To perform the cross-cultural adaptation into Spanish and the psychometric validation of the Nasal Polyposis Quality of Life Questionnaire (NPQ) for use in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP).
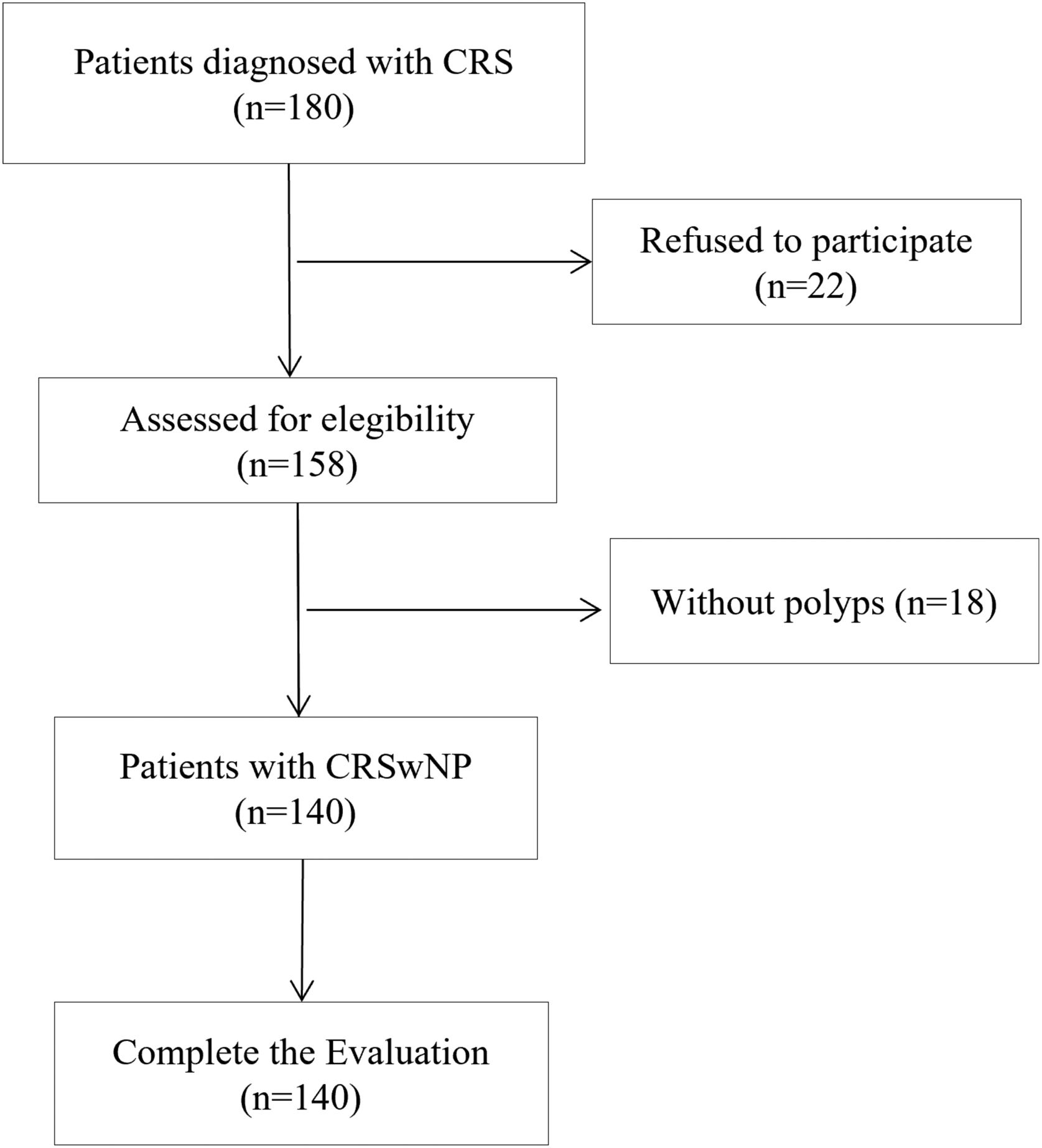
MethodsA total of 140 adult patients diagnosed with CRSwNP were included. The original NPQ was adapted from Italian into Spanish following established international guidelines. Construct validity was assessed through exploratory factor analysis (EFA) with principal components. Internal consistency was analyzed using Cronbach’s alpha coefficient. Test–retest reliability was determined by the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC). Concurrent validity was examined using Pearson correlations with the SNOT-22 and NOSE-E questionnaires. Discriminant validity was analyzed using ROC curves.
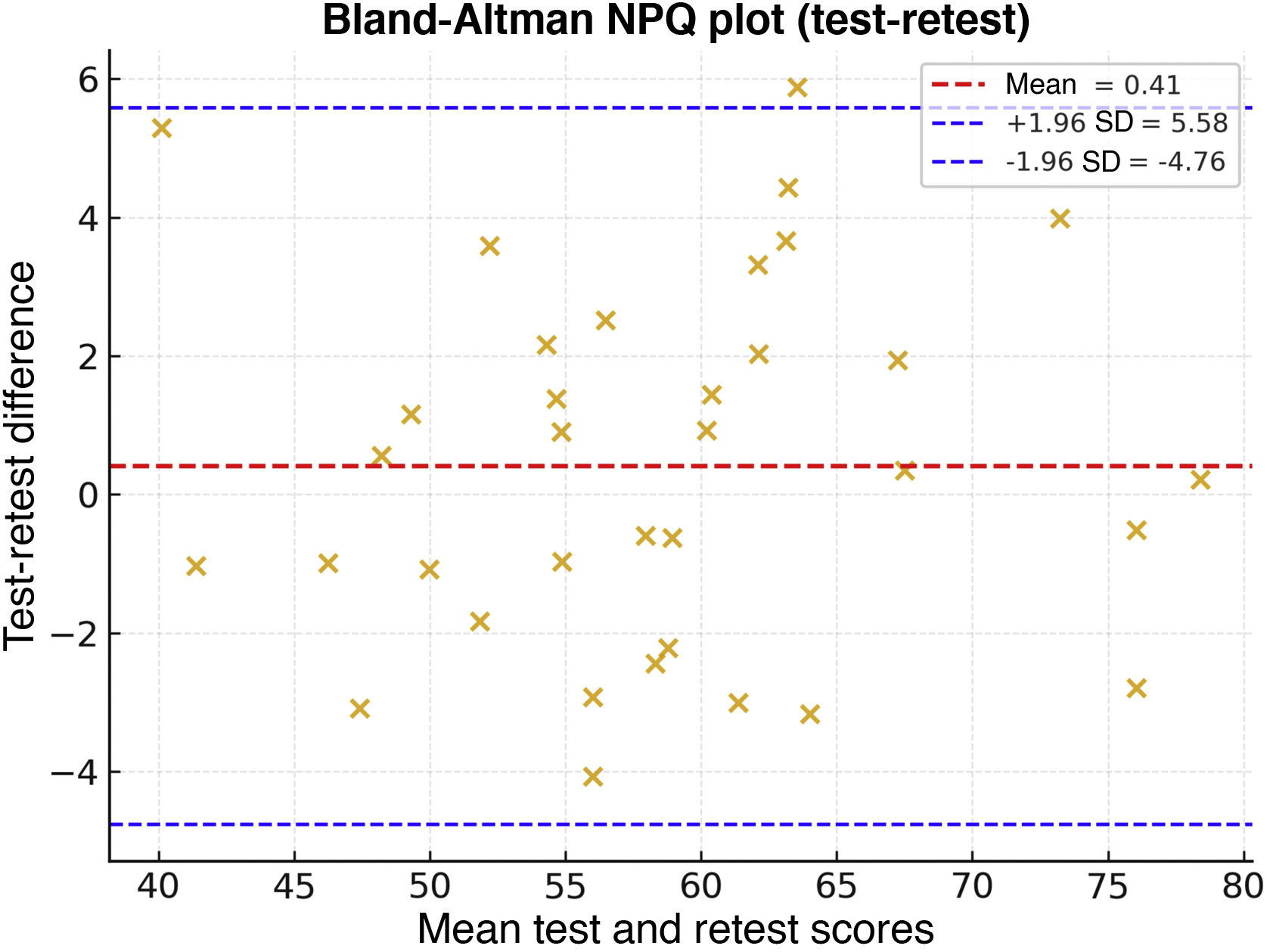
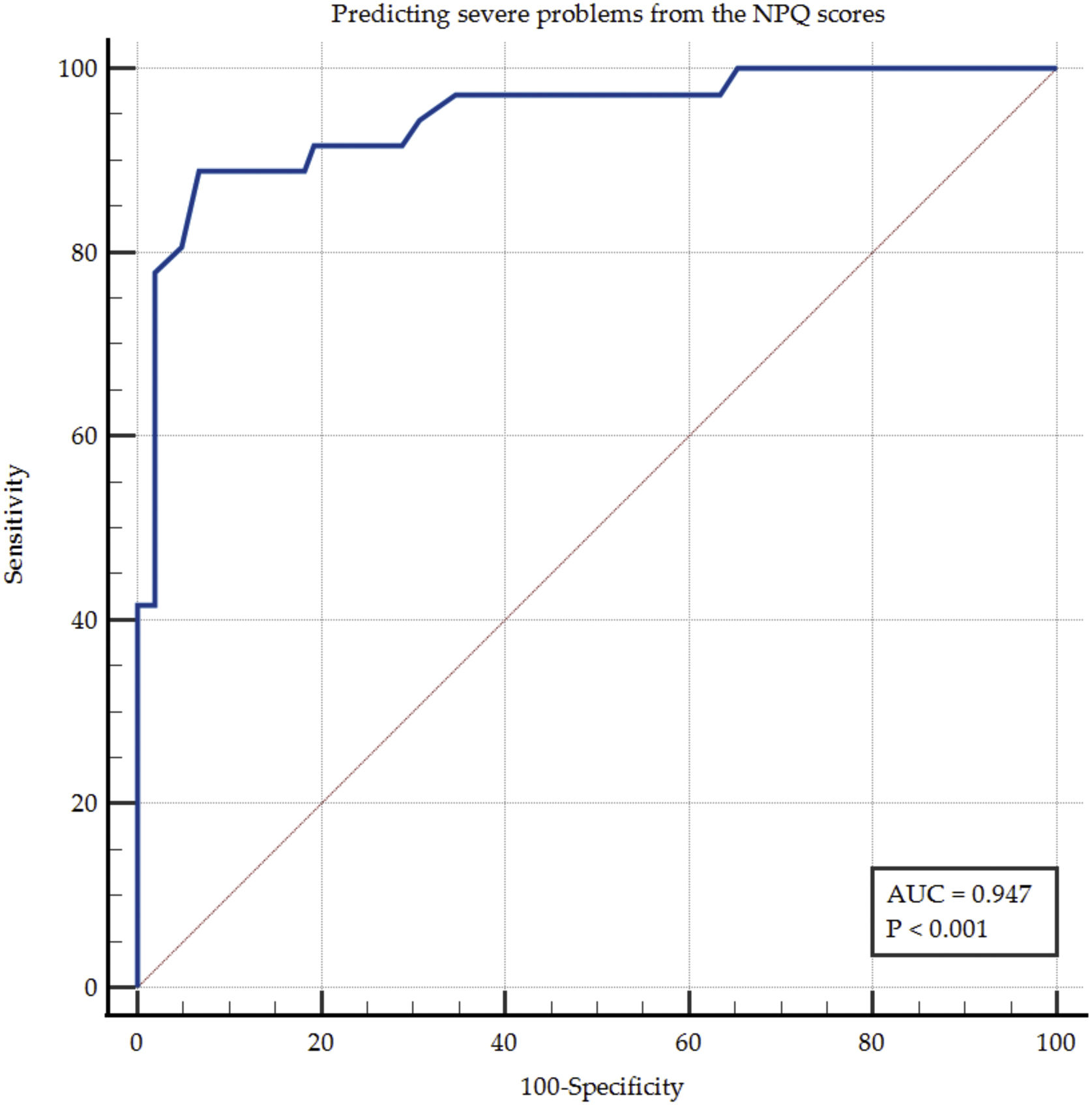
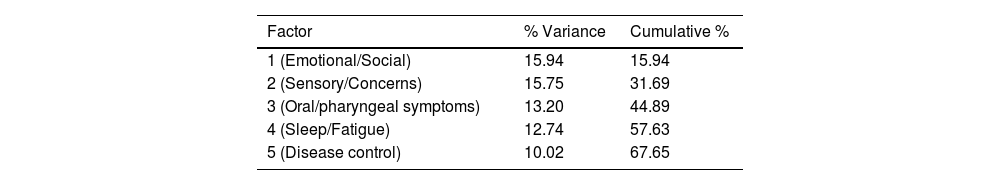
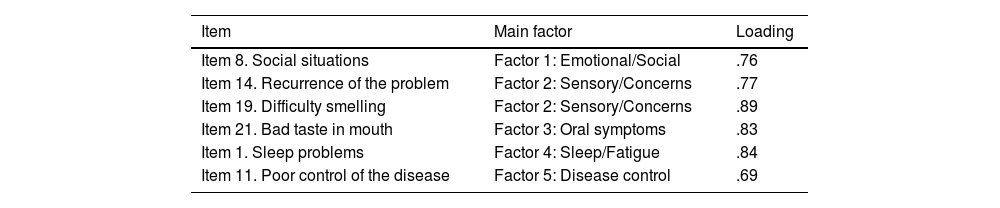
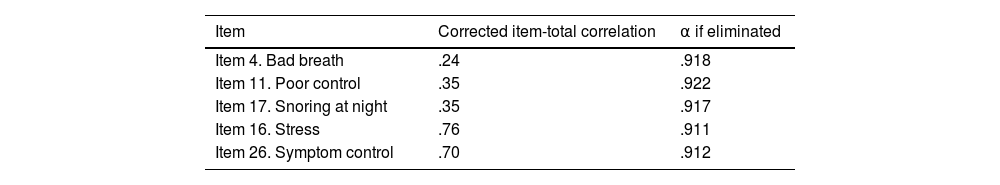
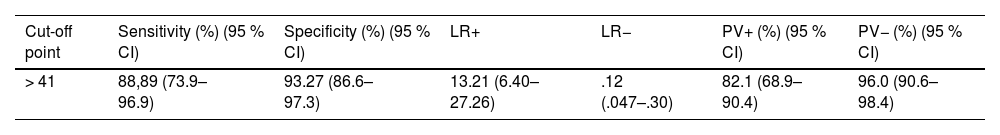
ResultsEFA revealed a five-factor structure explaining 67% of the total variance. The Spanish NPQ showed excellent internal consistency (Cronbach’s α = 0.917) and high test–retest reliability (ICC = 0.991; 95% CI: 0.983–0.996). The standard error of measurement (SEM) was 2 points, and the minimal detectable change (MDC95) was 5 points. Strong correlations were observed with the NOSE-E (r = 0.802) and SNOT-22 (r = 0.870). The NPQ total score demonstrated high discriminative ability for severe symptoms (AUC = 0.947), with a cutoff point >41 providing 88.9% sensitivity and 93.3% specificity.
ConclusionsThe Spanish version of the NPQ is a valid, reliable, and clinically useful instrument for assessing symptom burden in patients with CRSwNP. Its multidimensional structure allows capturing the specific impact of this phenotype and supports its use in both clinical practice and research.
Realizar la adaptación transcultural al español y la validación psicométrica del cuestionario Nasal Polyposis Quality of Life Questionnaire (NPQ) para su uso en pacientes con rinosinusitis crónica con pólipos nasales (RSCcPN).
MetodologíaSe incluyeron 140 pacientes adultos diagnosticados de RSCcPN. El cuestionario original NPQ fue adaptado del italiano al español siguiendo las directrices internacionales establecidas. La validez de constructo se evaluó mediante análisis factorial exploratorio (AFE) con componentes principales. La consistencia interna se analizó con el coeficiente alfa de Cronbach. La fiabilidad test–retest se determinó mediante el coeficiente de correlación intraclase (CCI). La validez concurrente se examinó mediante correlaciones de Pearson con los cuestionarios SNOT-22 y NOSE-E. La validez discriminativa se analizó mediante curvas ROC.
ResultadosEl AFE reveló una estructura de cinco factores que explicaban el 67 % de la varianza total. El NPQ en español mostró una excelente consistencia interna (α de Cronbach = 0,917) y una alta fiabilidad test–retest (CCI = 0,991; IC 95 %: 0,983–0,996). El error estándar de medida (EEM) fue de 2 puntos, y el cambio mínimo detectable (CMD95) de 5 puntos. Se observaron correlaciones fuertes con el NOSE-E (r = 0,802) y el SNOT-22 (r = 0,870). La puntuación total del NPQ presentó una alta capacidad discriminativa para síntomas graves (AUC = 0,947), con un punto de corte >41 que ofreció una sensibilidad del 88,9 % y una especificidad del 93,3 %.
ConclusionesLa versión española del NPQ es un instrumento válido, fiable y clínicamente útil para evaluar la carga sintomática en pacientes con RSCcPN. Su estructura multidimensional permite captar el impacto específico de este fenotipo y respalda su uso en la práctica clínica y en investigación.