Laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR) is a disease characterized by the presence of symptoms, signs and tissue damage caused by retrograde flow of gastric contents to the upper aerodigestive tract. It represents up to 10% of otolaryngology consultations.
The aim of the study is to describe the findings obtained by applying the salivary pepsin test (PEP-test) in a sample of patients with the clinical suspicion of LPR.
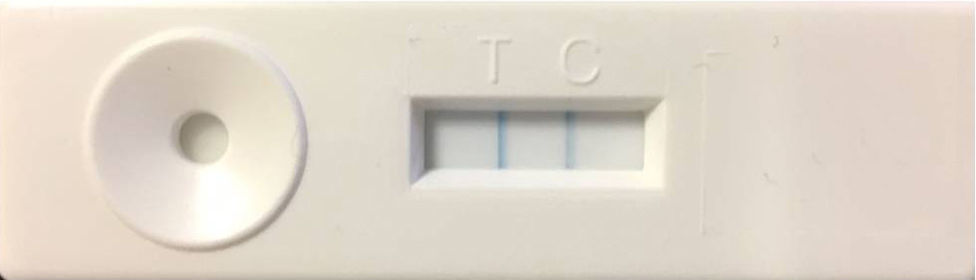
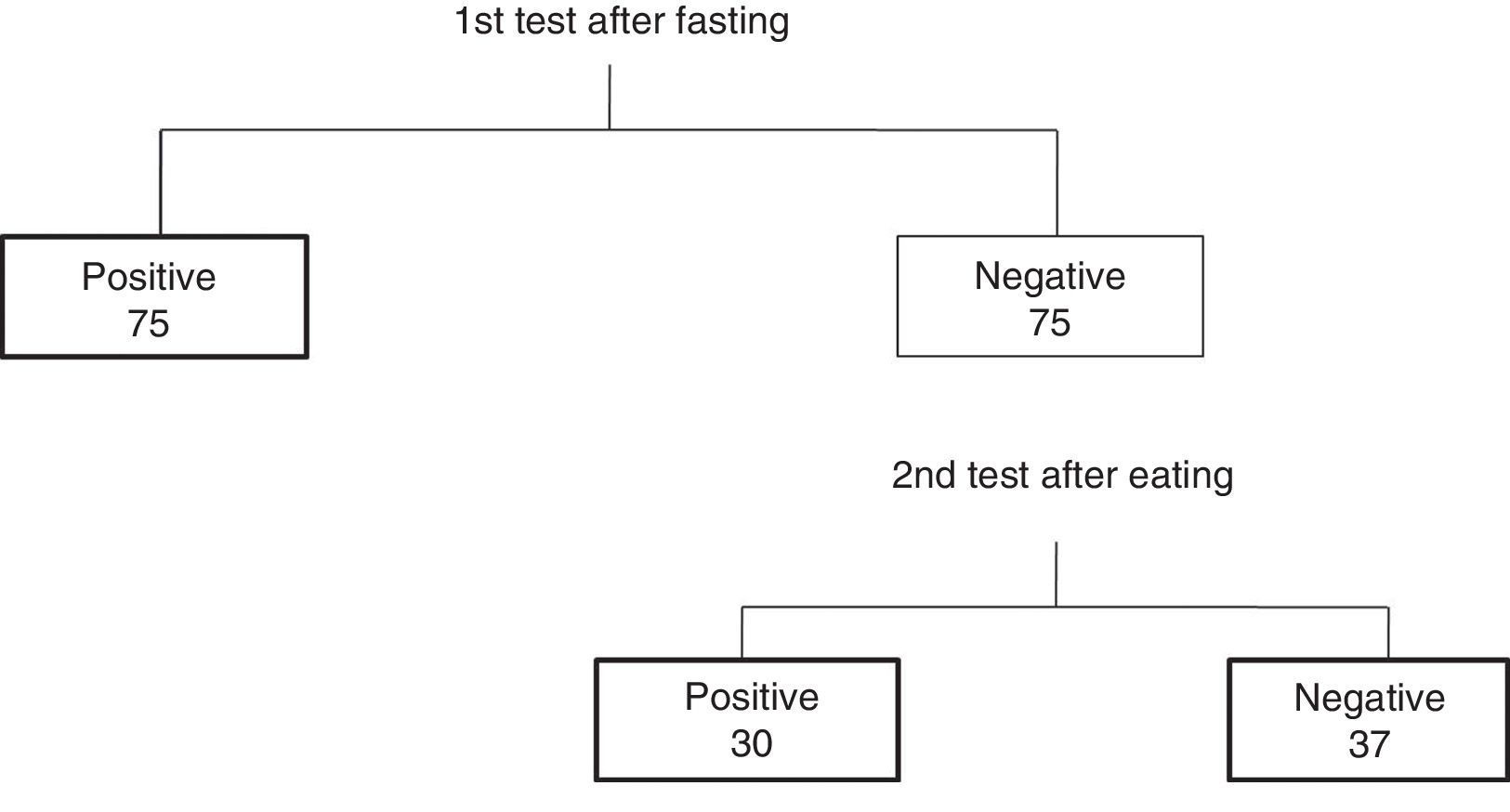
Material and methodsOur descriptive clinical study included 142 subjects with symptoms suggestive of LPR and a score above 13 on the RSI scale. The subjects underwent laryngeal endoscopy to rule out other pathologies that could justify the symptoms and the salivary pepsin test (PEP-test). The latter was carried out on fasting subjects and a second test one hour after eating, only on those with negative results.
ResultsThe results obtained in the tests performed on the 142 patients included in the study were: 105 (73.94%) presented positive results in some of the salivary pepsin tests and the results of both tests were negative in 37 subjects (26.06%).
ConclusionThe salivary pepsin test is a simple, low-cost, non-invasive and easily repeatable tool which could minimize empirical treatments and invasive tests for LPR diagnosis, although further research is needed for its validation.
El reflujo faringo-laríngeo (RFL) es una enfermedad caracterizada por la presencia de síntomas, signos y alteraciones tisulares, consecuencia del movimiento retrógrado del contenido gastrointestinal hacia el tracto aerodigestivo superior. Representa hasta el 10% de las consultas en otorrinolaringología.
El objetivo de nuestro trabajo es describir los hallazgos obtenidos al aplicar el test de determinación de pepsina en saliva (PEP-test) en una muestra de pacientes con signos clínicos sugestivos de RFL.
Material y métodosEn nuestro estudio clínico descriptivo se han incluido 142 sujetos con síntomas sugestivos de RFL que obtuvieron puntuaciones por encima de 13 en la escala RSI. A todos ellos se les realizó una endoscopia laríngea para descartar otras enfermedades que pudieran justificar los síntomas y el PEP-test. Ésta se realizó en ayunas a todos los sujetos, y en aquellos con resultados negativos se realizó una segunda determinación una hora después de comer.
ResultadosLos resultados obtenidos en las pruebas realizadas en los 142 sujetos incluidos fueron los siguientes: 105 pacientes (73,94%) presentaron resultados positivos en alguna de las determinaciones de pepsina en saliva y en 37 sujetos (26,06%) los resultados de ambas determinaciones fueron negativos.
ConclusiónEl PEP-test es un método sencillo, económico, no invasivo y fácilmente repetible que podría minimizar el uso de tratamientos empíricos y pruebas invasivas para el diagnóstico del RFL, si bien son necesarias más investigaciones para la validación del mismo.