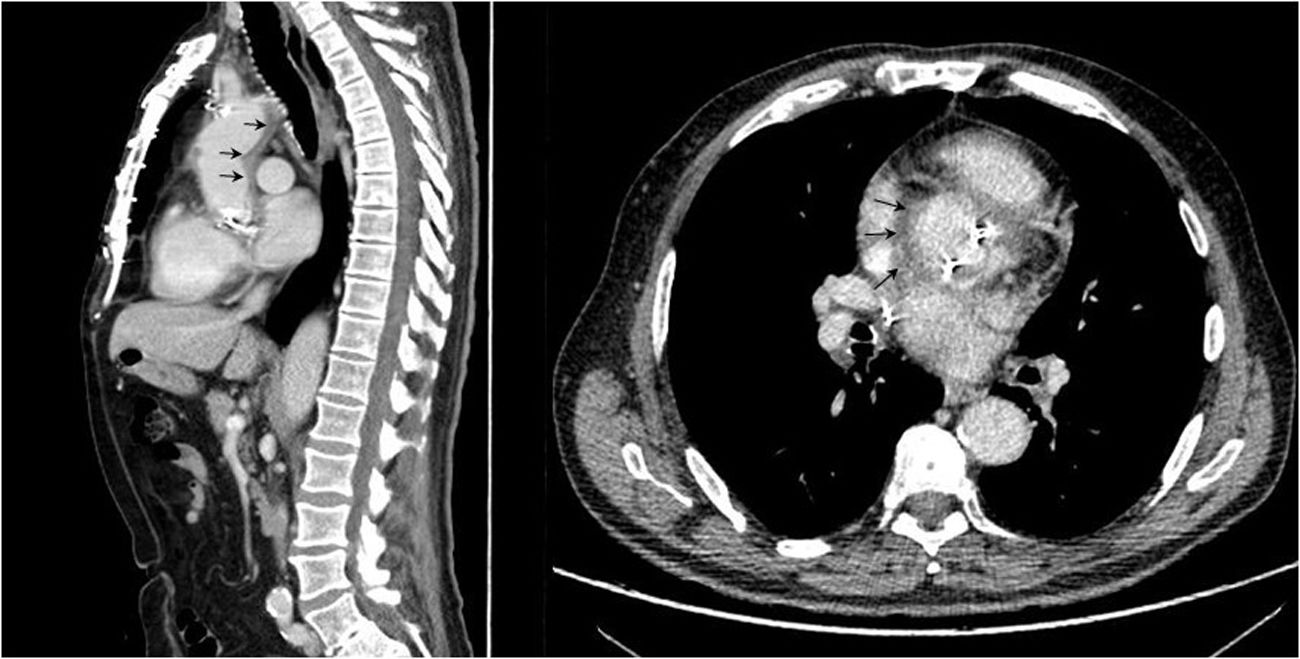
We report a case of Pseudomonas monteilii and Acinetobacter nosocomialis endocarditis with a fatal outcome in a patient with a recent history of prosthetic aortic valve replacement. Transesophageal echocardiography and computed tomography confirmed the presence of vegetation on the prosthetic valve and aortic pseudoaneurism with an aortic root abscess. Valve cultures yielded P. monteilii and A. nosocomialis. The patient underwent surgery and received antibiotics, but his condition deteriorated and he died 44 days after surgery. To our knowledge, this is the first case of P. monteilii and A. nosocomialis endocarditis reported in the literature. These organisms have been described as environmental contaminants; however, they must be considered potential pathogens, particularly in patients with prosthetic valves.
Presentamos el caso de una endocarditis por Pseudomonas monteilii y Acinetobacter nosocomialis con un fatal desenlace. El paciente tenía una historia reciente de reemplazo valvular aórtico. La ecografía transesofágica y la tomografía computarizada confirmaron la presencia de vegetación en la válvula protésica y un seudoaneurisma aórtico con un absceso en laraíz aórtica. El cultivo de la válvula demostró P. monteilii y A. nosocomialis. El paciente fue tratado con cirugía y antibióticos, pero sufrió un deterioro y murió 44 días tras la cirugía. En nuestroconocimiento este es el primer caso de endocarditis producida por P. monteilii y A. nosocomialis publicado en la literatura. Estas bacterias han sido descritas como contaminantes ambientales;sin embargo, deben ser consideradas como potenciales patógenos, en especial en pacientes conválvulas protésicas.