Auditory hallucinations (AH) are one of the most prevalent symptoms of schizophrenia. They might cause several brain alterations, especially changes in the volumes of hippocampus and amygdala, regions related to the relay and processing of auditory cues and emotional memories.
Material and methodsWe have recruited 41 patients with schizophrenia and persistent AH, 35 patients without AH, and 55 healthy controls. Using their MRIs, we have performed semiautomatic segmentations of the hippocampus and amygdala using Freesurfer. We have also performed bilateral correlations between the total PSYRATS score and the volumes of affected subregions and nuclei.
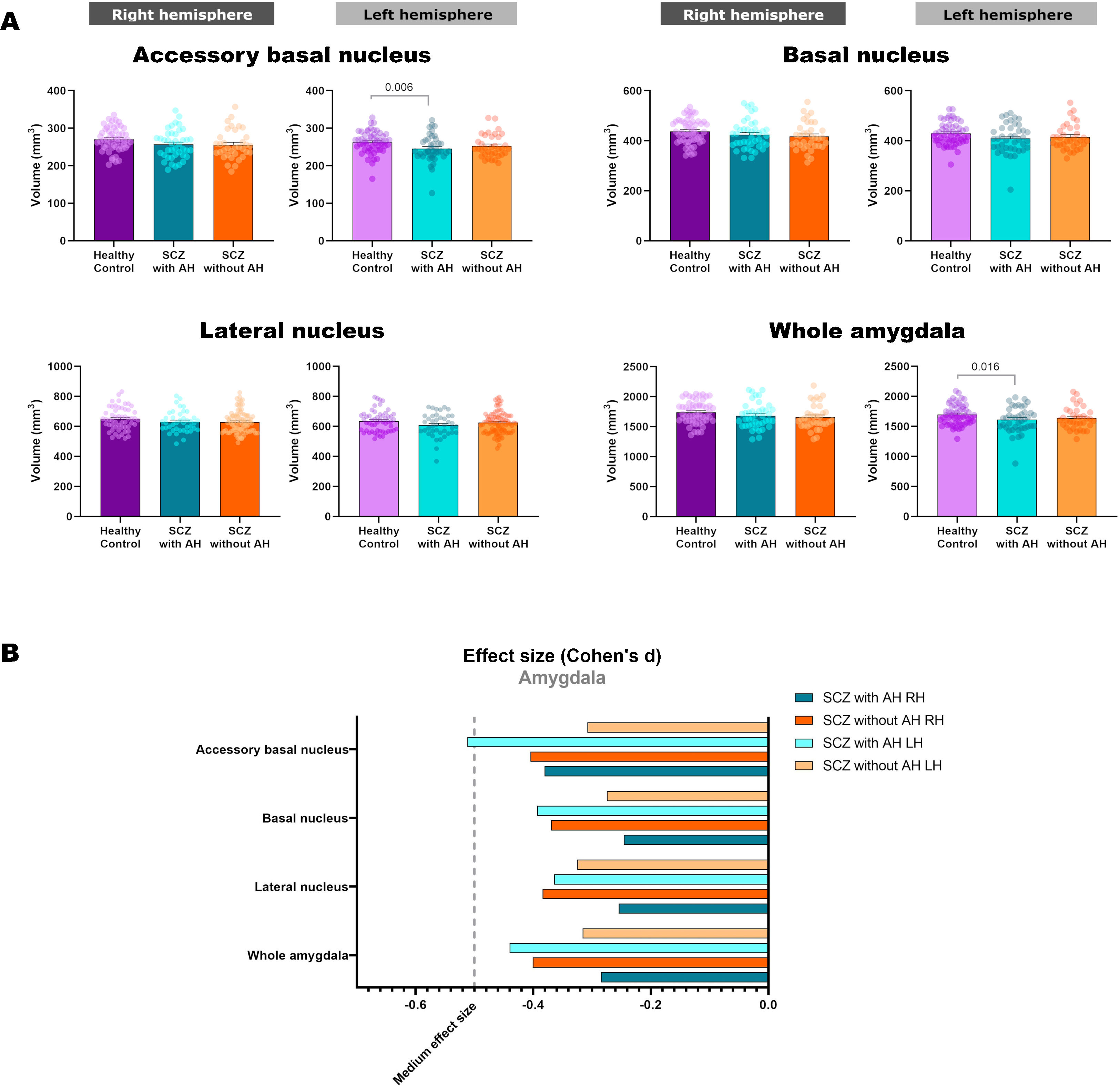
ResultsIn the hippocampus, we found bilateral increases in the volume of its hippocampal fissure and decreases in the right fimbria in patients with and without AH. The volume of the right hippocampal tail and left head of the granule cell layer from the dentate gyrus were decreased in patients with AH. In the amygdala, we found its left total volume was shrunk, and there was a decrease of its left accessory basal nucleus in patients with AH.
ConclusionsWe have detected volume alterations of different limbic structures likely due to the presence of AH. The volumes of the right hippocampal tail and left head of the granule cell layer from the dentate gyrus, and total volume of the amygdala and its accessory basal nucleus, were only affected in patients with AH. Bilateral volume alterations in the hippocampal fissure and right fimbria seem inherent of schizophrenia and due to traits not contemplated in our research.
Article
(Sociedad Española de Psiquiatría y Salud Mental)
Diríjase al área de socios de la web de la SEPSM, (https://sepsm.org/revista/) y autentifíquese.