The diagnosis of drug induced liver injury (DILI) is based primarily on the exclusion of alternative causes. To assess the frequency of alternative causes in initially suspected DILI cases, we searched the Medline database with the following terms: drug hepatotoxicity, drug induced liver injury, and hepatotoxic drugs. For each term, we used the first 100 publications. We reviewed references, selected those reports relevant to our study, and retrieved finally 15 publications related to DILI and alternative causes. A total of 2,906 cases of initially assumed DILI were analyzed in these 15 publications, with diagnoses missed in 14% of the cases due to overt alternative causes. In another 11%, the diagnosis of DILI could not be established because of confounding variables. Alternative diagnoses included hepatitis B, C, and E, CMV, EBV, ischemic hepatitis, autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cirrhosis, primary sclerosing cholangitis, hemochromatosis, Wilson’s disease, Gilbert’s syndrome, fatty liver, non alcoholic steatohepatitis, alcoholic liver diseases, cardiac and thyroid causes, rhabdomyolysis, polymyositis, postictal state, tumors, lymphomas, chlamydial and HIV infections. Causality assessment methods applied in these 15 publications were the CIOMS (Council for International Organizations of Medical Sciences) scale alone (n = 5) or combined with the Maria and Victorino (MV) scale (n = 1), the DILIN (Drug-Induced Liver Injury Network) method (n = 4), or the Naranjo scale (n = 1); the qualitative CIOMS method alone (n = 3) or combined with the MV scale (n = 1). In conclusion, alternative diagnoses are common in primarily suspected DILI cases and should be excluded early in future cases, requiring a thorough clinical and causality assessment.
Drug induced liver injury (DILI) is no specific disease entity but bundles multiple diseases with variable clinical manifestations caused by numerous drugs with different chemical structures. DILI is of idiosyncratic nature and occurs at recommended doses, excluding thereby cases with overdose. The variability includes clinical symptoms, latency periods, dechallenge characteristics, laboratory results, immunological signs, hepatotoxicity criteria, histological findings, outcome, natural disease history, and incidence, with details thoroughly being discussed in recent publications.1–7 This heterogeneous appearance provides particular clinical and pharmacovigilance challenges, since the diagnosis of DILI still is one of exclusion, lacking positive diagnostic biomarkers that are validated and universally applicable for all cases.8,9 Future challenges will have to focus on biomarkers in patients with established DILI causality, bearing in mind the characteristics of its idiosyncratic nature. Results from animal studies and data after acute administration of high drug doses certainly do not reflect the idiosyncratic features of DILI in humans.
As a diagnosis of exclusion, DILI competes with some hundred drug unrelated liver diseases, which are to be excluded as far as possible.10,11 However, important clinical elements for the diagnosis of DILI often were underreported, as described in detail after reviewing numerous published cases.12 Some reports did not provide initial ALT (alanine aminotransferase) or ALP (alkaline phosphatase) activities, and data on abnormal results including ALT and ALP from serial liver tests frequently were absent. Others studies reported negative tests for hepatitis A, B, and C, but the descriptions were vague without presentation of specific serological parameters used as basis for exclusion. Competing viral etiologies were reported as excluded in less than half of the analyzed cases. These shortcomings in case data quality led to the question whether correct diagnoses unrelated to drugs may have been missed in reports of initially assumed DILI.
In this study, we analyze case series of 2,906 DILI cases for frequency and type of alternative diagnoses in initially assumed DILI.
Material and MethodsLiterature searchWe searched the Medline database in March 2013 with the following terms: drug hepatotoxicity, drug induced liver injury, and hepatotoxic drugs. For each term, we used the first 100 publications representing single case reports, case series, review articles, or letters to the editor. Based on these publications, we reviewed the references, selected reports relevant to the aim of our study, and retrieved 102 English language publications related to DILI.
Publication selectionOur initial assessment of the 102 DILI publications showed that only case series specifically addressed the question of alternative diagnoses in assumed DILI cases. They provided alternative causes in 15 publications as specified confirmed diagnoses; cases with DILI causality gradings of excluded, unlikely, unrelated, or possible for the individual drug, implied that alternative causes exist but are not specifically presented as diagnoses; or cases with unspecified alternative causes.13–27 In the analyzed 15 publications, causality for DILI cases was assessed by the CIOMS scale (Council for International Organizations of Medical Sciences),28 which is quantitative and the commonly used diagnostic algorithm for suspected hepatotoxicity;29–34 the rarely applied qualitative CIOMS method35 as the precursor of the CIOMS scale;28 the MV scale (Maria & Victorino);36 the DILIN method (Drug-Induced Liver Injury Network);22,37 and the Naranjo scale.38
Assessment approachThe principal goals were assessing the frequency of alternative causes and evaluating further the cases with confirmed alternative diagnoses in the 15 case series with initially suspected DILI. In addition, we looked at the frequency of verified DILI cases and assessed those cases with unverified DILI regarding major confounding variables.
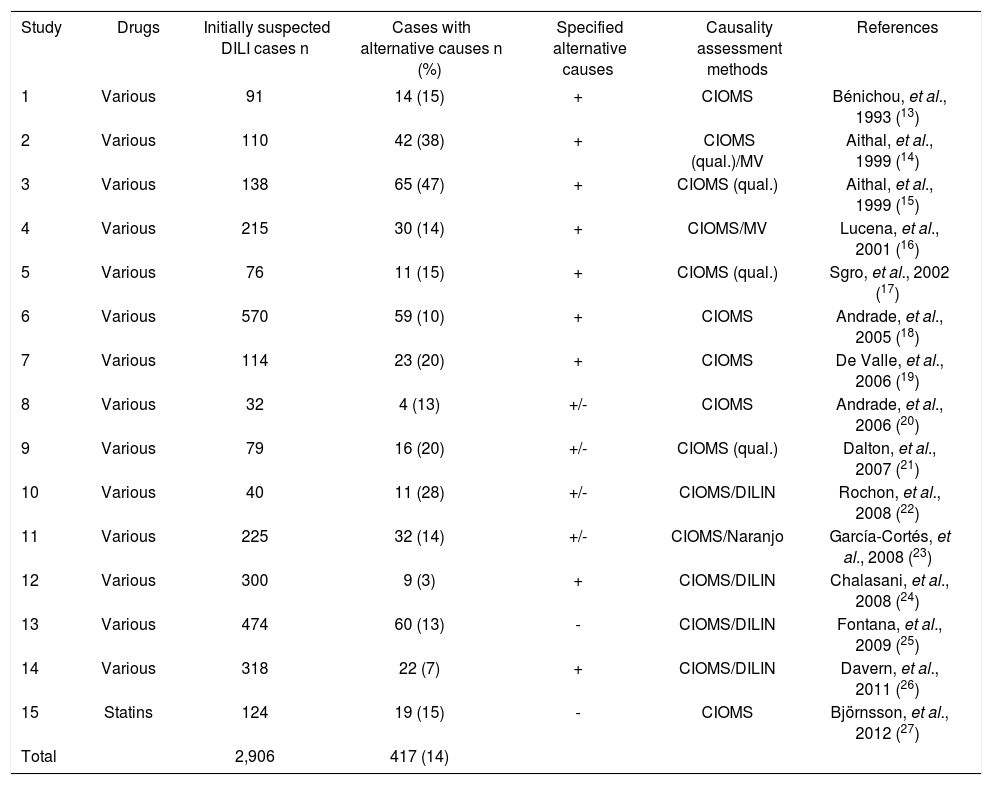
ResultsStudy cohortThe study cohort was retrieved from 15 publications of case series with assumed DILI addressing alternative causes (Table 1). In 14/15 publications, multiple drugs for various treatment indications were involved, in one publication several different statins were reported. A total of 2,906 cases of initially assumed DILI were analyzed in these 15 publications, with an average of 194 cases (range 32-570 cases) per publication (Table 1). These reports mentioned alternative diagnoses in 417/2,906 cases (14%), with details of all specific alternative diagnosis presented in 9 studies; both specified and unspecified alternative causes were presented in 4 studies, and in 2 others, none of the alternative causes was specified. Therefore, in only 281/417 cases specific alternative causes were presented (Tables 2 and 3). Causality assessment methods in these 15 publications were the CIOMS scale alone (n = 5), combined with the MV scale (n = 1), the DILIN method (n = 4), or the Naranjo scale (n = 1); the qualitative CIOMS scale alone (n = 3) or combined with the MV scale (n = 1) (Table 1).
Frequency of alternative causes in initially suspected DILI cases.
| Study | Drugs | Initially suspected DILI cases n | Cases with alternative causes n (%) | Specified alternative causes | Causality assessment methods | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Various | 91 | 14 (15) | + | CIOMS | Bénichou, et al., 1993 (13) |
| 2 | Various | 110 | 42 (38) | + | CIOMS (qual.)/MV | Aithal, et al., 1999 (14) |
| 3 | Various | 138 | 65 (47) | + | CIOMS (qual.) | Aithal, et al., 1999 (15) |
| 4 | Various | 215 | 30 (14) | + | CIOMS/MV | Lucena, et al., 2001 (16) |
| 5 | Various | 76 | 11 (15) | + | CIOMS (qual.) | Sgro, et al., 2002 (17) |
| 6 | Various | 570 | 59 (10) | + | CIOMS | Andrade, et al., 2005 (18) |
| 7 | Various | 114 | 23 (20) | + | CIOMS | De Valle, et al., 2006 (19) |
| 8 | Various | 32 | 4 (13) | +/- | CIOMS | Andrade, et al., 2006 (20) |
| 9 | Various | 79 | 16 (20) | +/- | CIOMS (qual.) | Dalton, et al., 2007 (21) |
| 10 | Various | 40 | 11 (28) | +/- | CIOMS/DILIN | Rochon, et al., 2008 (22) |
| 11 | Various | 225 | 32 (14) | +/- | CIOMS/Naranjo | García-Cortés, et al., 2008 (23) |
| 12 | Various | 300 | 9 (3) | + | CIOMS/DILIN | Chalasani, et al., 2008 (24) |
| 13 | Various | 474 | 60 (13) | - | CIOMS/DILIN | Fontana, et al., 2009 (25) |
| 14 | Various | 318 | 22 (7) | + | CIOMS/DILIN | Davern, et al., 2011 (26) |
| 15 | Statins | 124 | 19 (15) | - | CIOMS | Björnsson, et al., 2012 (27) |
| Total | 2,906 | 417 (14) |
Specified and in detail presented alternative causes were provided for all (+), some (+/-), or none (-) of the cases. Causality assessment methods refer to the CIOMS scale (Council for International Organizations of Medical Sciences),29 which is quantitative and represents the most commonly used algorithm;29–34 the qualitative CIOMS method lacking any quantitative criteria;35 the MV scale of Maria and Victorino;36 and the method of DILIN (Drug-Induced Liver Injury Network).22,37
Analysis of alternative causes of initially suspected DILI cases.
| Alternative causes in initially suspected drug induced liver injury |
|---|
| •Hepatitis B. Hepatitis B cirrhosis 1/138 cases.15 |
| •Hepatitis C. Acute hepatitis C 4/254 cases;24 Chronic hepatitis C 2/40 cases.22 |
| •Hepatitis E. 10/45 cases,21 9/318 cases.26 |
| •CMV Hepatitis. 2/138 cases.15 |
| •EBV Hepatitis. 2/138 cases.15 |
| •Viral hepatitis. Unspecified viral hepatitis 2/91 cases,13 5/215 cases,16 11/570 cases.18 |
| •Ischemic hepatitis. 4/91 cases,13 1/110 cases,14 10/138 cases,15 3/215 cases,16 6/570 cases.18 |
| •Autoimmune hepatitis. |
| ° 5/110 cases,14 8/138 cases,15 7/215 cases,16 6/570 case,18 7/114 cases,19 2/32 cases,20 2/474 cases.25 |
| • Primary biliary cirrhosis. 3/114 cases.19 |
| • Primary sclerosing cholangitis. 3/114 cases.19 |
| • Hemochromatosis. 1/91 cases (13), 1/40 cases.22 |
| • Wilson’s disease. 1/215 cases,16 1/570 cases.18 |
| • Gilbert’s syndrome. 3/138 cases.15 |
| • Fatty liver. Steatosis 3/138 cases,15 1/95 cases;17 Non alcoholic fatty liver 5/114 cases.19 |
| • Non alcoholic steatohepatitis. 5/215 cases,16 4/570 cases.18 |
| • Alcoholic liver disease. |
| ° 6/110 cases,14 3/138 cases;15 Alcoholic hepatitis 1/215 cases,16 3/570 cases.18 |
| ° 2/114 cases;19 Chronic alcoholism in 1/95 cases.17 |
| • Liver injury by other comedication. 9/73 cases.27 |
| • Paracetamol overdose. 2/138 cases,15 2/474 cases.25 |
| • Benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis. 1/254 cases.24 |
| • Biliary diseases. |
| ° Biliary obstruction 5/91 cases;13 Cholangitis 1/138 cases;15 |
| ° Choledocholithiasis 3/215 cases,16 13/570 cases,18 1/114 cases;19 |
| ° Common bile duct stone 12/138 cases,15 Oddi spasms 2/95 cases.17 |
| • Cardiac hepatopathy. Cardiac failure 1/91 cases,13 3/95 cases.17 |
| • Thyroid hepatopathy. Hypothyroidism 1/215 cases,16 2/570 cases,18 Thyrotoxicosis 1/138 cases.15 |
| • Rhabdomyolysis. 1/95 cases.17 |
| • Polymyositis. 1/254 cases.24 |
| • Postictal. 2/138 cases.15 |
| • Tumor. |
| ° 11/110 cases,14 3/215 cases,16 10/570 cases;18 |
| ° Metastatic bladder cancer 1/95 cases;17 Liver metastasis from carcinoid tumor 1/114 cases.19 |
| • Lymphoma. 2/138 cases.15 |
| • Systemic sepsis. 2/110 cases,14 12/138 cases,15 1/215 cases,16 3/570 cases.18 |
| • Chlamydial infection. 1/91 cases.13 |
| • HIV infection. End-stage HIV disease 1/95 cases.17 |
| • Past liver transplantation |
| ° Transplant related complications 17/110 cases;14 |
| ° Liver or bone marrow transplant prior to DILI onset 2/474 cases.25 |
| • Unknown liver disease |
| ° 3/254 cases;24 Abnormal liver biochemical tests 3/40 cases;22 ? Isolated ?-glutamyltransferase increase 1/95 cases.17 |
| • Preexisting liver cirrhosis. Cryptogenic cirrhosis 1/138 cases;15 Unspecified cirrhosis 1/40 cases.22 |
Missed diagnoses in cases of initially suspected DILI cases including the respective references. CMV: cytomegalovirus. EBV: Epstein Barr virus. HSV: herpes simplex virus. LKM: liver kidney microsomes. SMA: smooth muscle antibodies. VZV: varicella zoster virus.
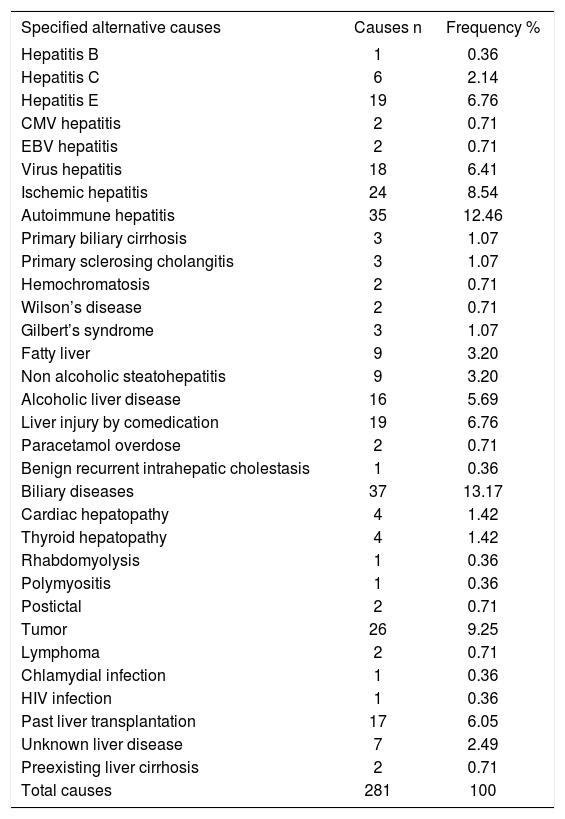
Frequency of specified alternative causes of DILI.
| Specified alternative causes | Causes n | Frequency % |
|---|---|---|
| Hepatitis B | 1 | 0.36 |
| Hepatitis C | 6 | 2.14 |
| Hepatitis E | 19 | 6.76 |
| CMV hepatitis | 2 | 0.71 |
| EBV hepatitis | 2 | 0.71 |
| Virus hepatitis | 18 | 6.41 |
| Ischemic hepatitis | 24 | 8.54 |
| Autoimmune hepatitis | 35 | 12.46 |
| Primary biliary cirrhosis | 3 | 1.07 |
| Primary sclerosing cholangitis | 3 | 1.07 |
| Hemochromatosis | 2 | 0.71 |
| Wilson’s disease | 2 | 0.71 |
| Gilbert’s syndrome | 3 | 1.07 |
| Fatty liver | 9 | 3.20 |
| Non alcoholic steatohepatitis | 9 | 3.20 |
| Alcoholic liver disease | 16 | 5.69 |
| Liver injury by comedication | 19 | 6.76 |
| Paracetamol overdose | 2 | 0.71 |
| Benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis | 1 | 0.36 |
| Biliary diseases | 37 | 13.17 |
| Cardiac hepatopathy | 4 | 1.42 |
| Thyroid hepatopathy | 4 | 1.42 |
| Rhabdomyolysis | 1 | 0.36 |
| Polymyositis | 1 | 0.36 |
| Postictal | 2 | 0.71 |
| Tumor | 26 | 9.25 |
| Lymphoma | 2 | 0.71 |
| Chlamydial infection | 1 | 0.36 |
| HIV infection | 1 | 0.36 |
| Past liver transplantation | 17 | 6.05 |
| Unknown liver disease | 7 | 2.49 |
| Preexisting liver cirrhosis | 2 | 0.71 |
| Total causes | 281 | 100 |
Among the cases with suspected DILI (Table 1), there was a broad spectrum of alternative causes (Table 2) in a total of 281 cases (Table 3). Of concern are missed virus hepatitis diagnoses with 48/ 281 cases corresponding to 17%, including cases of hepatitis B, C, and E, CMV, EBV and other viral hepatitis types (Tables 2 and 3). Hepatitis E with 19/281 cases alone accounted for almost 7% of the alternative causes (Table 3), and were mentioned only in 2/15 publications (Tables 1 and 2). Ischemic hepatitis was overlooked in 24/281 cases and represented 8.5% of the alternative diagnoses, and autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cirrhosis and primary sclerosing cholangitis were found in a total of 41/281 cases corresponding to 14.6% (Tables 2 and 3). Genetic liver diseases like hemochromatosis and Wilson’s disease were missed in 2 cases each. In 3 patients, Gilbert’s syndrome – commonly lacking increased liver values – was misidentified as DILI (Table 3). Fatty liver, non alcoholic steatohepatitis, and alcoholic liver diseases are commonly observed in the general population and were misinterpreted in 34/281 cases (12%) of this study cohort (Tables 2 and 3). Liver injury by comedication other than the incriminated drug was found in 19/281 cases corresponding to 6.8%, whereas paracetamol overdose, an intrinsic but not an idiosyncratic form of liver injury, was causal in 2 cases (Table 3).
Rare alternative extrahepatic causes include cardiac failure and thyroid diseases, rhabdomyolysis, polymyositis, and postictal states (Tables 2 and 3). With 26/281 cases (9.3%), solid tumors were misdiagnosed as DILI, rarely also lymphomas (Table 3). In 1 case each, chlamydial and HIV infections were incorrectly classified as DILI (Table 2 and 3).
In 26/281 additional cases, DILI was erroneously attributed to patients with a history of liver transplantation and associated transplant related complications (n = 17), with unknown or questionable liver disease (n = 7), and with preexisting liver cirrhosis (n = 2) (Tables 2 and 3). There are numerous alternative causes in extrahepatic diseases with liver involvement, with biliary diseases being the most frequent alternative cause, accounting for 37/ 281 cases (13.2%) of all alternative causes (Table 3) within the broad spectrum of this particular disease (Table 2).
All alternative diagnoses as presented in the respective quoted reports were included as such in the present study, not requiring additional diagnostic evaluation of each individual case of interest or changes of the diagnoses. Cases with the diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis were included, unless specified in the published report as drug induced variety. Alternative diagnoses were recognized at various levels of assessing causality, some already in the spontaneous report system intended to quickly detect hepatotoxicity “signals”, others at later stages of the evaluating process when publication of a case series was considered. Interestingly, some cases with alternative diagnoses subsequently served as control groups in comparison to true DILI cases. Whenever alternative diagnoses were recognized, these cases were excluded from further DILI analysis in the published reports.
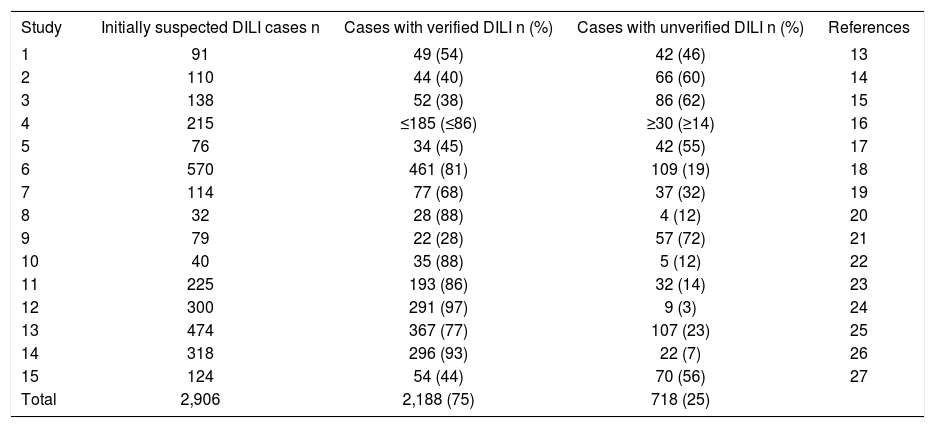
Verified DILI casesOut of 2,906 cases with initially suspected DILI, the diagnosis of DILI was presented as established in 2,188 cases, which corresponds to 75%; in the other 25%, DILI remained unverified (Table 4) with alternative causes accounting for 14% (Table 1). Analysis of the cases without verified DILI as presented in the 15 studies showed various confounding variables that impeded valid causality adjunctions to a drug initially suspected as cause for the liver disease (Table 5).
General problems of evaluation of unassessable, initially suspected DILI cases.
| Study | Initially suspected DILI cases n | Cases with verified DILI n (%) | Cases with unverified DILI n (%) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 91 | 49 (54) | 42 (46) | 13 |
| 2 | 110 | 44 (40) | 66 (60) | 14 |
| 3 | 138 | 52 (38) | 86 (62) | 15 |
| 4 | 215 | ≤185 (≤86) | ≥30 (≥14) | 16 |
| 5 | 76 | 34 (45) | 42 (55) | 17 |
| 6 | 570 | 461 (81) | 109 (19) | 18 |
| 7 | 114 | 77 (68) | 37 (32) | 19 |
| 8 | 32 | 28 (88) | 4 (12) | 20 |
| 9 | 79 | 22 (28) | 57 (72) | 21 |
| 10 | 40 | 35 (88) | 5 (12) | 22 |
| 11 | 225 | 193 (86) | 32 (14) | 23 |
| 12 | 300 | 291 (97) | 9 (3) | 24 |
| 13 | 474 | 367 (77) | 107 (23) | 25 |
| 14 | 318 | 296 (93) | 22 (7) | 26 |
| 15 | 124 | 54 (44) | 70 (56) | 27 |
| Total | 2,906 | 2,188 (75) | 718 (25) |
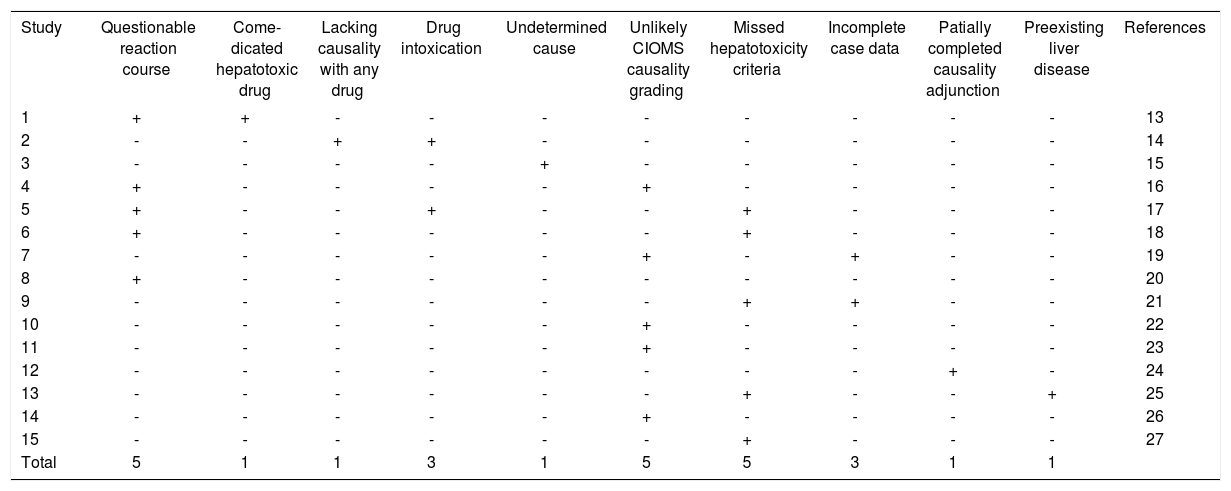
Compilation of major confounding variables in cases with unverified DILI.
| Study | Questionable reaction course | Come-dicated hepatotoxic drug | Lacking causality with any drug | Drug intoxication | Undetermined cause | Unlikely CIOMS causality grading | Missed hepatotoxicity criteria | Incomplete case data | Patially completed causality adjunction | Preexisting liver disease | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 13 |
| 2 | - | - | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | 14 |
| 3 | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | 15 |
| 4 | + | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | 16 |
| 5 | + | - | - | + | - | - | + | - | - | - | 17 |
| 6 | + | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | 18 |
| 7 | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | + | - | - | 19 |
| 8 | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 20 |
| 9 | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | - | - | 21 |
| 10 | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | 22 |
| 11 | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | 23 |
| 12 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | 24 |
| 13 | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | + | 25 |
| 14 | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | 26 |
| 15 | - | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | 27 |
| Total | 5 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
In this analysis of 2906 cases with initially reported liver injury attributed to a specific drug, the diagnosis of DILI was incorrect in 14% (Table 1) due to obvious alternative causes (Tables 1, 2 and 3), and could not be proven in another 11%, resulting in a total of 25% of cases without verified DILI (Table 4). Confounding variables described in all reports created additional major problems for causality assessment (Table 5).13–27 These percentages are based on 15 case series with unknown degrees of case selection, with 55-72% unproven DILI cases in 5 publications, compared to 3-14% in the 5 case series with the lowest number of unproven cases (Table 5). These data support the contention that assessments of suspected DILI cases may be problematic and require substantial efforts for valid causality attributions.
The high rate of 55-72% unverified DILI cases, published for some case series of initially suspected DILI (Table 4)14,15,17,21,27 indicate causality assessment problems. For instance, a rate of 55% for unverified DILI cases was published for cases that were reported by physicians, using a standardized notification form to report the case; the physician group consisted of 75 general practitioners, 5 gastroenterologists, and 59 specialists such as rheumatologists, psychiatrists, gynecologists, dermatologists, internists, and anesthesiologists.17 A comparable rate of 56% was obtained for reports of suspected DILI by statins received by the Swedish Adverse Drug Reactions Advisory Committee.27 DILI cases were not proven in 60% based on computerized histological records of patients with a histological diagnosis of DILI or cholestasis/hepatitis in Newcastle-upon-Tyne (UK),14 and in 62% of suspected DILI reports provided to the Committee on Safety of Medicines in the Northern region of the UK.15 Finally, a rate of 72% unverified DILI cases was found for patients attending the Jaundice Hotline service of a teaching hospital in the southwestern England.21 These problems will perpetuate if regulatory agencies use report numbers of hepatotoxicity cases for pharmacovigilance purposes without consideration whether causality was established or not, as has recently been published for cases of herb induced liver injury (HILI).11 This approach inevitably leads to disputes of regulatory case overdiagnosing and over-reporting.
Major issues in DILI case assessments are possible alternative causes, which may explain on average 14% of all DILI cases with a maximum of 47% of all primarily suspected DILI cases in the 15 analyzed publications (Table 1).13–27 Alternative causes are manifold and include hepatic diseases and extra-hepatic disorders with hepatic involvement (Tables 2 and 3). A careful analysis of 65 patients with DILI unrelated alternative causes revealed that the primary underlying diagnoses were not recognized by the reporting physician in 35 cases.15 The delay in reaching the correct diagnosis in these patients was considerable, with a medium of 88.5 days (range 2-1,480 days) in the hospital group and 122 days (range 30-982 days) in the general practitioner group. In the other 30 patients, the primary underlying diagnosis was recognized and treated at time that the reaction was reported but it was incorrectly attributed to a drug.15
Missed primary diagnoses, unrelated to the erroneously implicated herbal product, are also a problem in cases of suspected HILI cases, again with a broad range of alternative causes22 similar to the present analysis of suspected DILI cases (Tables 2 and 3). In the HILI study, 23 publications with 573 suspected HILI cases were analyzed, alternative causes were evident in 278/573 cases (48.5%). For suspicion of both DILI and HILI cases, causality assessment requires substantial improvement at the level of the physician caring for these patients, best achieved by the liver specific and well validated CIOMS scale.13,28–34 Accurate diagnoses are needed to avoid possible health hazards for the patients, due to missed diagnoses and delayed treatment.
ConclusionsAmong 15 publications with 2,906 suspected cases of DILI, the correct diagnosis was missed in 14% with evident alternative causes, and DILI diagnosis could not be proven in another 11% due to confounding variables such as low data quality. A thorough clinical evaluation with firm exclusion of alternative causes and the use of the liver specific CIOMS scale should be mandatory for the physician caring for patients with suspected DILI to avoid delays in diagnosis and treatment.
AcknowledgementThe authors declare that they have no conflict on interest.