Pediatric epistaxis is very common. A child's illness can lead to depression and anxiety in the parents. The association between pediatric epistaxis and mothers’ anxiety has not been well documented.
ObjectiveThe present study is aimed at measuring depression and anxiety levels in mothers of children with mild, recurrent epistaxis.
MethodsThis prospective, clinical, questionnaire-based study examined 43 mothers of children with recurrent epistaxis and 42 mothers of healthy children. The depression and anxiety levels of the mothers in both the groups were assessed with the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI), the state-trait anxiety inventory–state (STAI-S), and the state-trait anxiety inventory–trait (STAI-T).
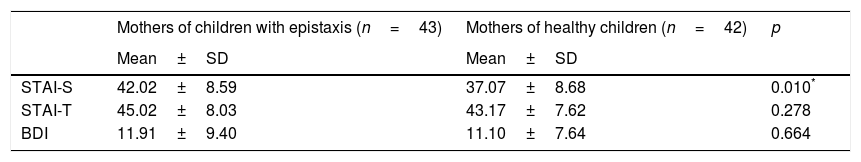
ResultsNo statistically-significant differences were found between the two groups of mothers in terms of educational level, employment, age, or economic status. The mean STAI-S scores were higher in the mothers of children with epistaxis (p=.010). However, no statistically-significant differences were found between the two groups for the BDI and STAI-T scores.
ConclusionsThe results of this comparative study suggest that mild, recurrent epistaxis in children can significantly increase their mothers’ state anxiety levels, but epistaxis has no significant effect on either depression or trait anxiety.
La epistaxis pediátrica es muy común. La enfermedad de un niño puede provocar depresión y ansiedad en los padres. La asociación entre la epistaxis pediátrica y la ansiedad de las madres no ha sido bien documentada.
ObjetivoEl presente estudio tuvo como objetivo medir los niveles de depresión y ansiedad en madres de niños con epistaxis recurrente leve.
MétodosEste estudio prospectivo, clínico y basado en cuestionarios, examinó a 43 madres de niños con epistaxis recurrente y 42 madres de niños sanos. Los niveles de depresión y ansiedad de las madres en ambos grupos se evaluaron con el Inventario de Depresión de Beck (BDI), el estado de inventario de ansiedad con rasgo de estado (STAI-S) y el rasgo de inventario de ansiedad con rasgo de estado (STAI-T).
ResultadosNo se encontraron diferencias estadísticamente significativas entre los 2 grupos de madres en términos de nivel educativo, empleo, edad o estado económico. Las puntuaciones promedio de STAI-S fueron más altas en las madres de niños con epistaxis (p=0,010). Sin embargo, no se encontraron diferencias estadísticamente significativas entre los 2 grupos para las puntuaciones BDI y STAI-T.
ConclusionesLos resultados de este estudio comparativo sugieren que la epistaxis leve y recurrente en los niños puede aumentar significativamente los niveles de ansiedad del estado de sus madres, pero la epistaxis no tiene un efecto significativo sobre la depresión o la ansiedad.