There is a great variability in diagnosis of obstructive Eustachian tube dysfunction and its treatment by balloon Eustachian tuboplasty (BET). The aim of this paper was to present a consensus on indications, contraindications, methodology, complications and results after BET.
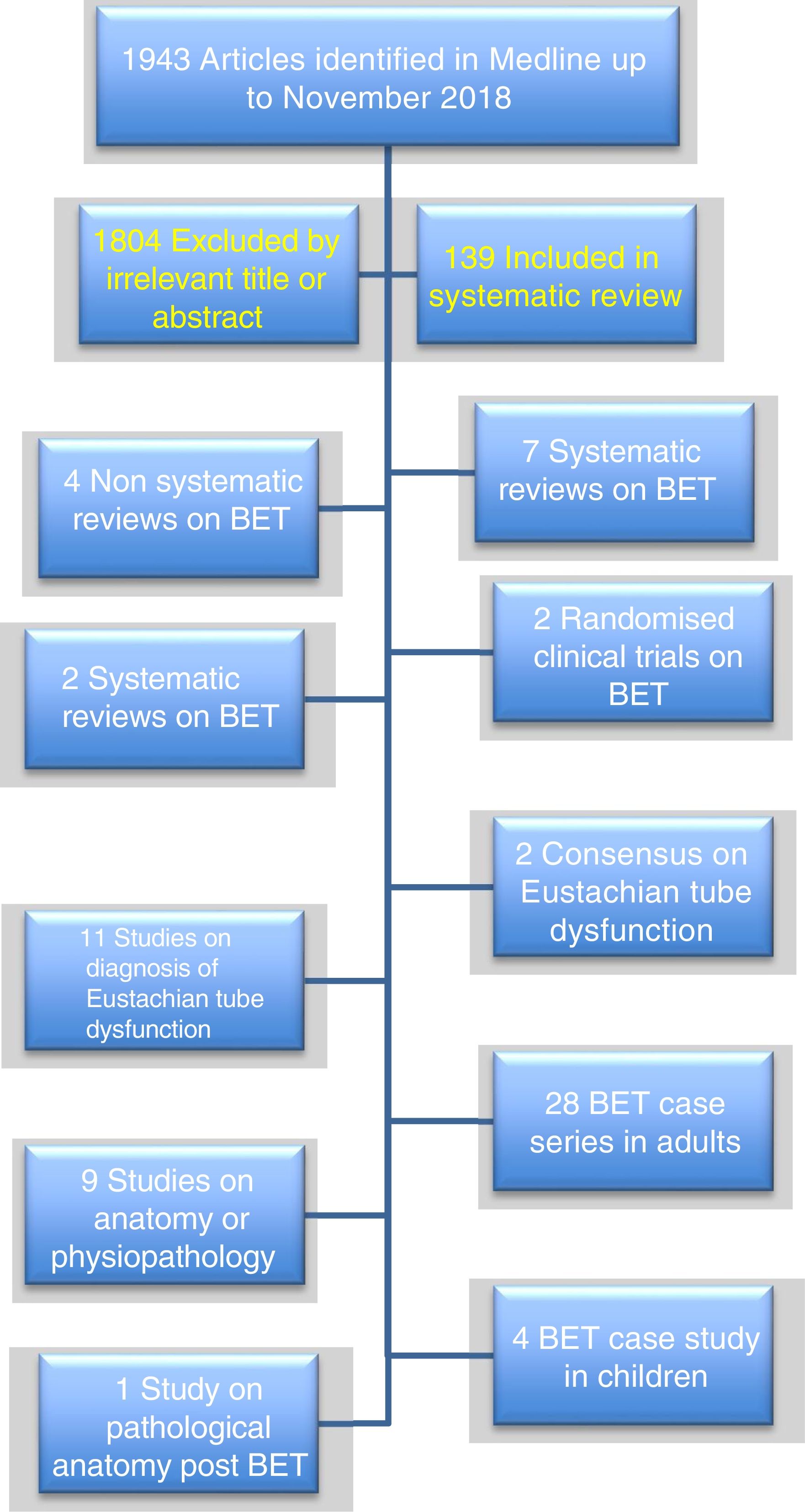
Material & MethodsWe obtained a consensus on BET, after a systematic review of the literature on BET from 1966 to November 2018, using MESH terms “Eustachian tube and (dilation or dysfunction)”, including a total of 1.943 papers in Spanish, English, German and French. We selected 139 papers with a relevant abstract, including two international consensuses, seven systematic revisions, and two randomised control trials on BET.
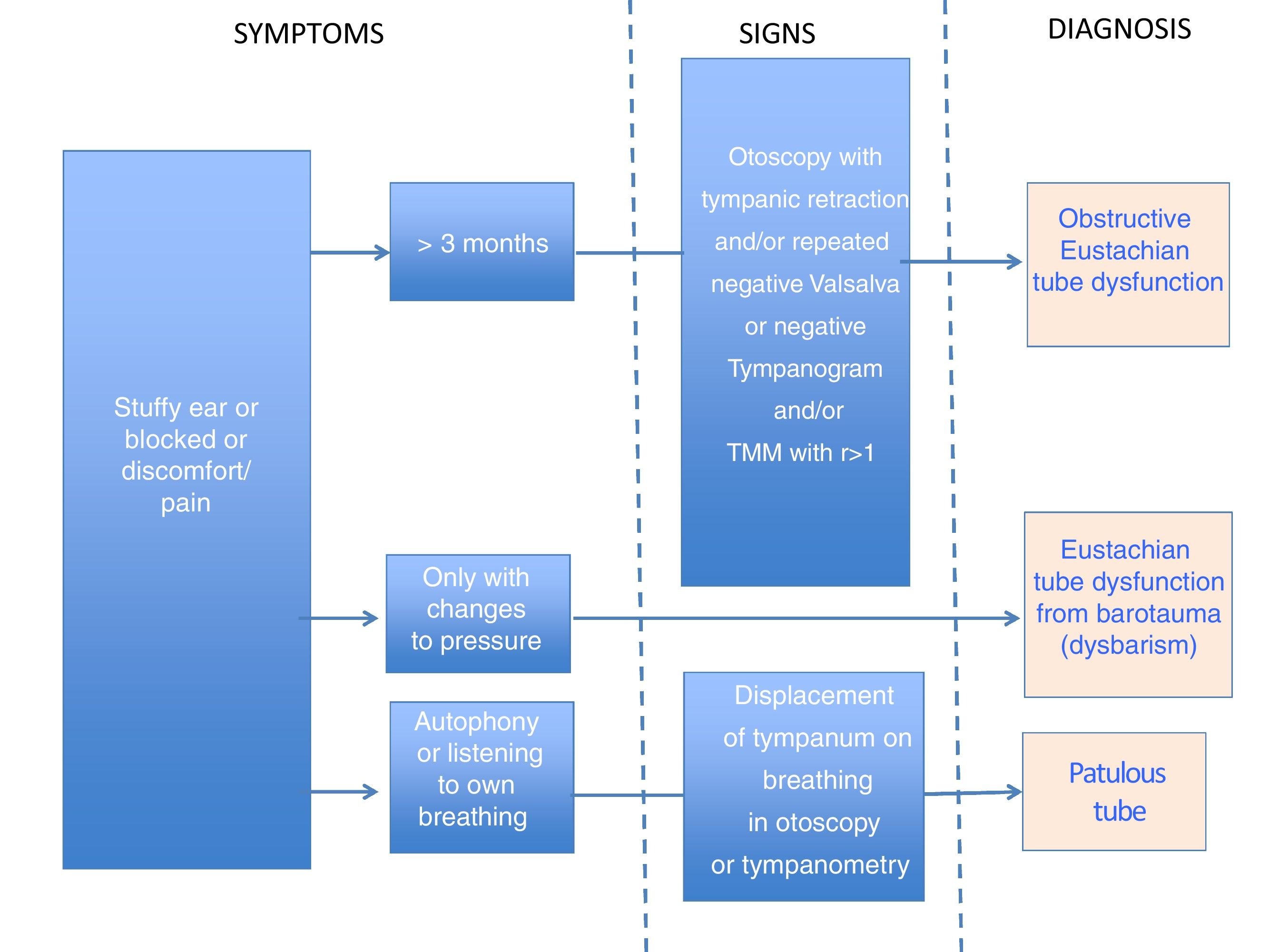
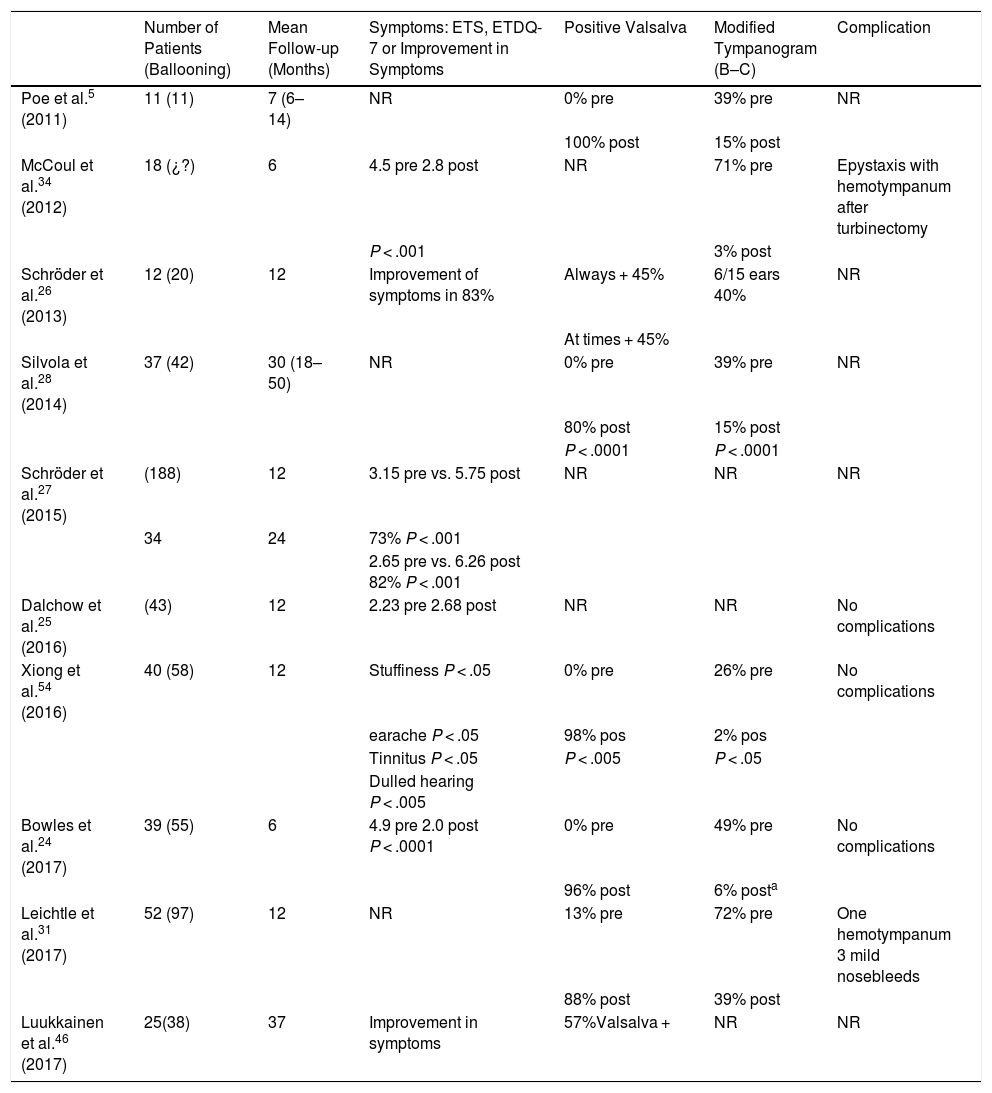
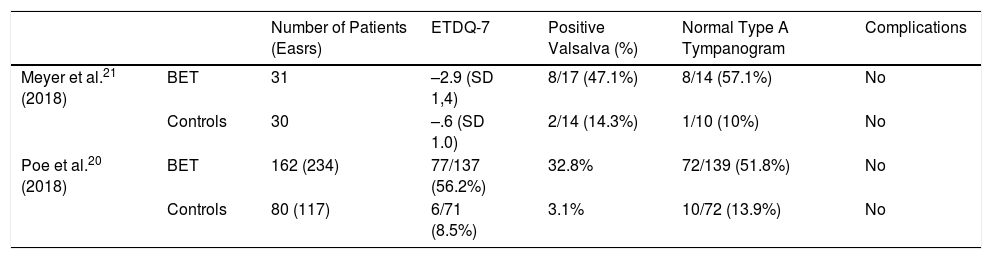
ResultsThe indications for BT are barotrauma, serous otitis media, adhesive otitis, atelectatic middle ear and failure after tympanoplasty, once obstructive Eustachian tube dysfunction is confirmed. BET is more effective in barotrauma and serous otitis media. There are high-evidence reports on BET showing good results that persist long-term, as compared to conservative medical treatment.
ConclusionsBET is a surgical, minimally invasive treatment that has shown its effectiveness and safety in obstructive Eustachian tube dysfunction in adults and children. It is most effective in barotrauma and serous otitis media.
Existe una gran variabilidad en el diagnóstico de la disfunción tubárica obstructiva y su tratamiento mediante la dilatación tubárica con balón (DTB). El objetivo de este trabajo es presentar unas recomendaciones de consenso sobre las indicaciones, contraindicaciones, metodología, complicaciones y resultados de la DTB.
Materiales y métodosPresentamos un consenso sobre la DTB, mediante revisión sistemática de la literatura desde 1966 hasta noviembre de 2018, términos MESH “Eustachian tube and (dilation or dysfunction)”, recogiendo un total de 1.943 artículos en español, inglés, alemán y francés. Del total de artículos revisados, se seleccionaron 139 cuyo abstract era relevante, incluyendo dos consensos internaciones sobre diagnóstico, siete revisiones sistemáticas y dos ensayos clínicos aleatorizados sobre la DTB.
ResultadosLas indicaciones de la DTB son el barotrauma, la otitis media secretora, la otitis media adhesiva, la atelectasia y el fracaso de una timpanoplastia, siempre que se haya podido demostrar una disfunción tubárica obstructiva crónica. La efectividad de la DTB es mayor en el barotrauma y la otitis media secretora. Hay estudios publicados de elevada evidencia sobre la DTB, cuyos buenos resultados se mantienen a largo plazo, frente a tratamiento médico conservador.
ConclusionesLa DTB es un procedimiento quirúrgico mínimamente invasivo que ha demostrado su efectividad y seguridad en el tratamiento de la disfunción tubárica crónica en adultos y en niños. Las indicaciones en las que es más efectiva son el barotrauma y la otitis media secretora.