoma, existiendo 27 proteínas exclusivas de pacientes con enfermedad glaucomatosa.