Even though notable advances in anaesthetic and surgical techniques have appeared in recent years, morbidity, and especially pain, associated with tonsillectomy is still an important clinical problem.
ObjectivesAssess the influence of a specific protocol for the control of postoperative pain and compare the frequency of complications in patients with and without it.
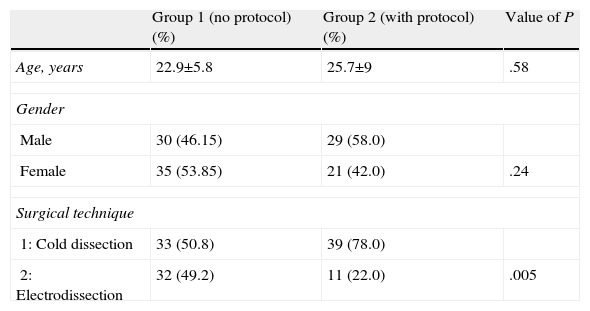
MethodsThis was a descriptive, observational and prospective study on adult tonsillectomy patients in outpatient surgery. There were 2 groups: group 1, with 65 patients to whom a variable analgesic treatment was given; and group 2, with 50 patients with analgesic protocol and preoperative nursing interview. For the evaluation of pain, a numerical scale from 0 to 10 was used. The surgical techniques used were cold dissection or electric dissection.
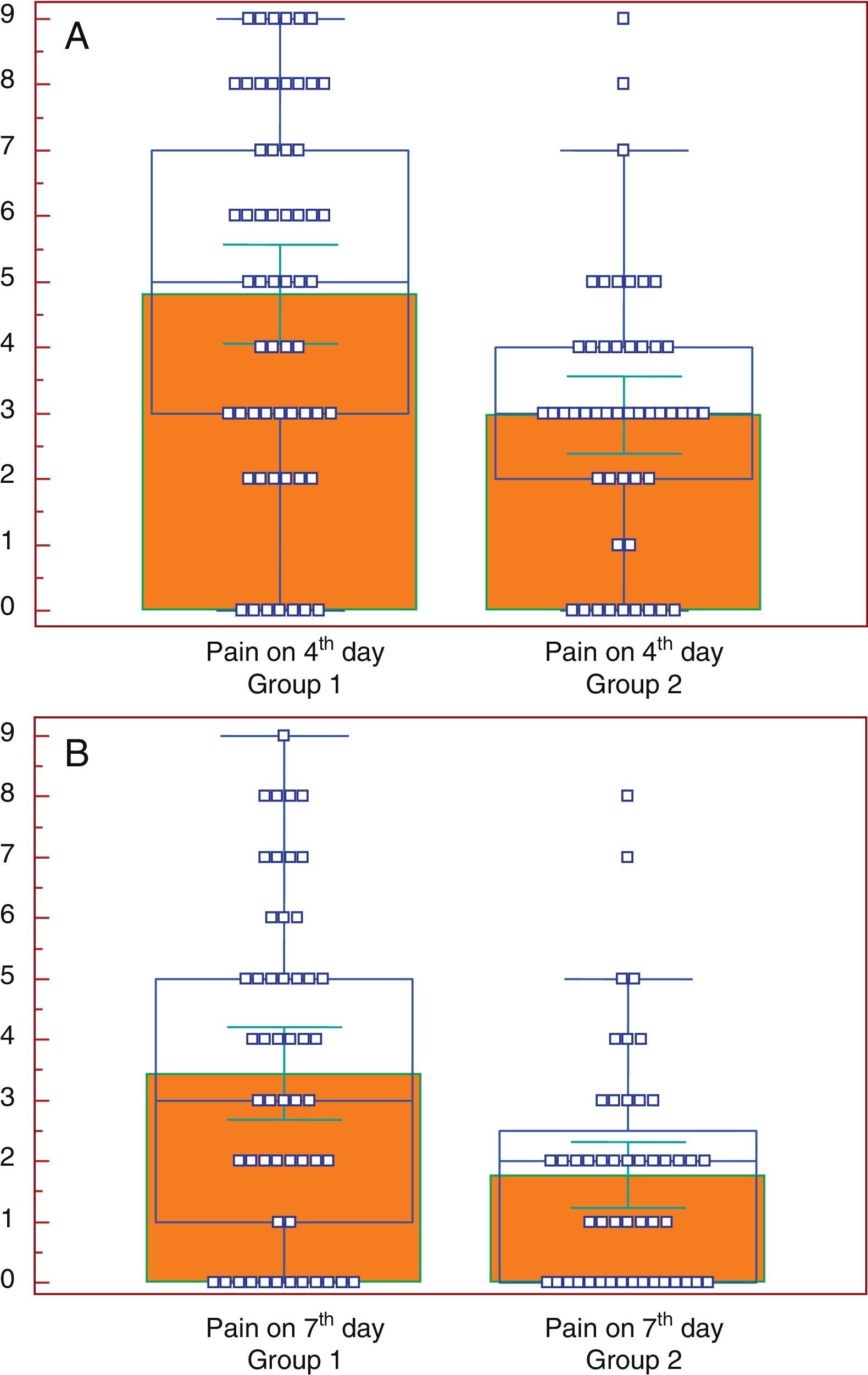
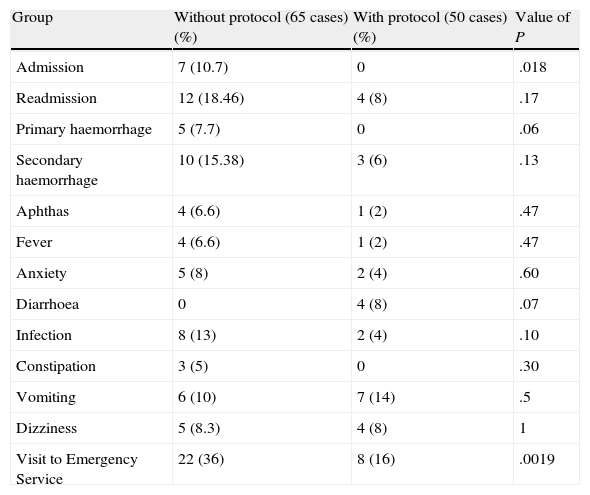
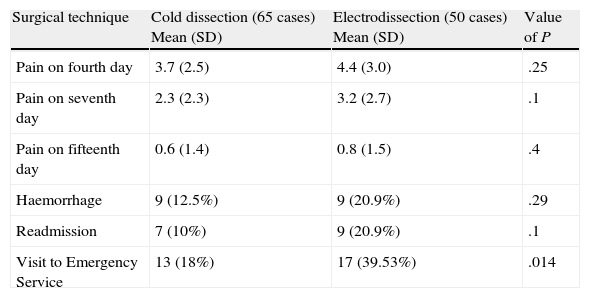
ResultsOn the 4th day, group 1 (without protocol) presented a mean pain of 4.8 points on a numerical scale from 0 to 10, while group 2 (with protocol) presented mean of 3 (P=.0002). From group 1, 22 patients (36%) had to go to the emergency service, while 8 (16%) in group 2 did so (P=.019). On the 4th day, patients operated with cold dissection presented 3.7 points, as opposed to those operated with electric dissection, who presented 4.4 points.
ConclusionsA specific protocol applied to adult tonsillectomy patients in outpatient surgery is useful to obtain less pain and fewer complications.
Aunque en los últimos años se han producido notables avances en las técnicas anestésicas y quirúrgicas, la morbilidad asociada a la amigdalectomía y especialmente el dolor, sigue siendo un importante problema clínico.
ObjetivosEvaluar la influencia del protocolo específico para el control del dolor postoperatorio y comparar la frecuencia de complicaciones en los pacientes con protocolo y sin él.
MétodosEstudio descriptivo, observacional y prospectivo. Pacientes adultos amigdalectomizados en régimen ambulatorio. Dos grupos: grupo 1: 65 pacientes a los cuales se les entregó un tratamiento analgésico variable; grupo 2: 50 pacientes con protocolo analgésico y entrevista preoperatoria de enfermería. Para la valoración del dolor se utilizó la Escala Numérica de 0 a 10. Las técnicas quirúrgicas: disección fría o electrobisturí.
ResultadosAl cuarto día, el grupo 1(sin protocolo) presentó una media de 4,8 puntos en la Escala Numérica de 0 a 10 para evaluación del dolor; el grupo 2 (con protocolo) presentó una media de 3, p=0,0002. Del grupo 1, 22 pacientes (36%) acudieron a Urgencias, del grupo 2 acudieron 8 pacientes (16%), p=0,019. Al cuarto día los pacientes intervenidos con disección fría presentaron 3,7 puntos en la Escala Numérica de 0 a 10, frente a los intervenidos con electrobisturí que presentaron 4,4 puntos.
ConclusionesUn protocolo específico en pacientes adultos intervenidos de amigdalectomía en régimen ambulatorio es útil para conseguir que los pacientes presenten menor dolor y complicaciones.