Erectile dysfunction (ED) is the inability to achieve or maintain erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual performance. Although the definition is well known, there are controversial issues about the effects of hormones and inflammation on ED.
ObjectivesWe aimed to compare the clinical value of the hormonal and inflammation parameters in sexual dysfunction.
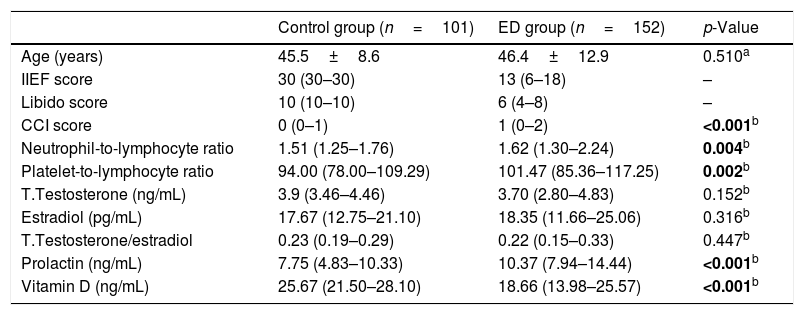
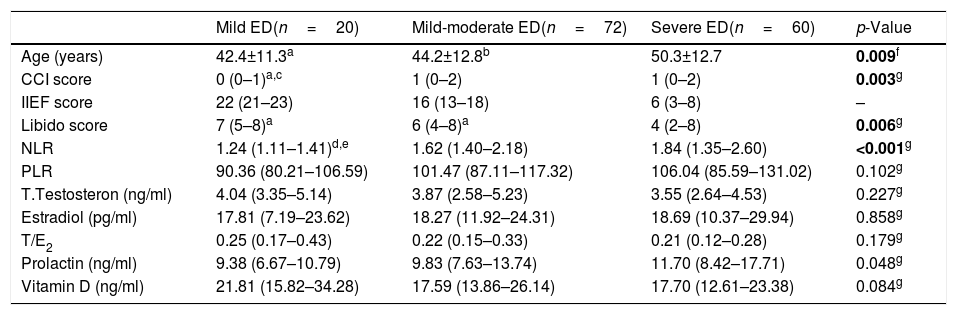
Materials and methodsA total of 152 patients diagnosed with erectile dysfunction between September 2018 and March 2019 and 101 healthy males were included in this prospective study as case group and control group, respectively. The 152 patients were divided into three groups based on their total International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF) scores: (I) severe ED, (II) mild-moderate ED and (III) mild ED. All groups were compared in terms of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) and total testosterone (TT), estradiol, prolactin, testosterone-to-estradiol ratio and 25 (OH) vitamin D.
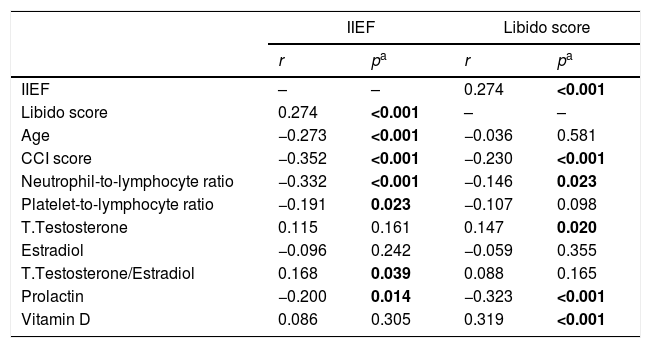
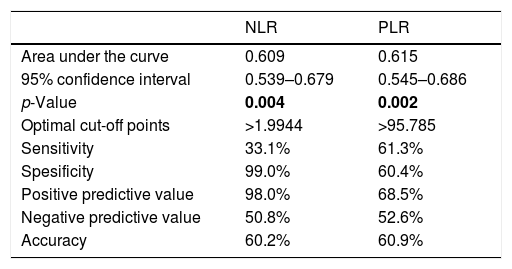
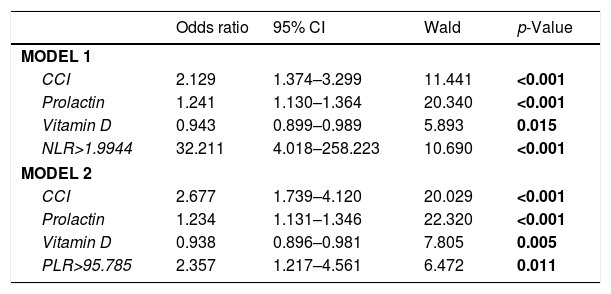
ResultsPatient and control groups differed significantly in term of NLR, PLR, prolactin and vitamin D (p<0.001, p=0.004, p=0.002, p<0.001, p<0.001, respectively). NLR was more significant in determining the severity of ED (p<0.001). It was observed that libido score (the total score of IIEF items #11 and #12) was negatively associated with prolactin and NLR (p<0.001, p=0.023, respectively), was positively associated with vitamin D and TT (p<0.001, p=0.02, respectively), and was lower in severe ED patients.
ConclusionsAlthough more clinical studies are needed, we think that our findings may be useful on these controversial issues of ED.
La disfunción eréctil (DE) es la incapacidad de lograr o mantener una erección suficiente para mantener relaciones sexuales satisfactorias. Aunque su definición es bien conocida, existen cuestiones controvertidas acerca de los efectos de las hormonas y la inflamación en la DE.
ObjetivosNuestro objetivo fue comparar el valor clínico de los parámetros hormonales e inflamatorios en la disfunción sexual.
Materiales y métodosIncluimos en este estudio prospectivo a un total de 152 pacientes diagnosticados de DE entre septiembre de 2018 y marzo de 2019, y 101 varones sanos como grupo de estudio y grupo control, respectivamente. Dividimos a los pacientes en 3 grupos, basándonos en las puntuaciones totales del International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF): I) DE grave, II) DE de leve a moderada y III) DE leve. Comparamos los grupos en términos de índice neutrófilo-linfocito (NLR), índice plaqueta-linfocito (PLR) y testosterona total (TT), estradiol, prolactina, índice testosterona-estradiol y 25 (OH) vitamina D.
ResultadosLos grupos de estudio y control difirieron significativamente en términos de NLR, PLR, prolactina y vitamina D (p<0,001, p=0,004, p=0,002, p<0,001 y p<0,001, respectivamente). El índice NLR fue más significativo para determinar la gravedad de la DE (p<0,001). Se observó que la puntuación de la líbido (puntuación total de los ítems 11 y 12 del IIEF) guardó una asociación negativa con prolactina y NLR (p<0,001 y p=0,023, respectivamente), una relación positiva con vitamina D y TT (p<0,001 y p=0,02, respectivamente), y fue inferior en los pacientes con DE grave.
ConclusionesAunque son necesarios más estudios clínicos, creemos que nuestros hallazgos podrían resultar útiles para estas cuestiones controvertidas de la DE.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora