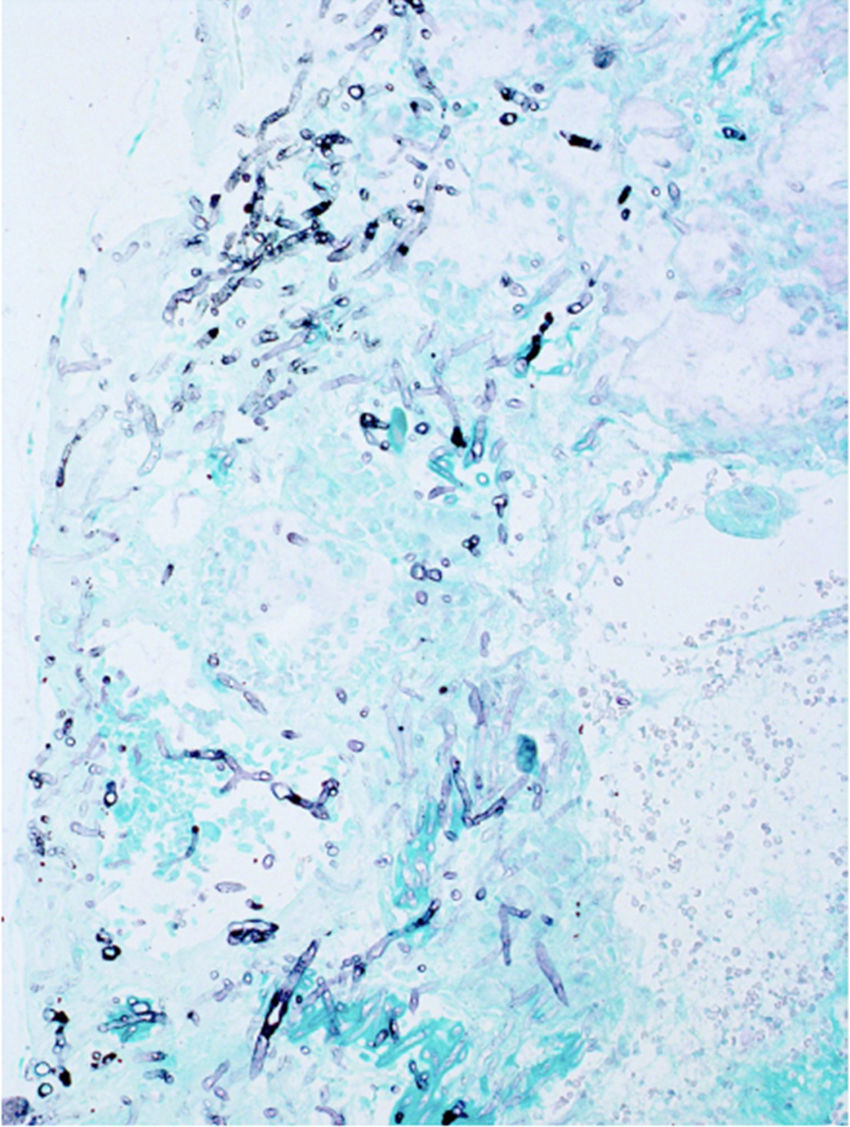
To describe the results of the treatment of invasive fungal sinusitis with nasal endoscopic surgery in an immunocompromised paediatric oncological population.
MethodsRetrospective study of all patients diagnosed with invasive fungal sinusitis operated in the National Paediatric Oncology Unit (UNOP) between 2012 and 2016. Data taken from their medical history included: epidemiological characteristics, oncological diagnosis, haematological data, symptoms, tomographic studies, surgical interventions, results of pathology and cultures, medications received, complications, evolution and survival.
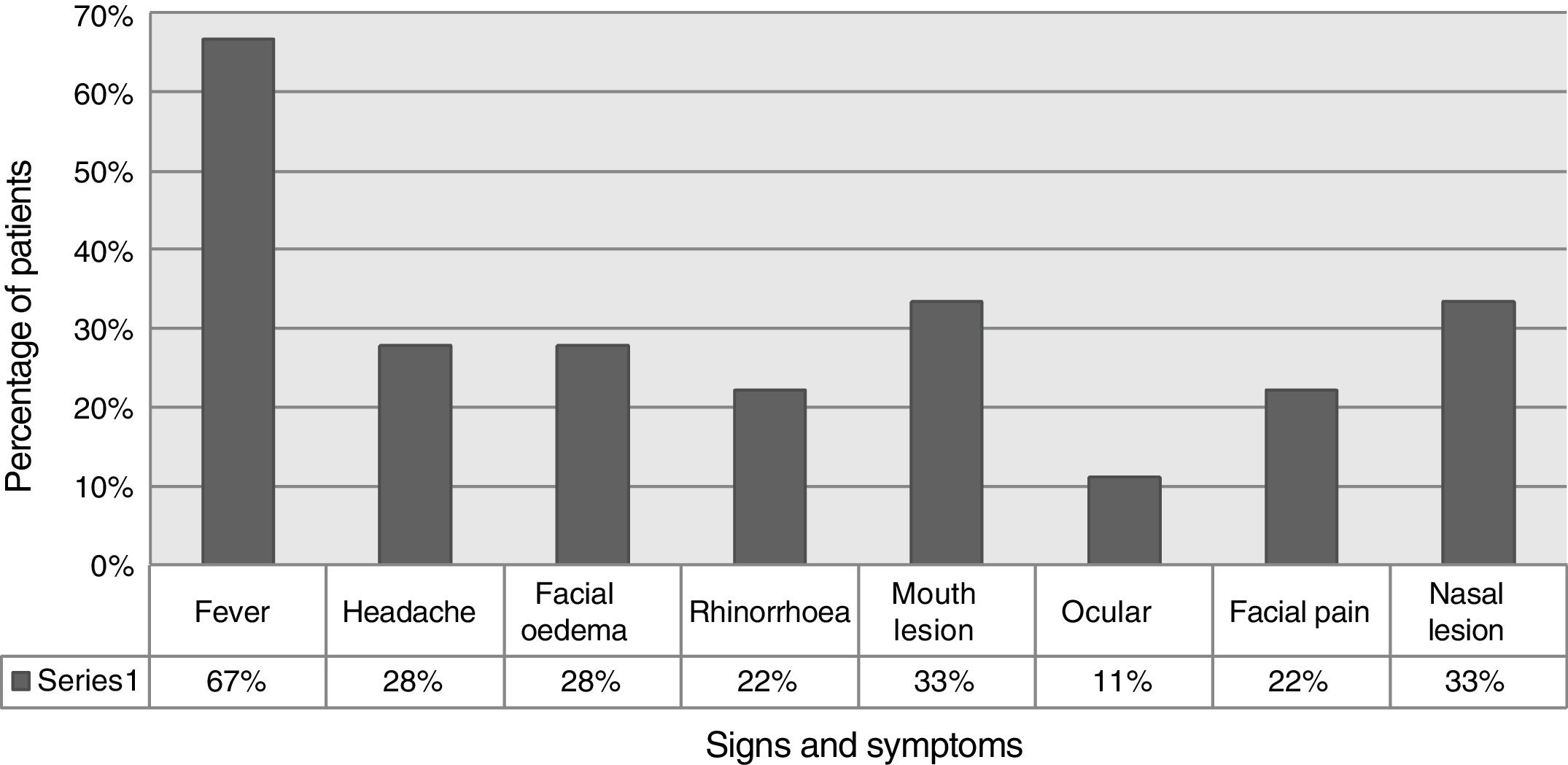
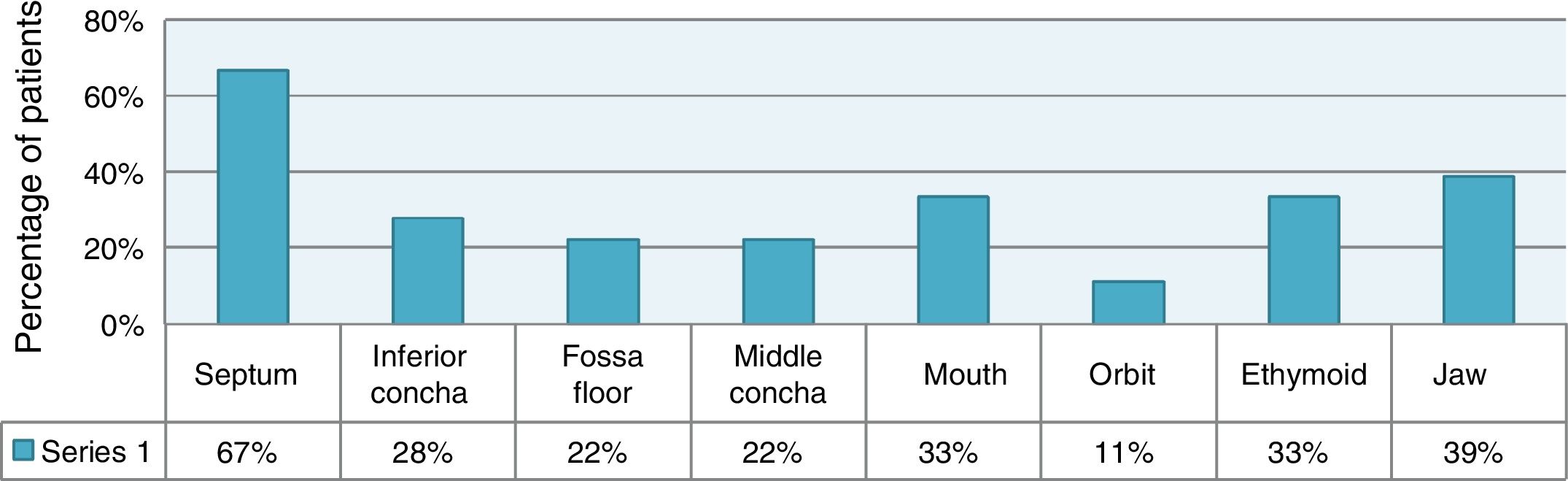
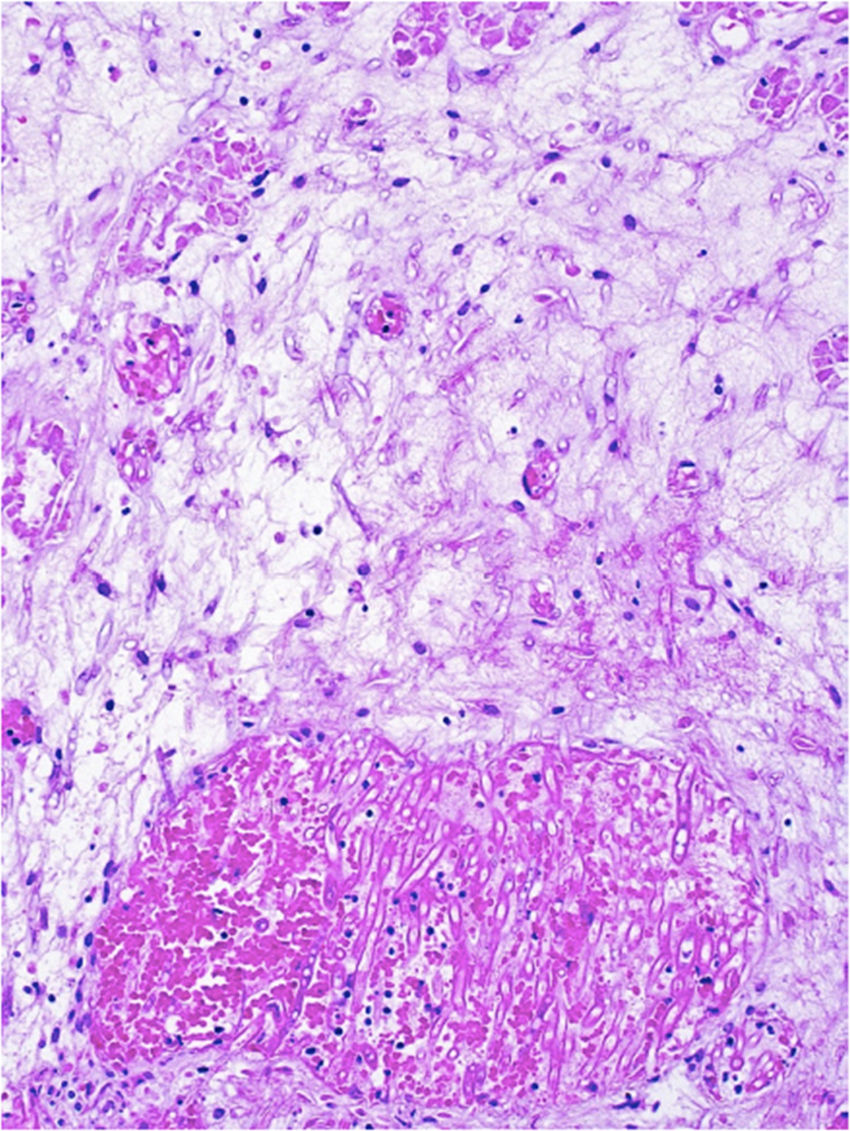
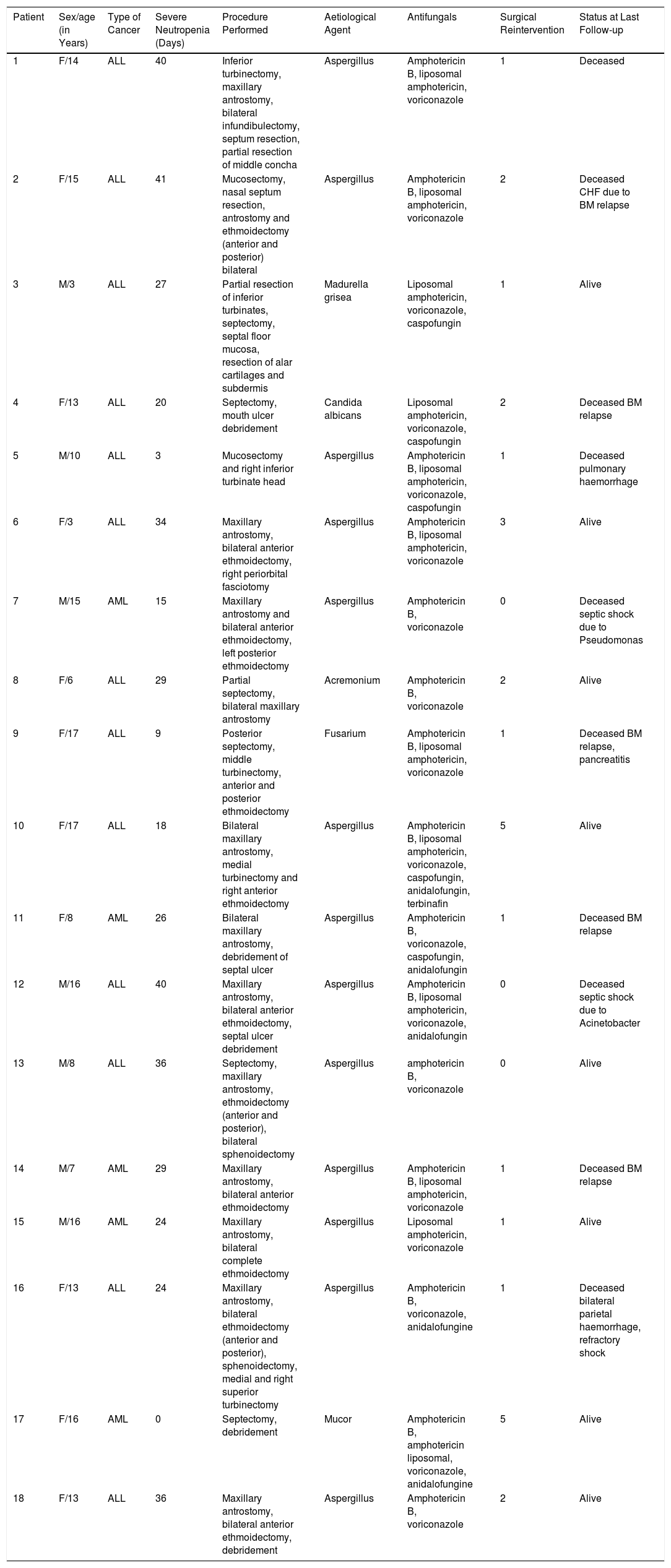
Results18 patients were identified, 7 male and 11 female. The average age was 12 years, 13 had a diagnosis of ALL and 5 of AML. Seventeen patients presented severe neutropenia at the time of diagnosis. The most frequently identified aetiological agent was Aspergillus in 13 patients. In 16 patients (89%) the disease was controlled with nasal endoscopic surgery. Ten patients died due to unrelated causes throughout the study.
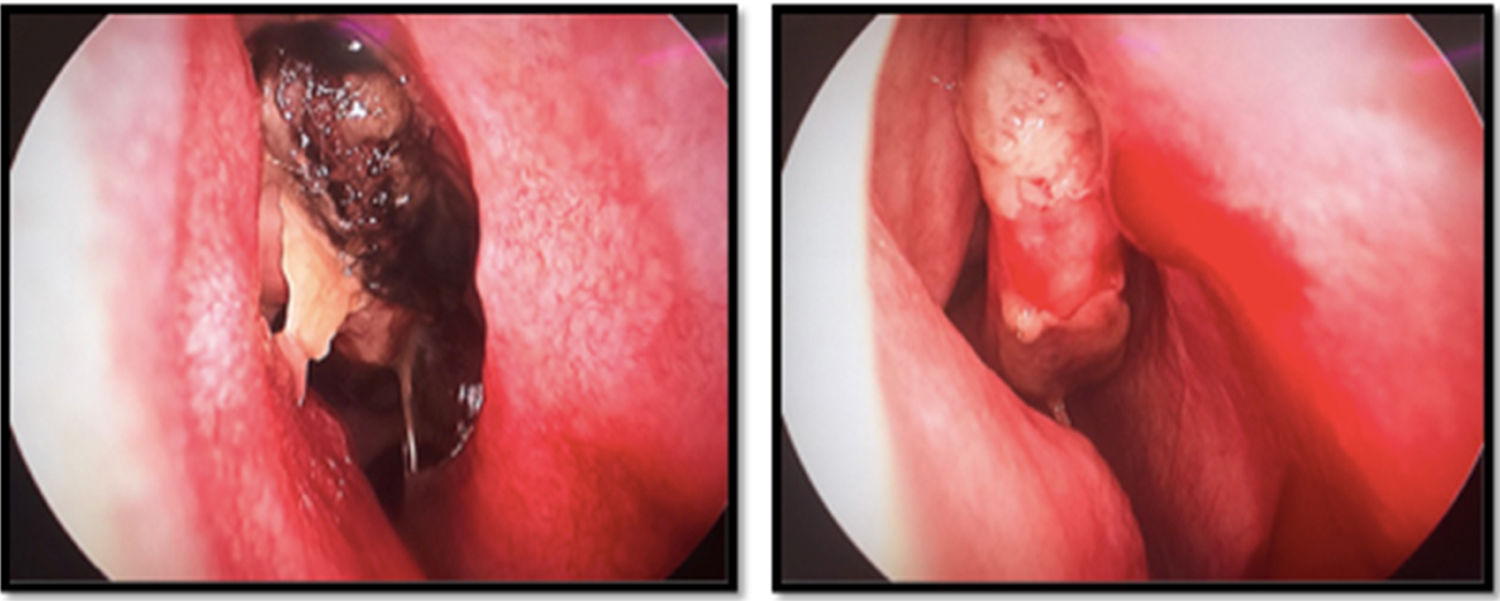
Discussion and ConclusionsInvasive fungal sinusitis should be considered a medical emergency due to its high mortality. The diagnosis is based on a high index of suspicion in patients with predisposing factors (leukaemia, neutropenia, persistent fever, nasogastric tube) and endoscopic nasal evaluation. Antifungal medical treatment and aggressive nasal endoscopic surgery is indicated regardless of the patient's condition to reduce the fungal burden and associated high mortality. The treatment must be provided by a multidisciplinary team that includes paediatrics, haemato-oncology, infectology and otorhinolaryngology
El objetivo del estudio ha sido describir los resultados del tratamiento de sinusitis fúngica invasiva con cirugía endoscópica nasal en una población oncológica pediátrica con inmunosupresión, e informar sobre la seguridad, eficacia y complicaciones del procedimiento
MétodosSe realizó un estudio retrospectivo de la totalidad de pacientes con diagnóstico de sinusitis fúngica invasiva operados en la Unidad Nacional de Oncología Pediátrica (UNOP) entre los años 2012 a 2016. Los datos tomados de su historial médico incluyeron: características epidemiológicas, diagnóstico oncológico, datos hematológicos, síntomas, estudios tomográficos, intervenciones quirúrgicas, resultados de patología y cultivos, medicamentos recibidos, complicaciones, evolución y supervivencia. Los datos fueron analizados utilizando estadística descriptiva, las variables continuas con medidas de tendencia central y las variables categóricas de forma porcentual.
ResultadosSe identificaron 18 pacientes, 7 de sexo masculino y 11 de sexo femenino. El promedio de edad fue de 12 años, 13 tuvieron diagnóstico de LLA y 5 de LMA. 17 pacientes presentaron neutropenia severa al momento del diagnóstico. El agente etiológico más frecuentemente identificado fue Aspergillus en 13 pacientes. En 16 pacientes (89%) se controló la enfermedad con cirugía endoscópica nasal. Diez pacientes fallecieron por causas no relacionadas a lo largo del estudio.
Discusión y conclusionesLa sinusitis fúngica invasiva es una patología cuya incidencia va en aumento entre pacientes con inmunosupresión y debe de considerarse una emergencia médica debido a su alta mortalidad. El diagnóstico se basa en un alto índice de sospecha en pacientes con factores predisponentes (leucemia, neutropenia, fiebre persistente, sonda nasogástrica) y la evaluación endoscópica nasal. El tratamiento médico antifúngico y cirugía endoscópica nasal agresiva está indicado independientemente del estado del paciente para disminuir la carga fúngica y la alta mortalidad asociada. El tratamiento debe de ser suministrado por un equipo multidisciplinario que incluye pediatría, hemato-oncología, infectología y otorrinolaringología.