Uroflowmetry and postvoid residual urine volume measurement remain essential in evaluating patients with lower urinary tract dysfunction. The objective was to identify patients with a high risk of infection or renal damage based on the lower urinary tract parameters.
Materials and methodsOver a one-year period we investigated patients who had an indication for uroflowmetry and postvoid residual urine volume measurement between 5–18 years of age. All parameters were prospectively recorded. After the initial evaluation, patients were divided into increased/normal postvoid residual urine volume groups. Lower urinary tract parameters, urinary tract infection and hydronephrosis status were analyzed.
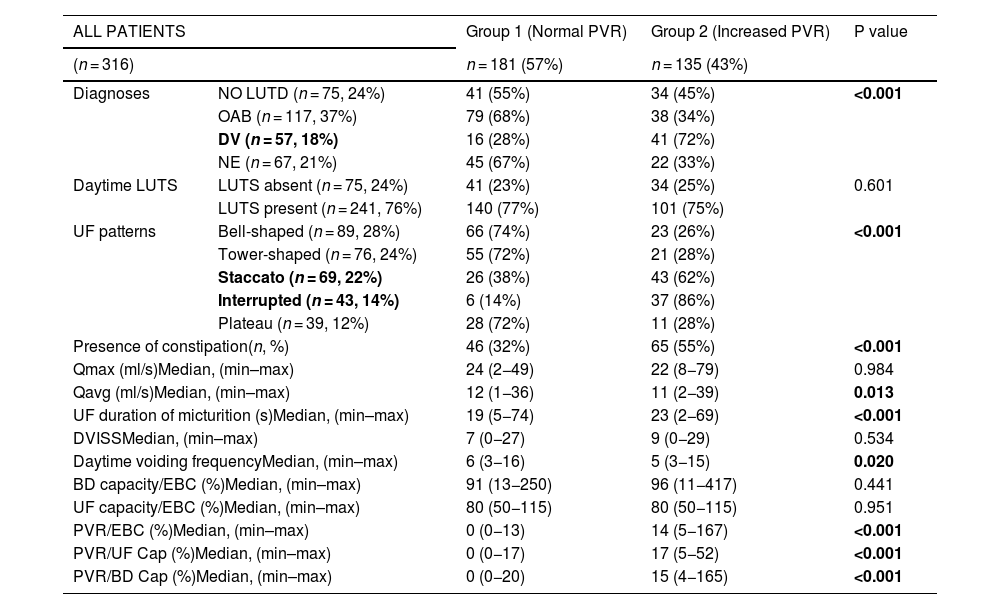
ResultsA total of 176 girls and 140 boys with an age of 9 (5–16) were assessed. When increased (n = 135)/normal postvoid residual urine volume (n = 181) groups of patients were analyzed, patients with a diagnosis of dysfunctional voiding, staccato and interrupted-shaped flow pattern, decreased Qavg, increased micrution duration, decreased daytime voiding frequency, and constipation were found to be prone to increased postvoid residual urine volume. A diagnosis of overactive bladder or dysfunctional voiding and high postvoid residual urine volume were both found to be related to infections.
ConclusionsWe contributed to the literature by evaluating different types of lower urinary tract conditions and their clinical parameters to better understand the predisposing factors to detect patients at risk of infections or renal damage such as dysfunctional voiding, staccato and interrupted-shaped flow pattern, constipation, decreased Qavg, prolonged duration of micturition and decreased daytime voiding frequency regardless of age and gender status.
La uroflujometría y la medición del residuo posmiccional siguen siendo esenciales en la evaluación de pacientes con disfunción del tracto urinario inferior. El objetivo de este estudio fue identificar a aquellos pacientes con un alto riesgo de infección o daño renal, según los parámetros del tracto urinario inferior.
Material y métodosDurante un período de un año evaluamos a pacientes entre 5 y 18 años que tenían indicación de uroflujometría y medición del residuo posmiccional. Todos los parámetros se registraron prospectivamente. Tras la evaluación inicial, los pacientes se dividieron en grupos según el volumen de orina residual posmiccional elevado/normal. Se analizaron los parámetros del tracto urinario inferior, la infección urinaria y la presencia de hidronefrosis.
ResultadosSe evaluó a un total de 176 niñas y 140 niños con una edad de 9 (5–16) años. Al analizar los grupos de pacientes con residuo posmiccional elevado (n = 135)/normal (n = 181), se observó que los pacientes con diagnóstico de disfunción miccional, flujo con curva en staccato e interrumpido, disminución del Qave, micción prolongada, disminución de la frecuencia miccional diurna y estreñimiento eran más propensos a presentar un residuo posmiccional elevado. Se observó una relación entre el diagnóstico de vejiga hiperactiva o disfunción miccional y residuo posmiccional y las infecciones.
ConclusionesHemos aportado a la bibliografía evaluando distintos tipos de patologías del tracto urinario inferior y sus parámetros clínicos. Conocer los factores predisponentes será de gran utilidad para detectar a aquellos pacientes en riesgo de infecciones o daño renal. Entre estos factores se incluyen la disfunción miccional, la curva de flujo en staccato e interrumpida, el estreñimiento, la disminución del Qave, la micción prolongada y la reducción de la frecuencia miccional diurna, independientemente de la edad y el sexo.