To assess the diagnostic performance of urinary dysfunction patterns associated with vesicoureteral reflux (VUR) in children over the age of 3 according to the result of the first endoscopic treatment (ENDT1), grouped into a classification designed by our group (CMD.URI-La Fe). Comparison with other current classifications such as that of Van Batavia et al.
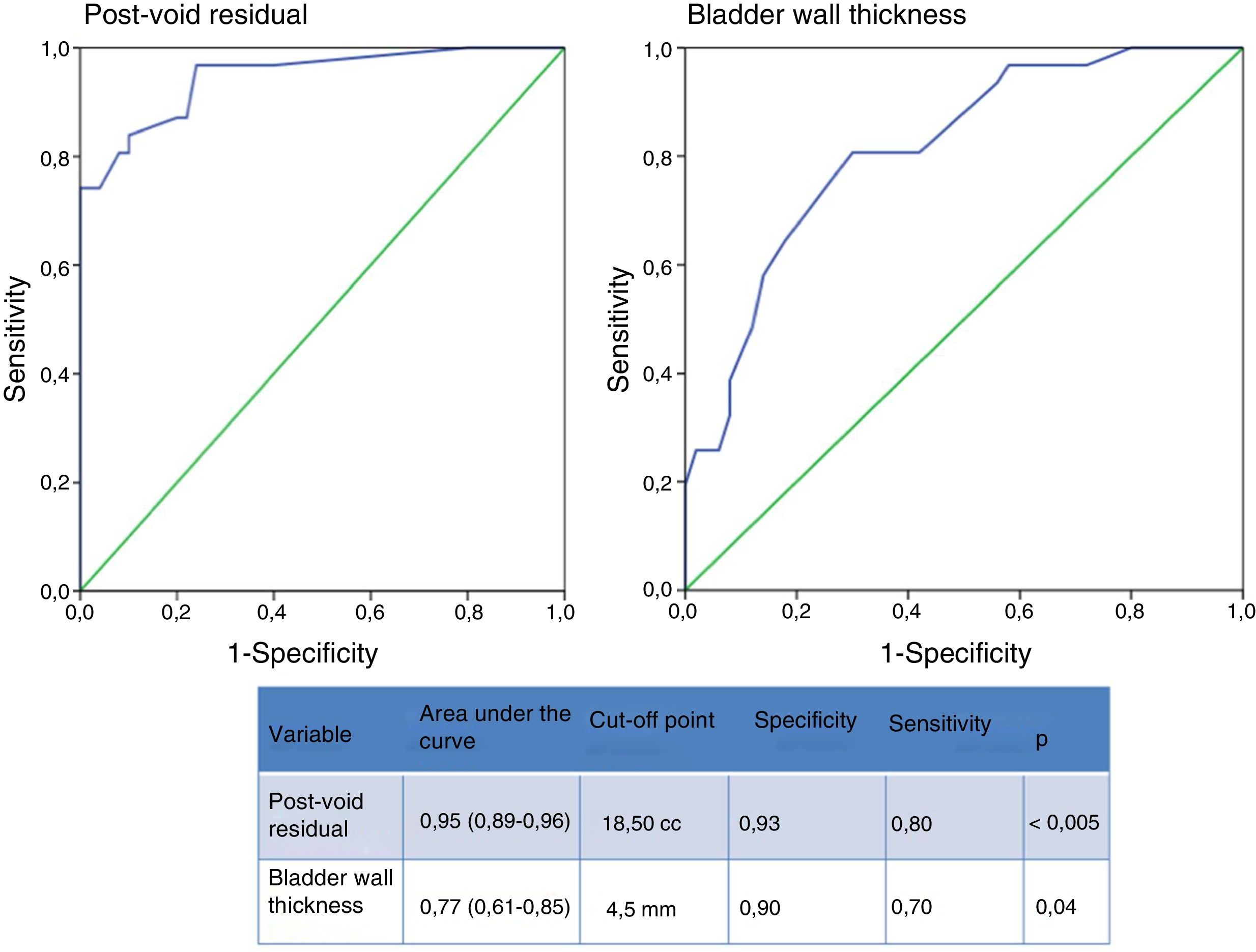
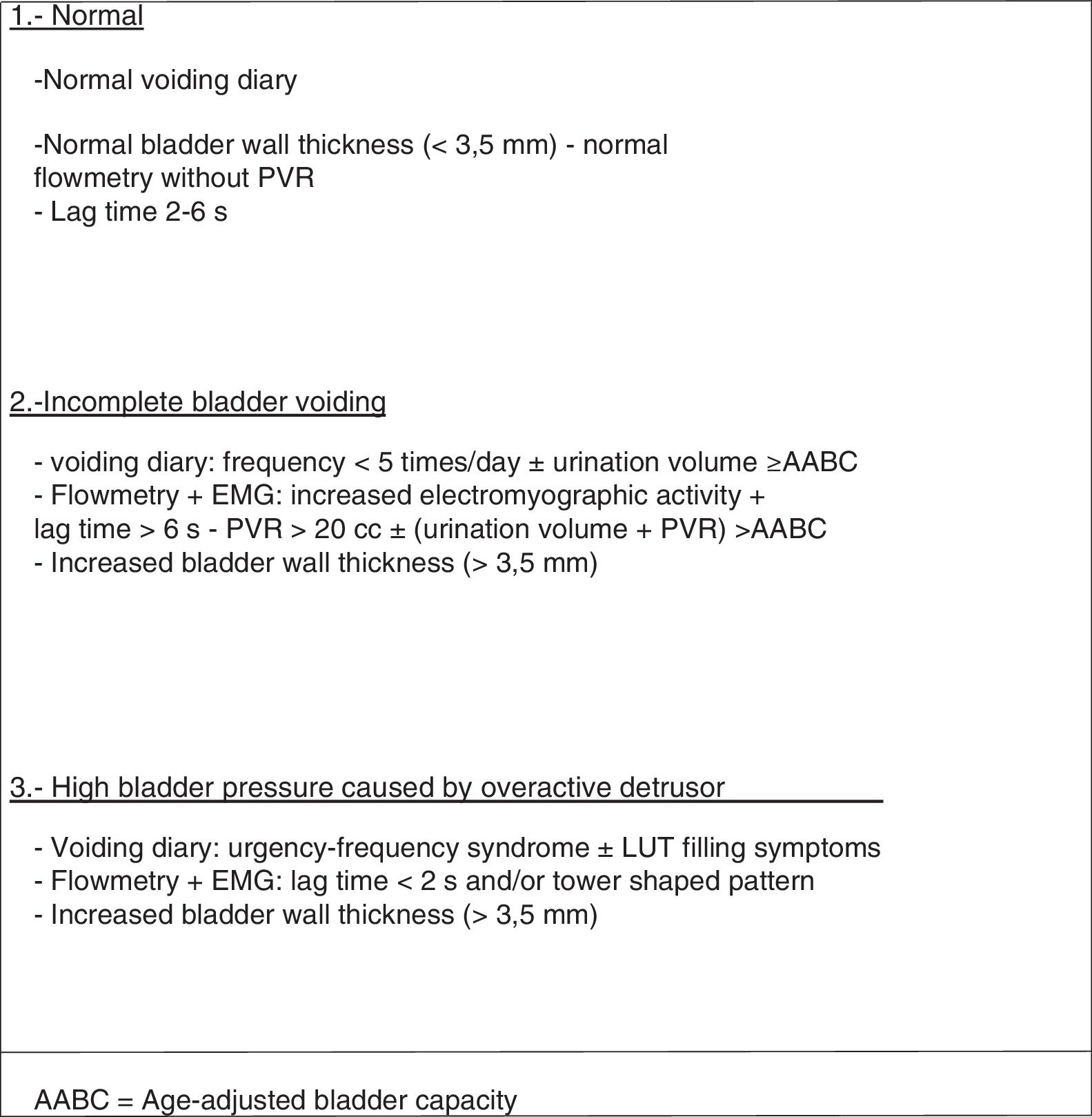
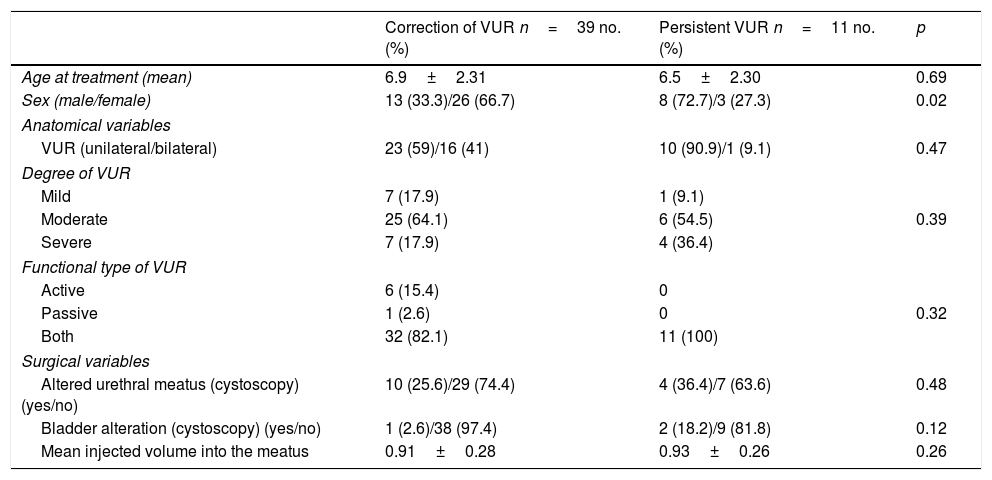
Material and methodsAmbispective cross-cutting study of a sample of 50 children. Exclusion criteria: previous ENDT, age≤3 years, anatomical or neurological anomalies and a history of ureteral or abdominopelvic surgery. Prior to the ENDT1, a bladder voiding function assessment by uroflowmetry+electromyography (UF-EMG) and post-mictional residue (ultrasound). Other variables from the bladder diary, pre-mictional bladder wall thickness and other clinical variables. The correction of VUR was assessed by isotope cystography 3 months after the treatment. Urinary patterns were classified according to the significant variables (URI-La Fe), and the diagnostic performance of this classification was assessed, comparing it to the classification of patients as proposed by Van Batavia et al.
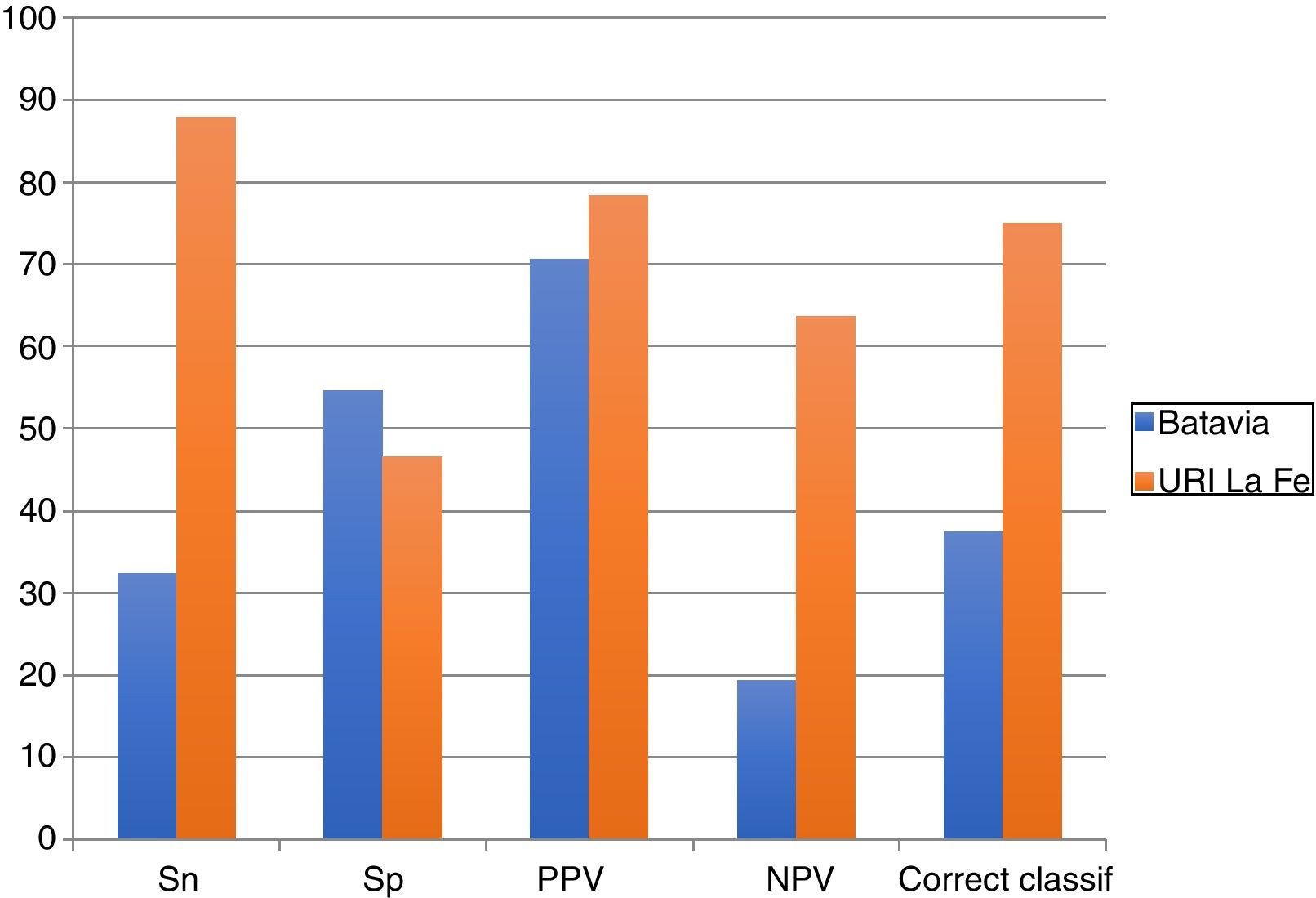
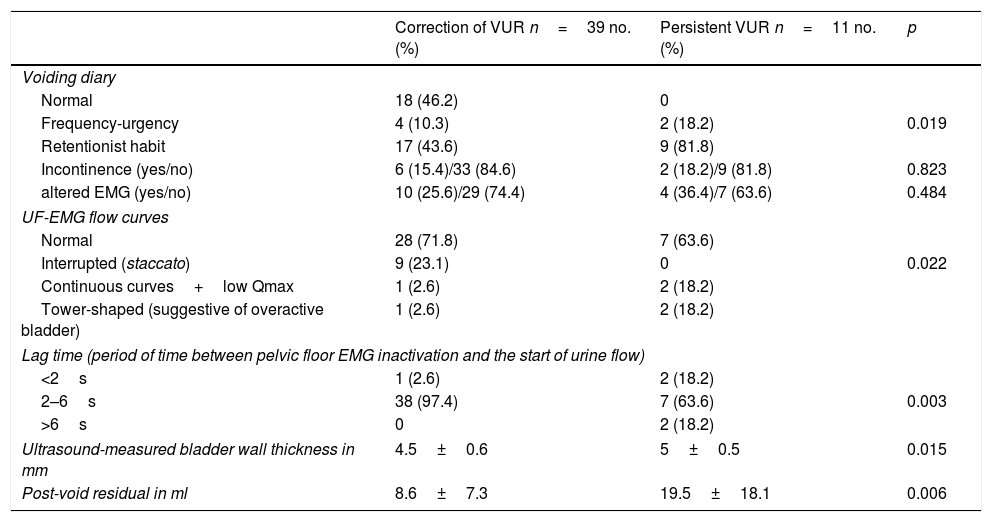
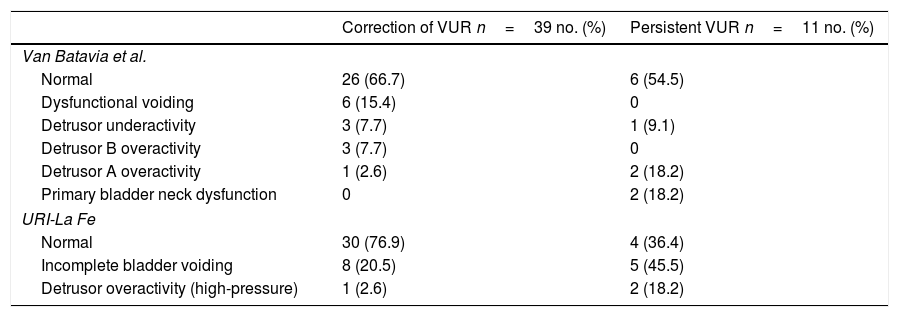
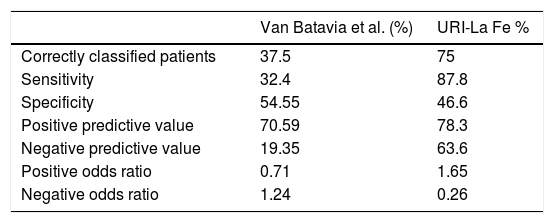
ResultsMean age: 6.8±2.28 years. Males/females (44%/56%). Grades of VUR (mild/moderate/severe). ENDT1 VUR correction rate: 77% (n=38). Diagnostic performance (Van Batavia; URI-La Fe): correct prediction (37.5%; 75%), sensitivity (32.4%; 87.8%), specificity (54.5%; 46.6%), positive predictive value (70.6; 78.3%) and negative predictive value (19.4%; 63.6%).
ConclusionsOur results show the usefulness of the non-invasive test and the classification of urinary dysfunction in children aged over 3 years prior to the first endoscopic treatment of VUR.
Valorar el rendimiento diagnóstico de los patrones de micción disfuncional asociados al reflujo vesicoureteral (RVU) en niños mayores de 3 años, en función del resultado del primer tratamiento endoscópico (T1END), agrupados en una clasificación diseñada por nuestro grupo (CMD.URI-La Fe) y su comparación con otras clasificaciones existentes como la de Van Batavia et al.
Material y métodosEstudio transversal ambispectivo de una muestra de 50 niños. Criterios de exclusión: TEND previo, edad ≤ 3 años, anomalías anatómicas o neurológicas y antecedentes de cirugía uretral o abdominopélvica. Previamente al T1END se realizó una valoración de la función de vaciado vesical mediante flujometría+electromiografía (UF-EMG) y del residuo posmiccional (ecografía). Se obtuvieron otras variables procedentes del diario miccional, el espesor de la pared vesical premiccional (ecografía), así como variables clínicas. La corrección del RVU fue valorada mediante cistografía isotópica a los 3 meses del tratamiento. Se realizó una clasificación de los patrones miccionales en función de las variables significativas (URI-La Fe) y se valoró su rendimiento diagnóstico, comparándola al clasificar a los pacientes según propone Van Batavia et al.
ResultadosMedia de edad: 6,8±2,28 años. Varones/mujeres (44%/56%). Grados de RVU: leve, moderado, severo. Tasa de corrección del RVU T1END: 77% (n=38). Rendimiento diagnóstico (Van Batavia; URI-La Fe): predicción correcta (37,5%; 75%), sensibilidad (32,4%; 87,8%), especificidad (54,5%; 46,6%), valor predictivo positivo (70,6; 78,3%) y valor predictivo negativo (19,4%; 63,6%).
ConclusionesNuestros resultados muestran la utilidad del estudio no invasivo y la clasificación de la disfunción miccional del niño mayor de 3 años previo al primer tratamiento endoscópico del RVU.