Regional anaesthesia is commonly preferred for arteriovenous fistula (AVF) creation. Previous studies suggest a shorter block duration in patients with chronic renal failure, maybe because of the changes in regional blood flow. The aim of our study was to evaluate the duration of the axillary block with 1.5% mepivacaine in patients with chronic renal failure scheduled for AVF compared with healthy controls.
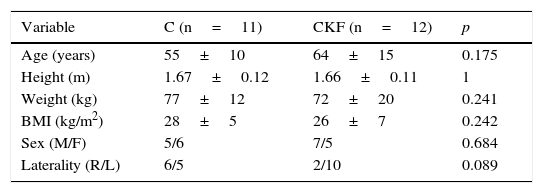
MethodsPatients scheduled for AVF creation for the first time (GIRC) were included. They were compared with patients without renal failure (GC), with similar anthropometric characteristics. Ultrasound-guided axillary blocks with 20ml of 1.5% mepivacaine were performed on all patients. We evaluated onset time, humeral artery diameter and blood flow before and after the block, as well as the block duration.
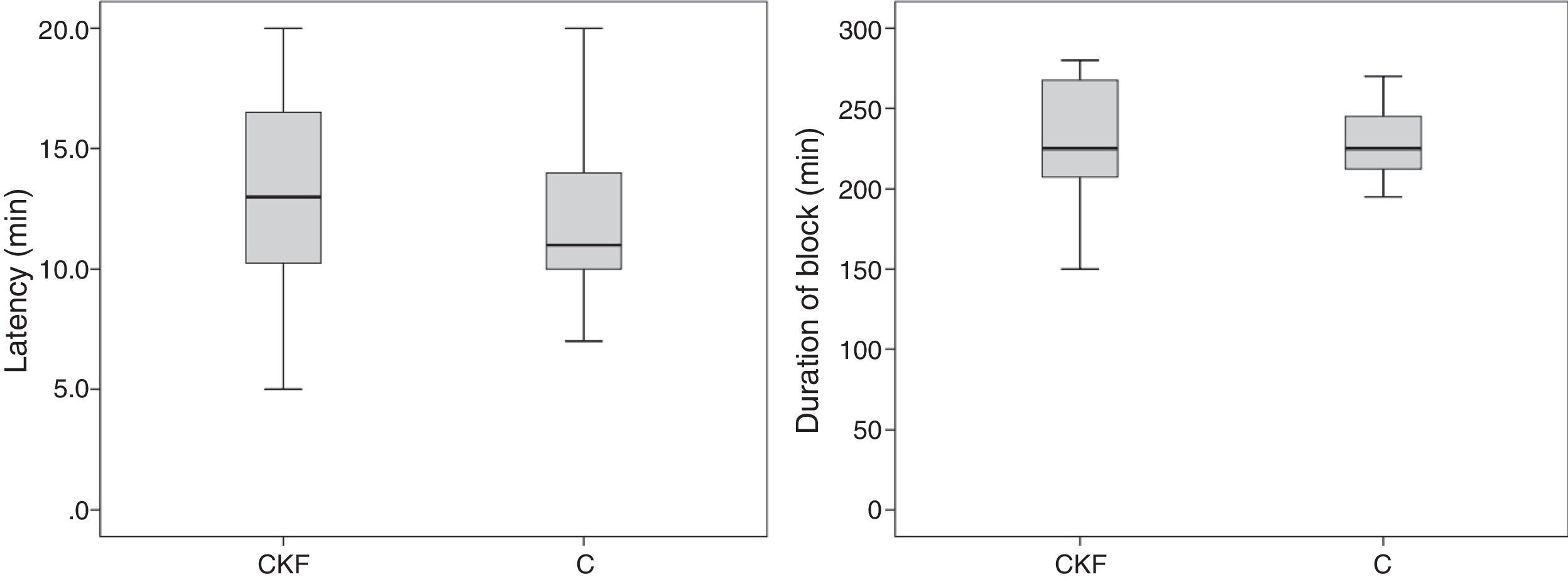
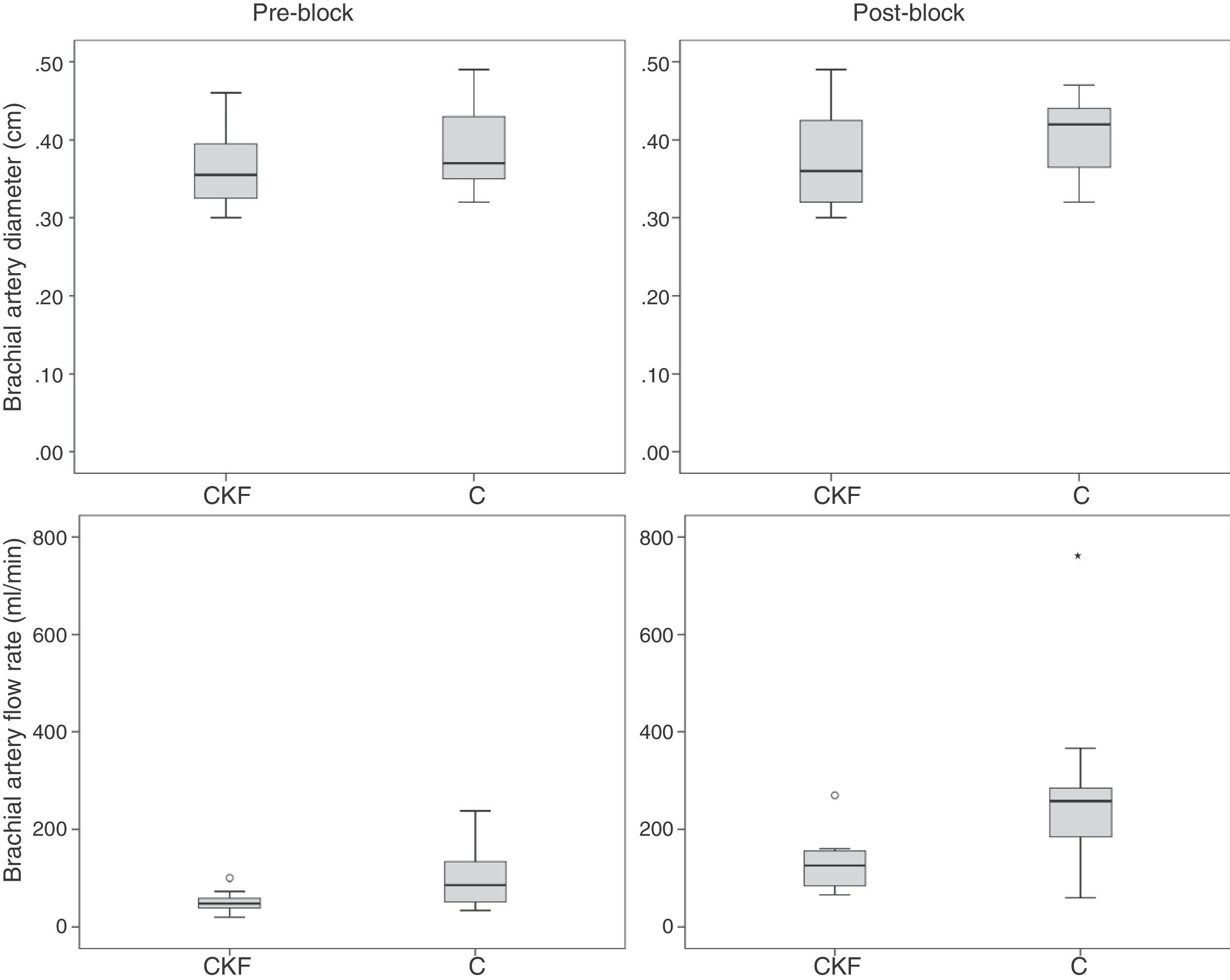
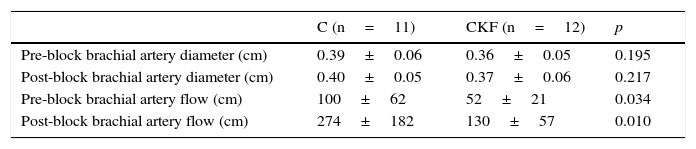
ResultsTwenty-three patients (GIRC: 12 and GC: 11) were included. No differences between groups were observed in block duration (GIRC: 227±43min vs GC: 229±27min; p=0.781), or in onset time (GIRC: 13±5min vs GC: 12.2±3min; p=0.477). The humeral blood flow before and after block was significantly lower in the GIRC (pre-block: GIRC: 52±21ml/min and GC: 100±62ml/min; p=0.034 and post-block: GIRC: 130±57ml/min and GC: 274±182ml/min; p=0.010). There was no significant correlation between the duration of the block and the preblock humeral blood flow (Spearman rho: 0.106; p=0.657) or the post-block humeral blood flow (Spearman rho: 0.267; p=0.254).
ConclusionThe duration of the axillary block with 1.5% mepivacaine in patients with chronic renal failure was similar to that of the control patients. The duration of axillary brachial plexus block seems not to be related to changes in regional blood flow.
El bloqueo del plexo braquial para la creación de fístula arteriovenosa (FAV) ha demostrado buenos resultados, si bien algunos autores han evidenciado una duración del bloqueo inferior al de los individuos sanos, probablemente por cambios en el flujo arterial regional. Nuestro objetivo fue evaluar la duración del bloqueo axilar con mepivacaína al 1,5% en pacientes con insuficiencia renal crónica programados para FAV y compararlo con controles sanos.
MétodosSe incluyó a pacientes con insuficiencia renal crónica en hemodiálisis, llevados por primera vez para la creación de una FAV (GIRC). Se compararon con pacientes sin insuficiencia renal (GC), con características antropométricas similares; todos bajo bloqueo axilar ecoguiado con 20mL de mepivacaína al 1,5%. Se evaluaron el tiempo de latencia, el flujo y el diámetro de la arteria humeral pre y posbloqueo, así como la duración del bloqueo.
ResultadosSe incluyó a 23 pacientes (GIRC: 12 y GC: 11). No se observaron diferencias en la latencia (GIRC: 13±5min vs. GC: 12,2±3min, p=0,477) ni en la duración del bloqueo (GIRC: 227±43min vs. GC: 229±27min, p=0,781). El flujo pre y posbloqueo fue significativamente menor en el GIRC (prebloqueo: GIRC: 52±21ml/min, GC: 100±62ml/min, p=0,034, y posbloqueo: GIRC: 130±57ml/min y GC: 274±182ml/min, p=0,010). No existió una correlación significativa entre la duración y el flujo arterial de la extremidad prebloqueo (rho de Spearman: 0,106; p=0,657) ni posbloqueo (rho de Spearman: 0,267; p=0,254).
ConclusiónLa duración del bloqueo axilar con mepivacaína al 1,5% en pacientes con insuficiencia renal crónica llevados por primera vez para creación de fístula arteriovenosa no es menor con respecto al grupo control y el flujo vascular como variable hemodinámica de la extremidad bloqueada no parece desempeñar un papel importante en la duración del mismo.