The surgical correction of the pectus excavatum (PE) is justified by the progressive cardiopulmonary involvement. There are few studies that analyze the hemodynamic changes during the intraoperative period.
ObjectivesTo describe the stroke volume index (SVI) changes during the intraoperative with the Nuss technique, through the monitoring of the invasive blood pressure curve (IAP).
Material and methodsA prospective observational study of pediatric patients undergoing Nuss surgery by right video-assisted thoracoscopy (VATS). By analyzing the IAP curve using the FloTrac monitor (Edwars®), the following dynamic parameters were evaluated: stroke volume index (SVI), cardiac index (CI), stroke volume variation (SVV). The dates were collected on 3 occasions: baseline, before bar placement (after preload optimization in search of the target IVS) and after bar placement.
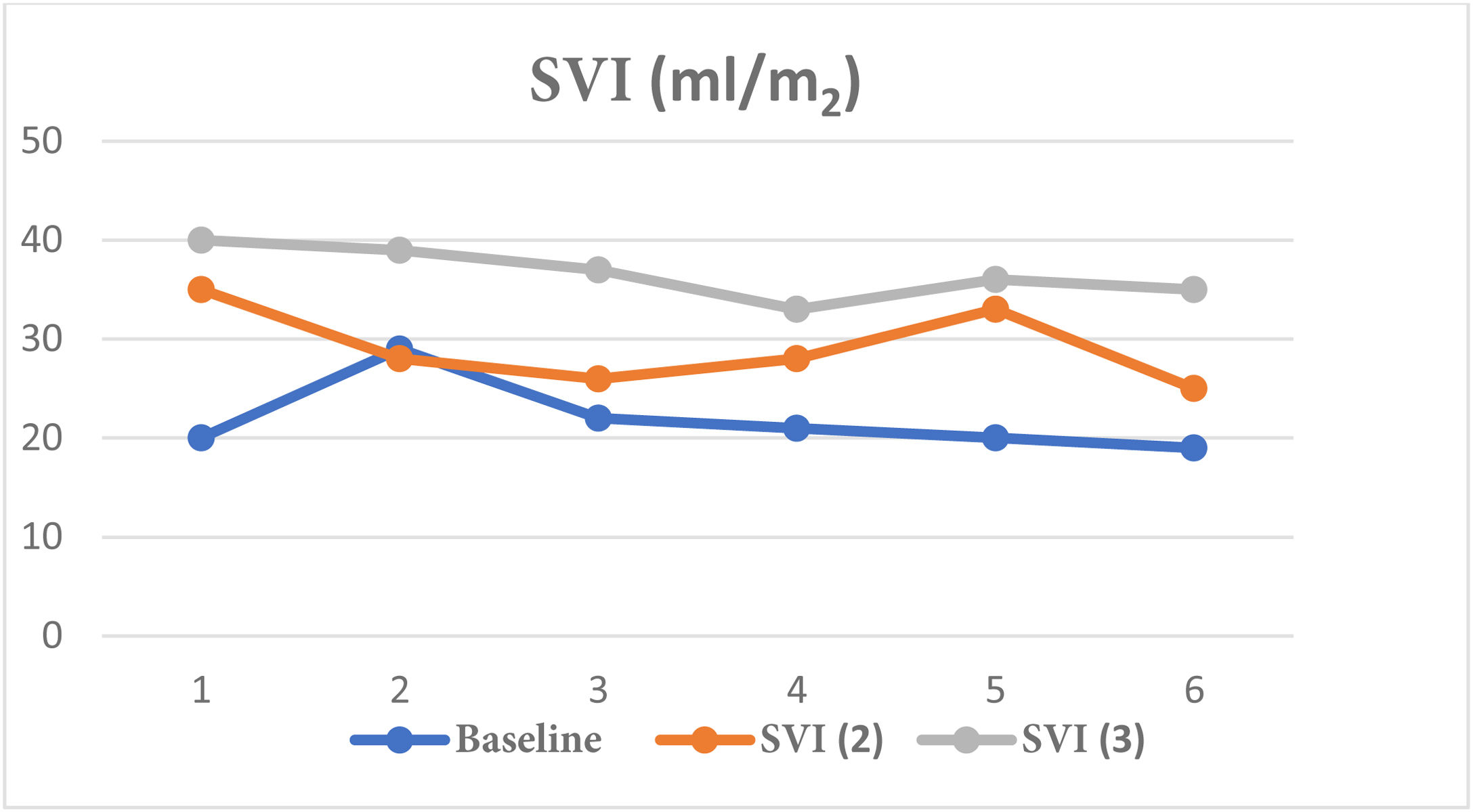
ResultsWere included 6 patients aged 14–16 years, 5/6 males. Five of six had cardiac MRI with decreased FEVD (33%–44%), 1/6 with FEVD 53%. At baseline, IVS and CI were decreased, 19−29 ml/lat/m2 and 1.1−1.9 L/min/m2. Two-Three overloads of volume were performed to reach target IVS (25−35 ml/lat/m2), with an increase of 0%–75%. After the placement of the bar, the IVS was increased by 8%–42% (35−40 ml/lat/m2) with respect to the target IVS, with normalization of the CI (2.5−3.5 L/min/m2).
ConclusionsPE produces compression of the VD, with descent of the IVS. After the placement of the Nuss bar, through the analysis of the IAP, we can objectifield an increase in the IVS and normalization of the CI.
La corrección quirúrgica del pectus excavatum (PE) está justificada por la progresiva afectación cardiopulmonar. Son limitados los estudios que analizan los cambios hemodinámicos durante el intraoperatorio.
ObjetivosDescribir los cambios que se producen en el índice de volumen sistólico (IVS) durante el intraoperatorio de la técnica de Nuss, mediante la monitorización de la curva de presión arterial invasiva (PAI).
Material y métodosEstudio observacional prospectivo de los pacientes pediátricos sometidos a cirugía de Nuss mediante videotoracoscopia (VATS) derecha. Mediante el análisis de la curva de PAI a través del monitor FloTrac (Edwars®), se evaluaron los siguientes parámetros dinámicos: índice de volumen sistólico (IVS), índice cardiaco (IC), variación de volumen sistólico (VVS). Los datos se recogieron en 3 ocasiones: de forma basal, antes de la colocación de la barra (tras la optimización de la precarga buscando el IVS objetivo) y después de la colocación de la misma.
ResultadosFueron incluidos 6 pacientes, con edades 14–16 años, 5/6 varones, 5/6 presentaban RMN cardiaca con FEVD disminuida (33%–44%), 1/6 con FEVD 53%. De forma basal, el IVS e IC estaban disminuidos, 19−29 ml/lat/m2 y 1,1−1,9 l/min/m2. Se realizaron 2–3 sobrecargas de volumen para alcanzar IVS objetivo (25−35 ml/lat/m2), con incremento 0%–75%. Tras la colocación de la barra, el IVS se incrementó un 8%–42% (35%−40 ml/lat/m2) con respecto al IVS objetivo, con normalización del IC (2,5−3,5 l/min/m2).
ConclusionesPE produce compresión del VD, con descenso del IVS. Tras la colocación de la barra de Nuss, mediante el análisis de la PAI, se puede objetivar un incremento del IVS y normalización del IC.