Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss (ISSHL) is defined as an abrupt hearing loss of at least 30dB of unknown cause. The hearing response obtained after intratympanic steroid injection as a salvage treatment after a prior failure of initial systemic steroid treatment was analysed.
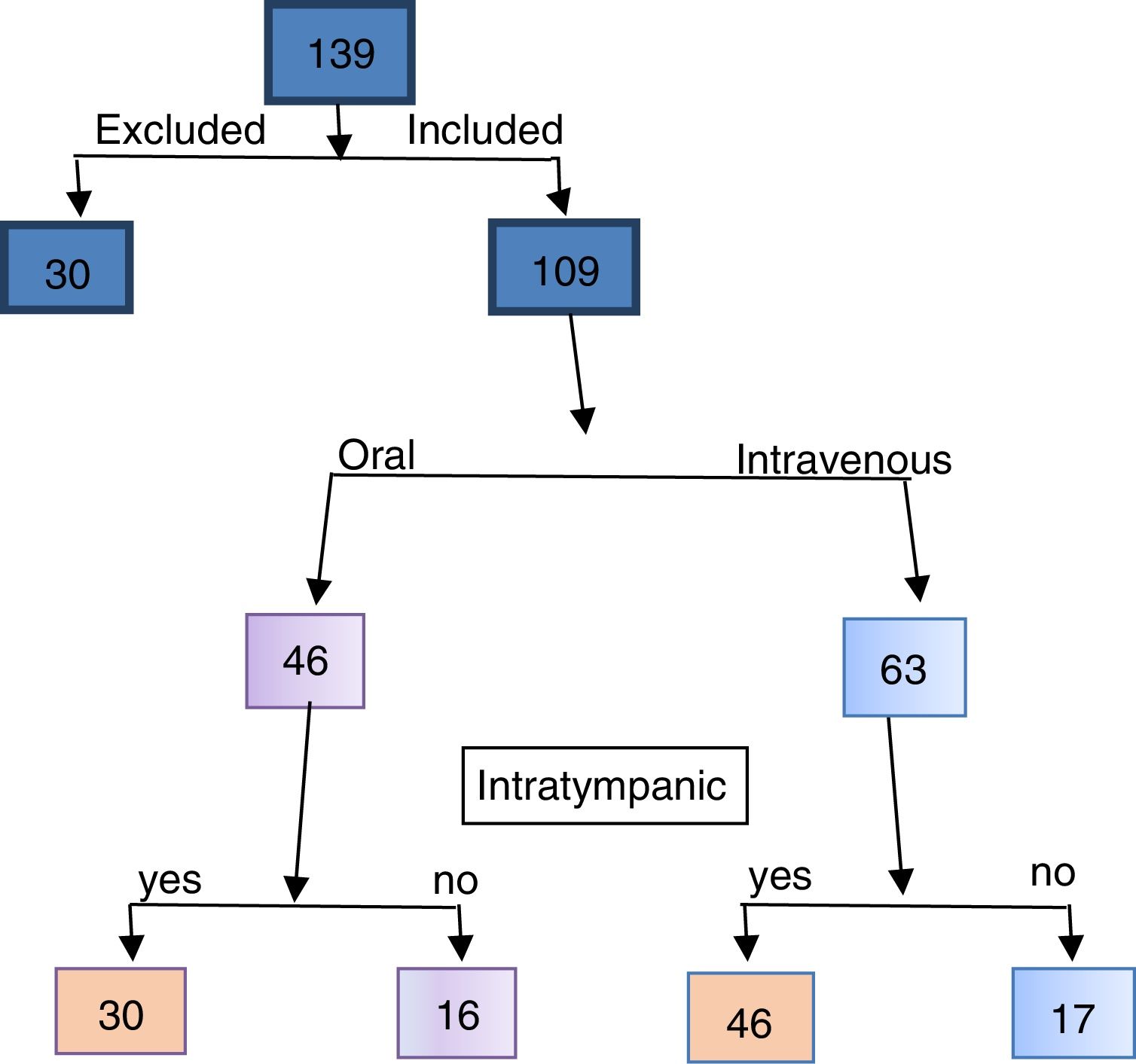
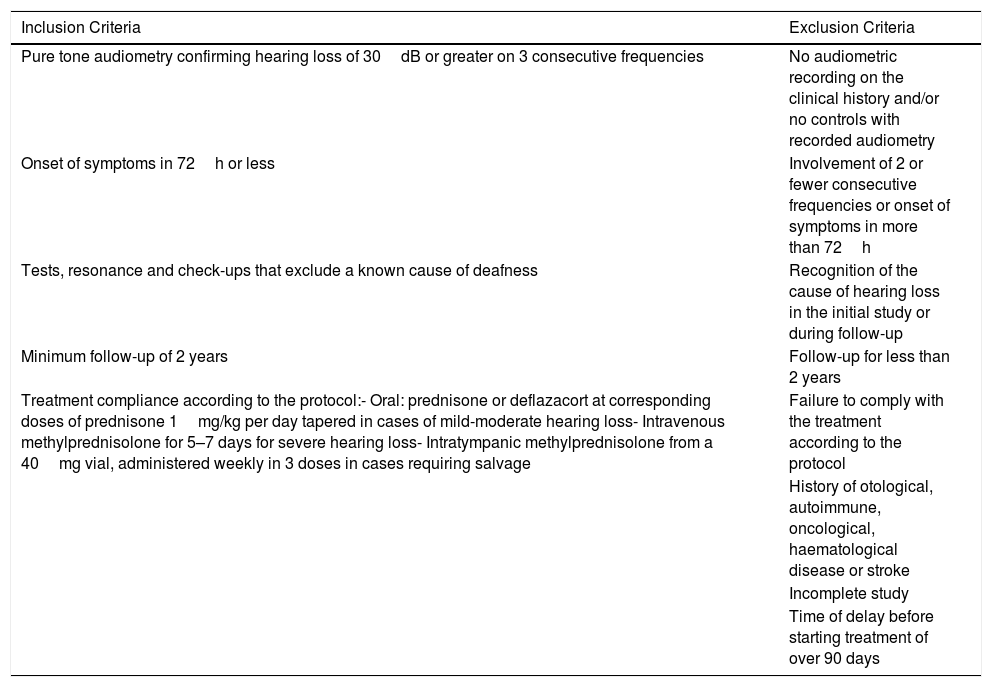
Material and methodAn observational study was performed on 125 cases of ISSHL who were diagnosed from 2006 to 2014. Sixteen achieved complete recovery after one week according to Siegel's criteria. The remaining 109 cases were analysed in two groups: one that received intratympanic corticosteroid salvage therapy (treatment group) and one that did not (control group). The recovery was analysed after 6 months and 2 years of follow-up.
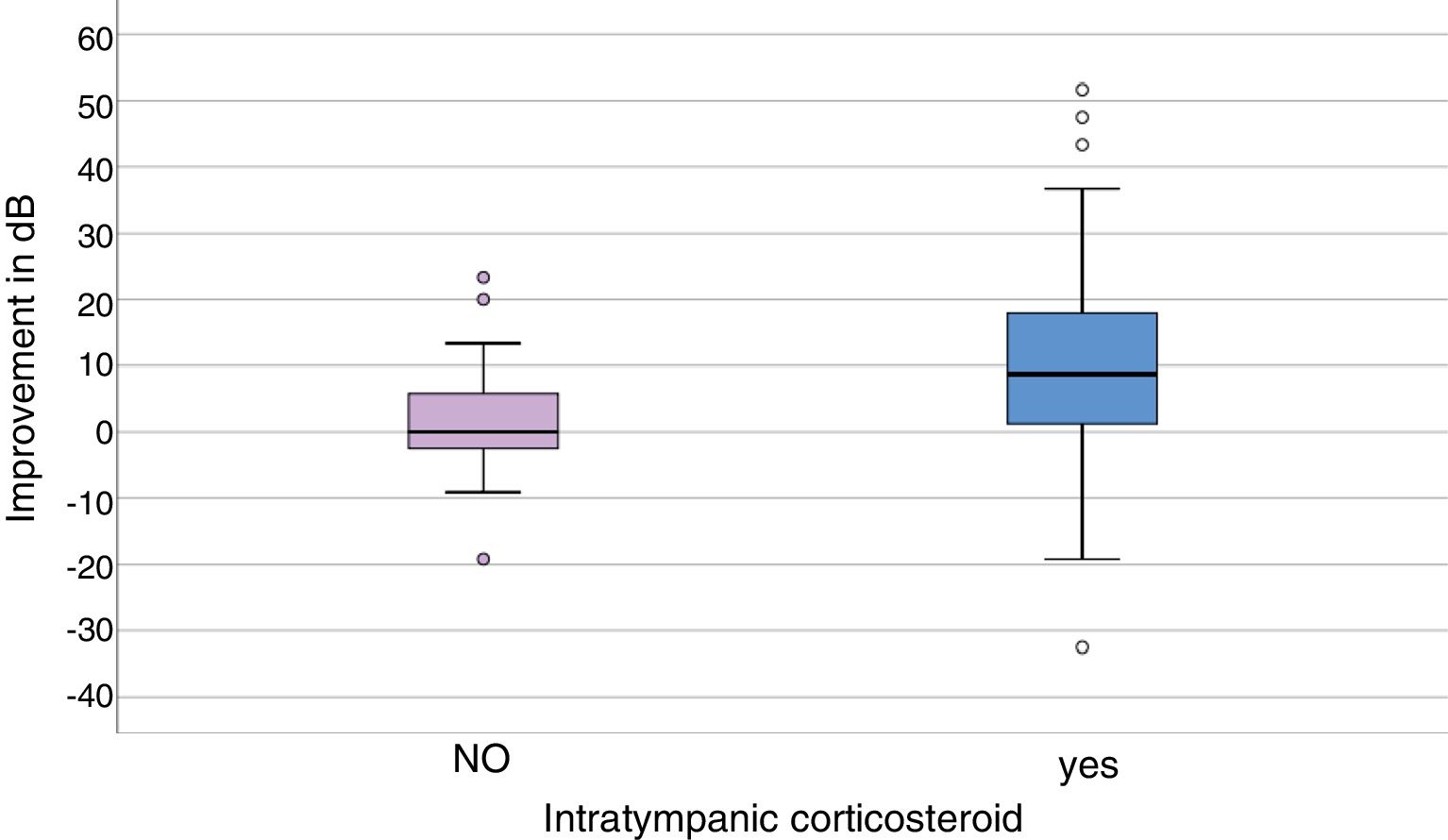
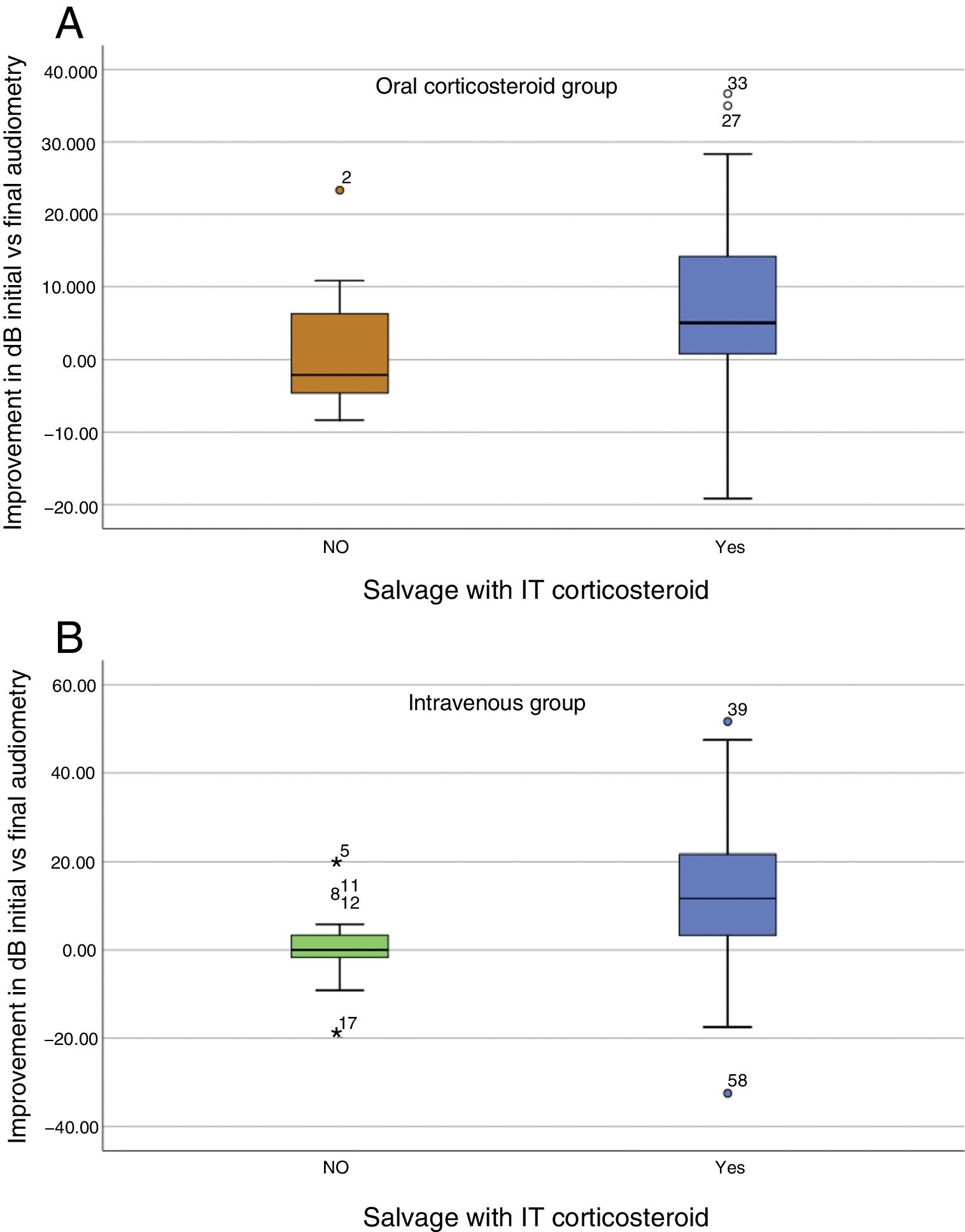
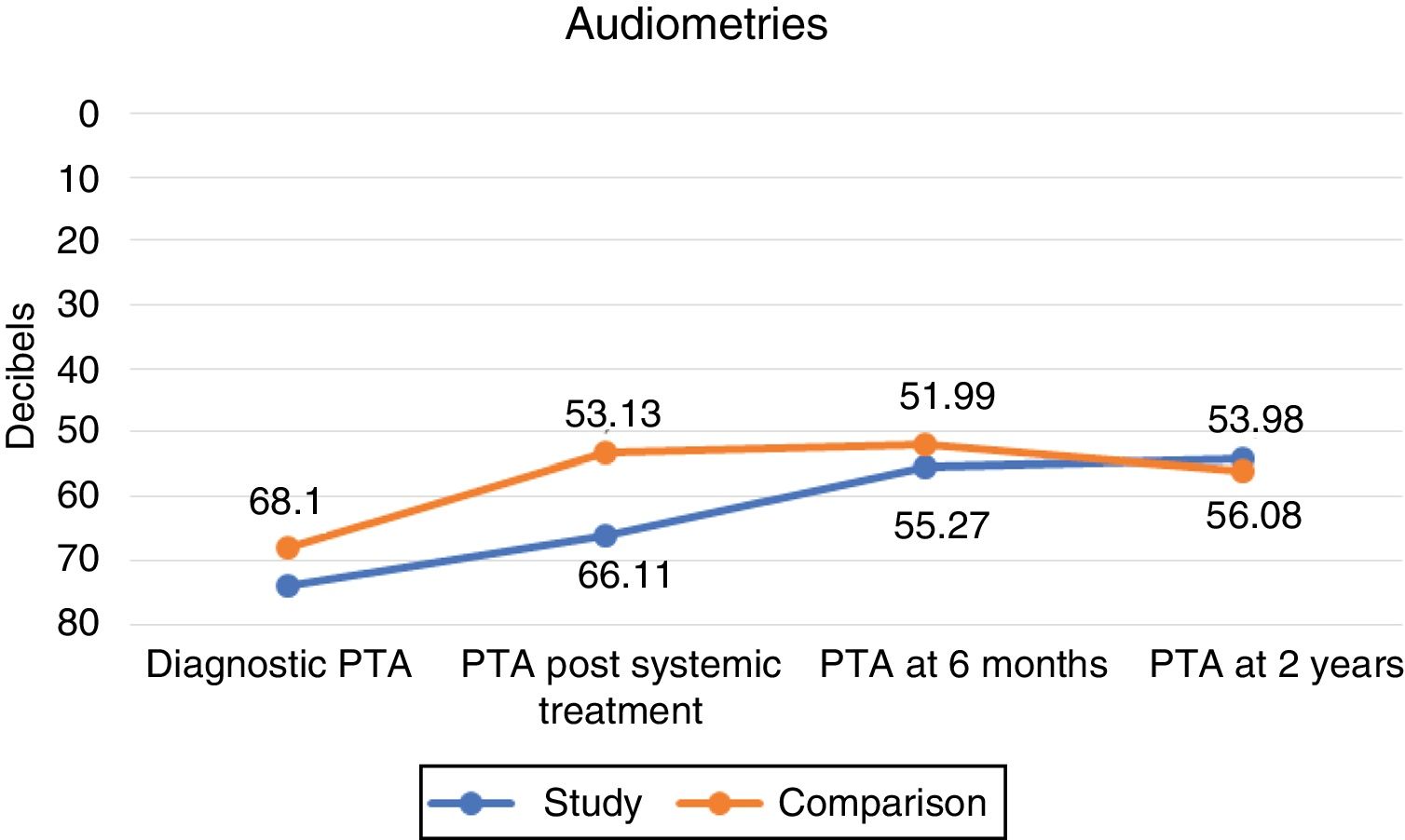
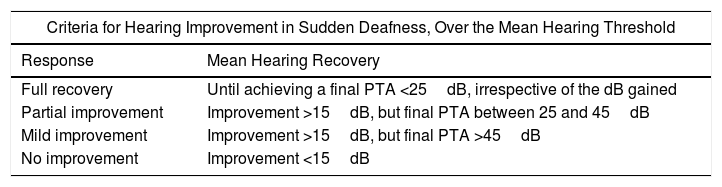
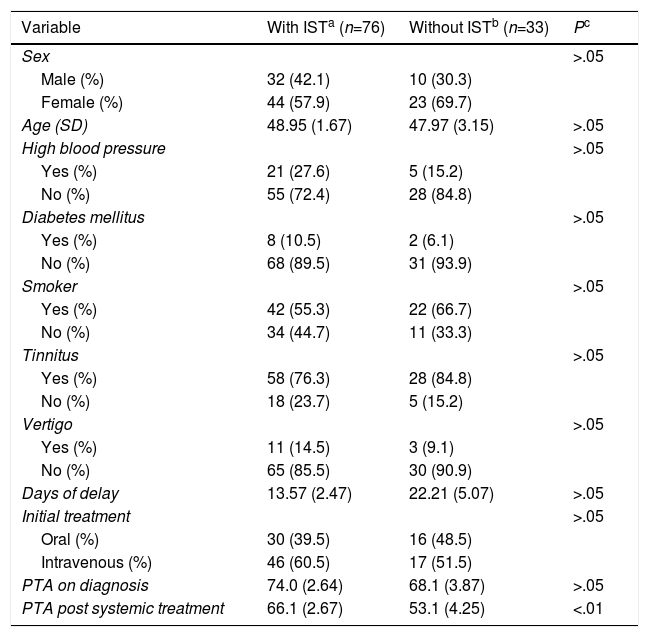
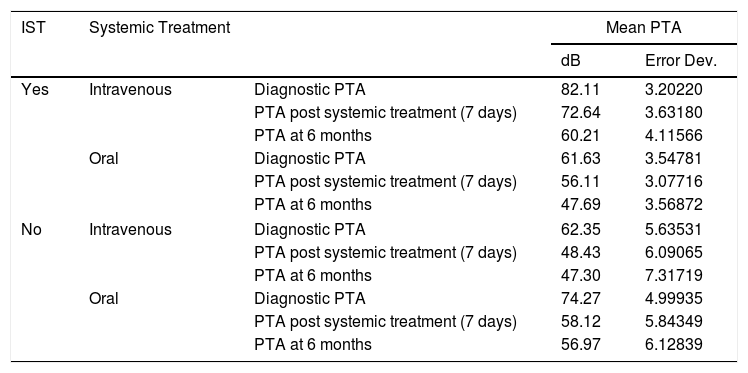
ResultsThe difference between each group at baseline were not statistically significant. After systemic treatment for 7 days, PTA in the control group was 53.13dB and 66.11dB in the treatment group (P<.01). After 6 months, the mean PTA improvement was 10.84dB in the treatment group, and 1.13dB in the control group, a significant difference (P<.0001). Only 10 cases achieved full hearing recovery after intratympanic corticosteroid salvage therapy, none of the patients did so in the control group.
ConclusionIntratympanic corticosteroid rescue for ISSHL achieved hearing improvement for the cases with failure of initial systemic corticosteroid treatment. However, this treatment did not provide complete hearing recovery according to Siegel's criteria in most cases.
La hipoacusia súbita neurosensorial idiopática (SSI) es la pérdida de al menos 30dB de causa desconocida. Dado que la recuperación auditiva en SSI es variable, el rescate con corticoides intratimpánicos (CIT) podría contribuir a la recuperación auditiva. Nuestro objetivo es analizar la respuesta auditiva tras CIT como rescate, en ausencia de recuperación completa tras tratamiento sistémico.
Material y métodoRealizamos un estudio observacional de cohortes históricas de los 125 casos detectados de SSI entre 2006 y 2014. De ellos, 16 obtuvieron a la semana recuperación completa según los criterios de Siegel. Los 109 casos restantes se analizaron en dos grupos: el que recibió CIT (grupo de tratamiento) y otro que no lo recibió (grupo control). Evaluamos la recuperación auditiva a los 6 meses y a 2 años.
ResultadosLa media de audición en la audiometría al diagnóstico no tenía diferencias significativas entre los grupos. Al séptimo día del tratamiento sistémico, el PTA obtenido fue de 53,13dB en el grupo control y de 66,11dB en el grupo de estudio (p<0,01). Tras 6 meses, la ganancia en decibelios obtenida tras el tratamiento con CIT de rescate fue de 10,84dB, y en el grupo control, de 1,13dB (p<0,0001). Tras CIT, solo se consiguió la recuperación completa en 10 pacientes. Ningún paciente del grupo control obtuvo recuperación completa.
ConclusiónEncontramos que el tratamiento de rescate con CIT en la SSI favorece la mejoría auditiva tras la ausencia de recuperación después de un tratamiento sistémico. Sin embargo, en la mayoría de los pacientes no consigue obtener una recuperación completa según criterios de Siegel.