To evaluate, by means of a meta-analysis, the effect of normal saline on mortality in intensive care patients, when compared with the use of balanced crystalloids.
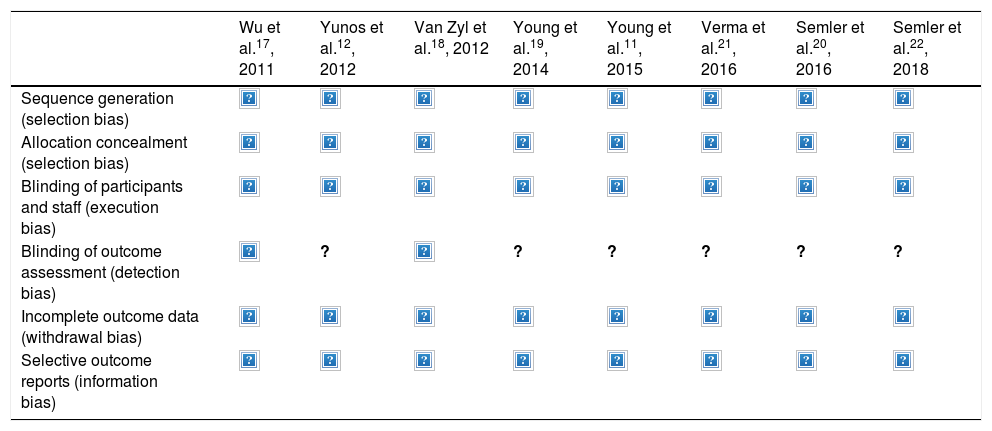
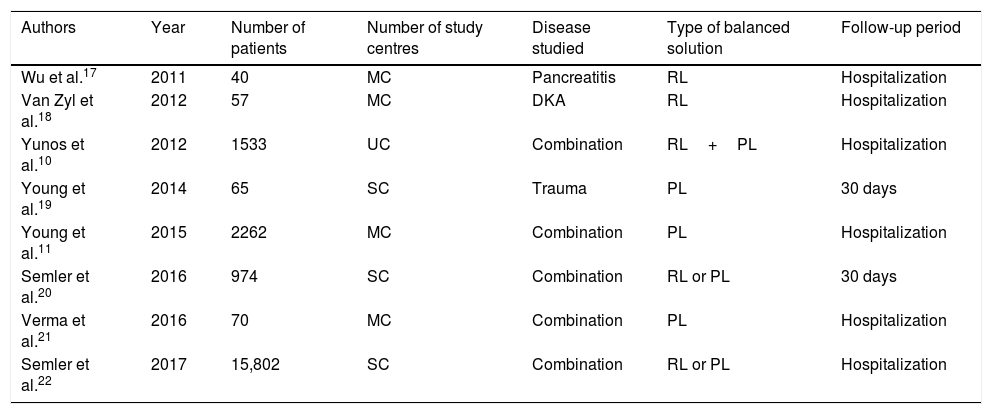
Material and methodPublished controlled clinical trials, randomized and sequential prospective studies in time, evaluating the mortality when physiological saline was used in patients admitted to intensive care units. Electronic search was performed in Medline, Embase, Cochrane Library, ISI Proceedings, and Web of Science, as well as a manual search of selected references. An independent evaluation was performed by 2 investigators. Discrepancies were resolved by consensus in the working group. Contingency tables were performed, and the OR with confidence intervals of each study were obtained. Heterogeneity was assessed by I2. Publication bias was assessed using funnel plot and Egger test.
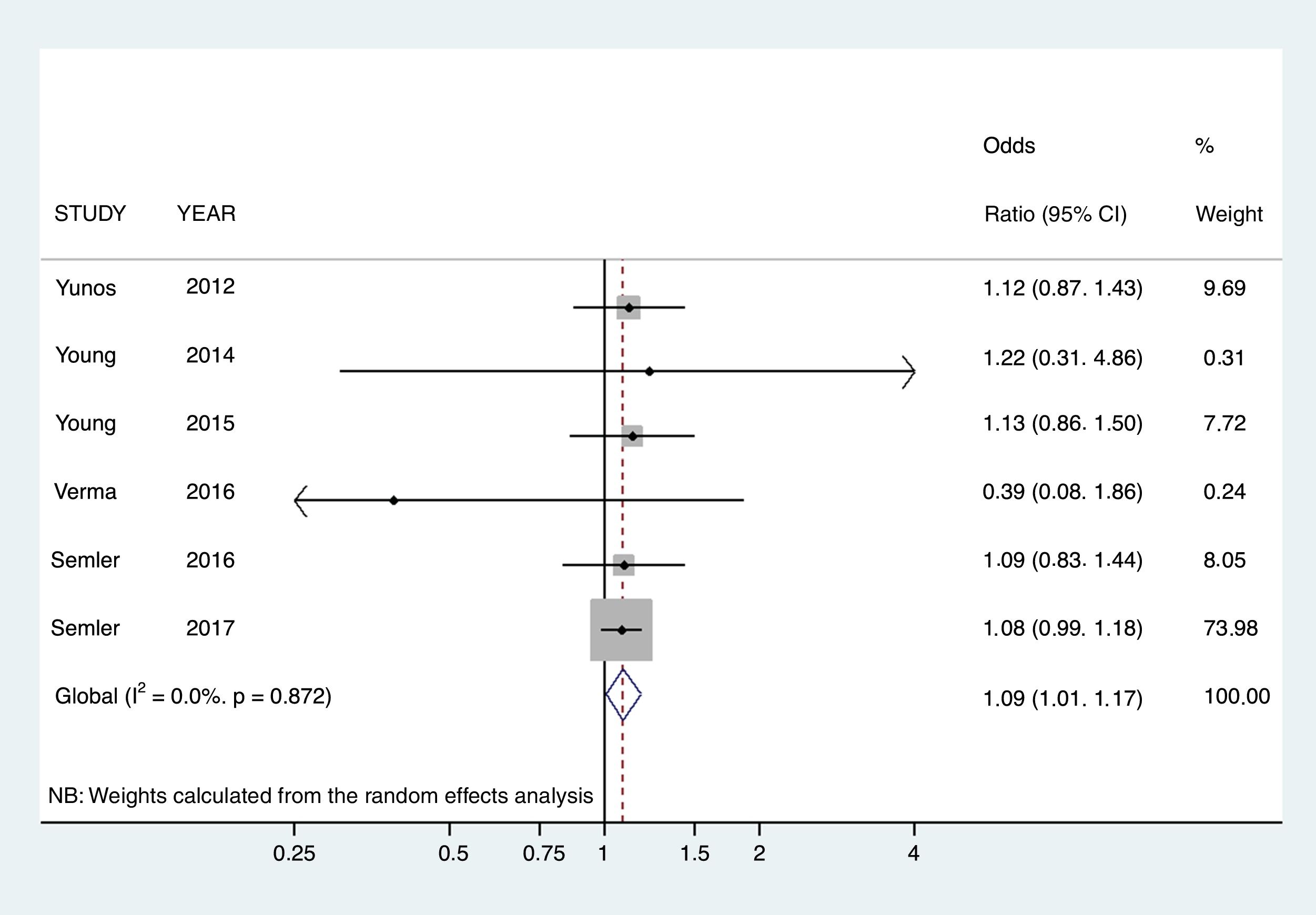
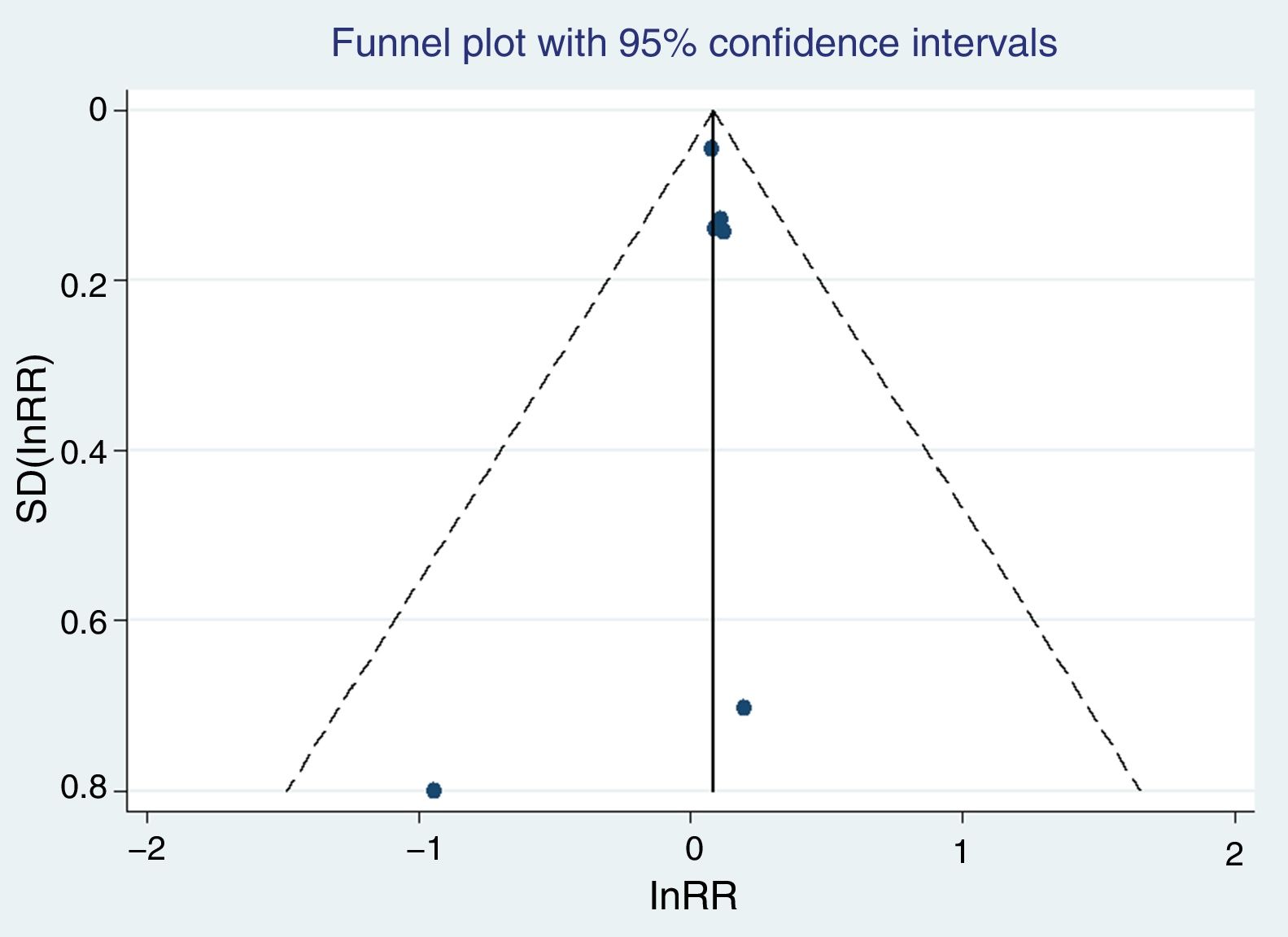
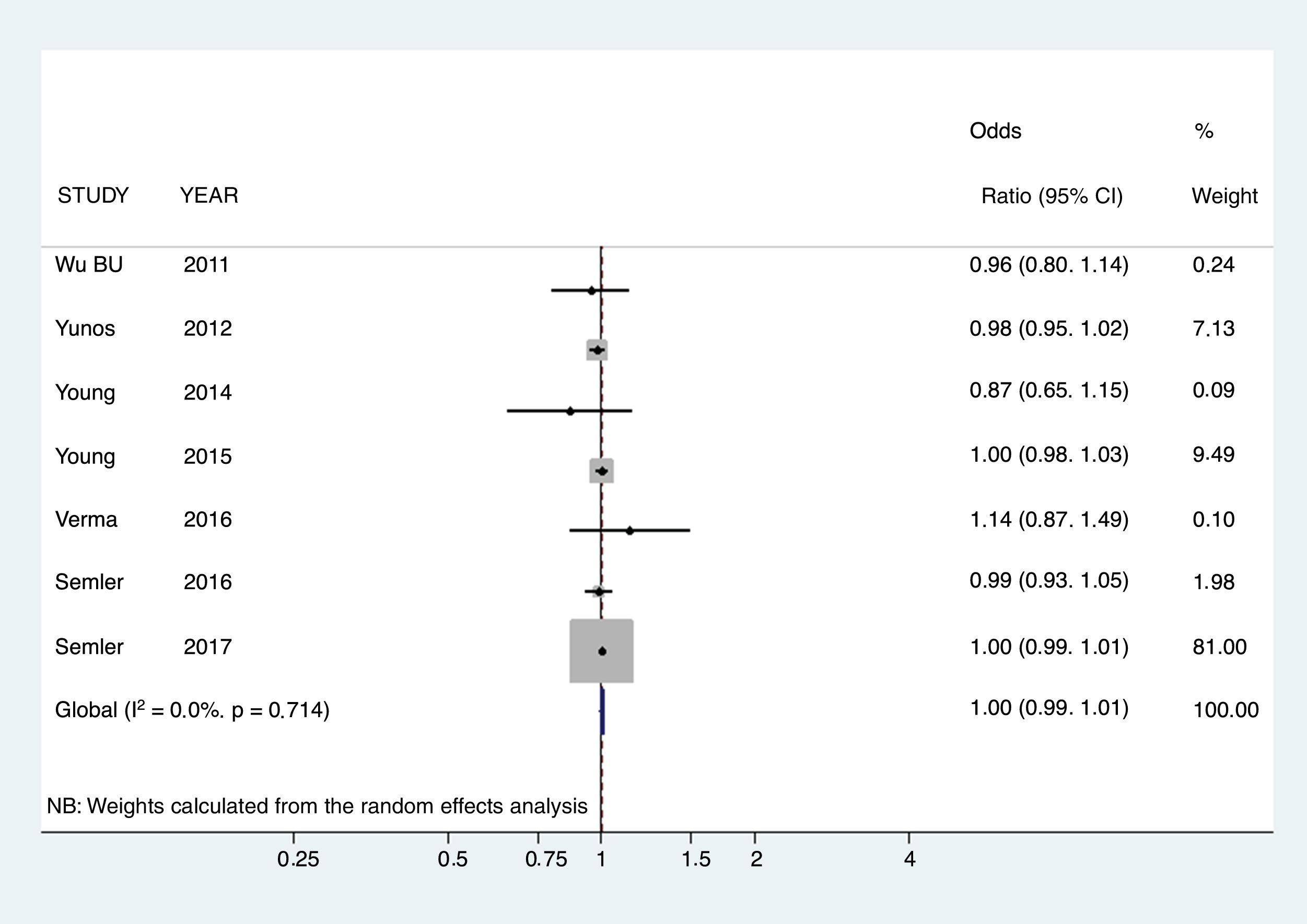
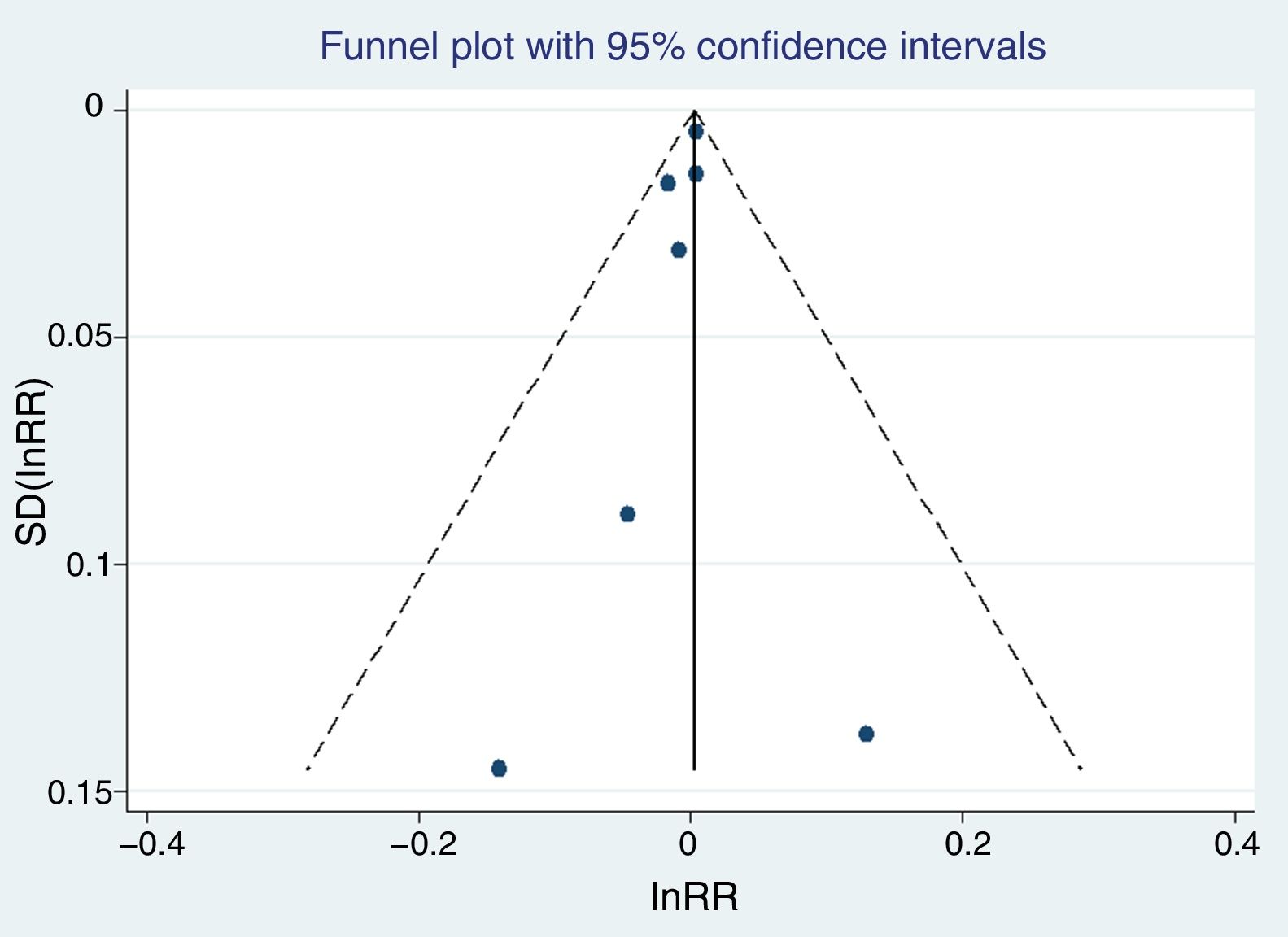
ResultsA total of 8 articles were selected for the meta-analysis of mortality, which included a total of 20,684 patients. A significant association was observed between the use of saline and mortality in intensive care patients (OR 1.0972; 95% CI 1.0049–1.1979), when compared to the use of balanced crystalloids. No statistical evidence of publication bias (Egger, P=.5349) was found. In the sensitivity analysis, none of the studies substantially modified the overall outcome if it was eliminated from the meta-analysis.
ConclusionsThere may be an increase in mortality associated with the use of saline in patients admitted to intensive care when comparing with the use of balanced crystalloids.
Evaluar, mediante un metaanálisis, el efecto del suero salino sobre la mortalidad en los pacientes de cuidados intensivos, cuando se compara su uso con el de cristaloides balanceados.
Material y métodoSe ha realizado un metaanálisis de ensayos clínicos controlados, aleatorizados y estudios prospectivos secuenciales en el tiempo, publicados, que evaluaron la mortalidad del suero salino en enfermos ingresados en unidades de cuidados intensivos. Se llevó a cabo una búsqueda electrónica en Medline, Embase, biblioteca Cochrane, ISI Proceedings y Web of Science y una búsqueda manual sobre las referencias seleccionadas. La extracción de datos fue realizada de forma independiente por 2 investigadores. Las discrepancias se resolvieron por consenso en el grupo de trabajo. El cálculo de la OR y su intervalo de confianza se realizó ponderando por el inverso de la varianza. La heterogeneidad se evaluó mediante I2. El sesgo de publicación se valoró mediante funnel plot y test de Egger.
ResultadosSe seleccionaron 8 artículos para el metaanálisis de mortalidad, que incluían un total de 20.684 pacientes. Se objetivó una asociación entre el uso de suero salino y la mortalidad en los enfermos de cuidados intensivos (OR 1,0972; IC 95%:1,0049–1,1979) cuando se comparaba con el uso de cristaloides balanceados. No se encontró evidencia de sesgo de publicación (prueba de Egger p=0,5349). En el análisis de sensibilidad ninguno de los estudios modificó sustancialmente el resultado global si se eliminaba del metaanálisis.
ConclusionesEs posible que exista un aumento de la mortalidad asociada al empleo de suero salino en los pacientes ingresados en cuidados intensivos cuando se compara con el empleo de cristaloides balanceados.