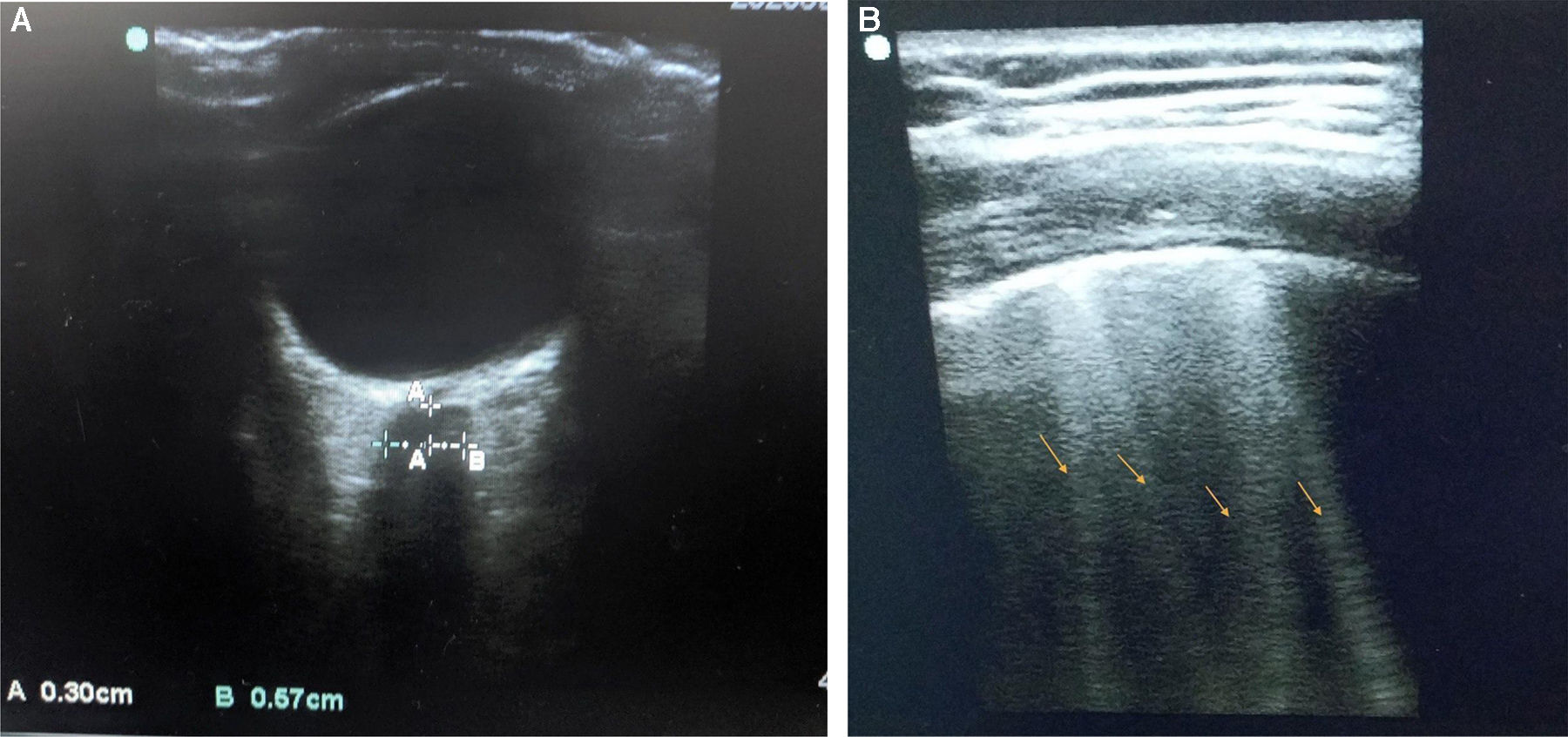
Complications of preeclampsia include cerebral and pulmonary edema which strongly correlate with optic nerve sheath diameter (ONSD) and lung ultrasound score (LUSS) respectively. This study was conducted to compare ONSD and LUSS in healthy and preeclamptic parturients.
MethodsIn this prospective observational analytical study, 35 healthy pregnant women and preeclamptic women each underwent ultrasound assessment for ONSD and LUSS (12 region lung technique). Severity of preeclampsia was noted. ROC analysis was performed to obtain a cutoff value for both ONSD and LUSS to predict complications of preeclampsia. A p-value of <0.05 was considered significant.
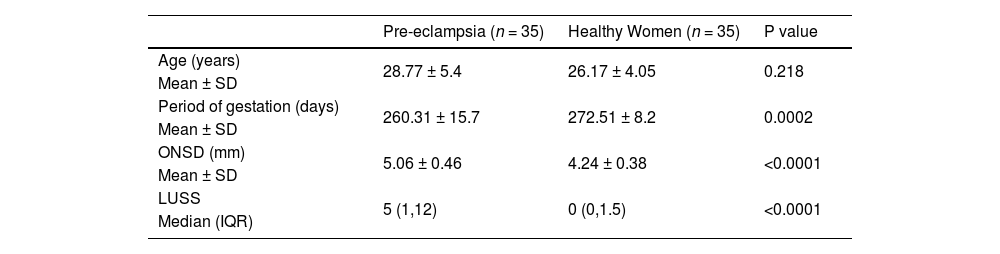
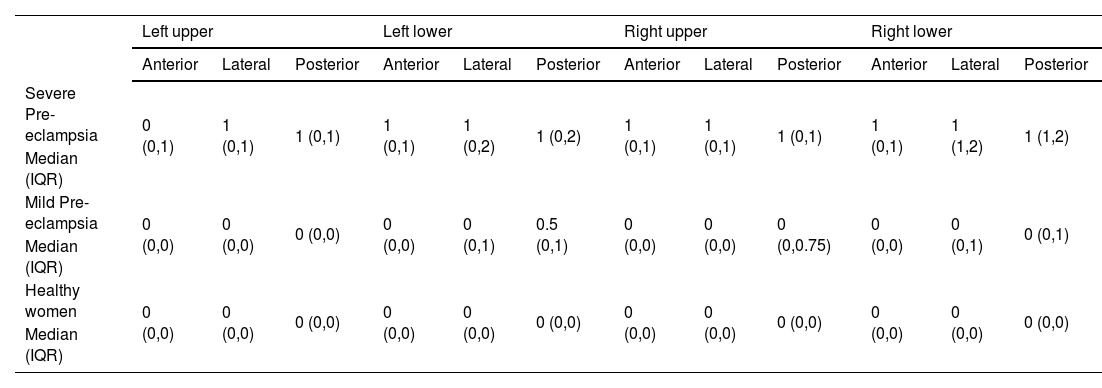
ResultsMean ONSD and LUSS were higher in preeclamptic compared to healthy parturients [5.06 ± 0.46 vs 4.24 ± 0.38 mm (p < 0.0001) and [5 (1–12) vs 0 (0–1.5); p value <0.0001], respectively. Mean ONSD in severe pre-eclampsia (5.36 ± 0.32 mm) was significantly higher as compared to mild pre-eclampsia (4.71 ± 0.35 mm; p < 0.0001). Women with severe preeclampsia had a higher LUSS as compared to the mild preclamptics and healthy parturients. However, no difference in ONSD and LUSS between mild preeclamptics and healthy parturients was observed. A mean ONSD of >4.65 mm and LUSS of >2 could predict preeclampsia with a sensitivity of 77.14% and 68.57% and specificity of 91.43% and 85.71% with an AUC of 0.907 and 0.806 respectively.
ConclusionBoth ONSD and LUSS can be used to assess severity and complications of preeclampsia. Early detection can be used to treat, guide fluid therapy and monitor response to treatment.
CTRI registrationCTRI/2019/12/022243 (https://ctri.nic.in/Clinicaltrials/pmaindet2.php?trialid=37940&EncHid=&userName=). IEC: LHMC/IEC/Thesis/2019/116 dated 29/10/2019.
Las complicaciones de la preeclampsia incluyen edema cerebral y pulmonar, que están fuertemente correlacionados con el diámetro de la vaina del nervio óptico (DVNO) y la puntuación LUS (lung ultrasound score) respectivamente. Este estudio fue realizado para comparar DVNO y LUS en parturientas sanas y mujeres con preeclamsia.
MétodosEn este estudio analítico observacional prospectivo, evaluamos ecográficamente el DVNO y la puntuación LUS en 35 embarazadas sanas y mujeres con preeclamsia (técnica pulmonar de 12 regiones), y registramos la gravedad de la preeclampsia. Se realizó un análisis ROC para obtener un valor de corte de DVNO y LUS, a fin de predecir las complicaciones de la preeclampsia. Se consideró significativo un valor p < 0,05.
ResultadosEl valor medio de DVNO y LUS fue más alto en mujeres con preeclamsia que en parturientas sanas (5,06 ± 0,46 vs 4,24 ± 0,38 mm (p < 0,0001)] y [5 (1-12) vs 0 (0-1,5); valor p < 0,0001], respectivamente. El valor medio de DVNO en la preeclamsia grave (5,36 ± 0,32 mm) fue significativamente más alto en comparación con la preeclampsia leve (4,71 ± 0,35 mm; p < 0,0001). Las mujeres con preeclamsia grave tuvieron una puntuación LUS más alta, en comparación con la preeclampsia leve y las parturientas sanas. Sin embargo, no se observaron diferencias en cuanto a DVNO y LUS entre las mujeres con preeclamsia leve y las parturientas sanas. Un valor medio de DVNO de >4,65 mm y LUSS de >2 podría predecir la preeclampsia con una sensibilidad del 77,14% y 68,57% y una especificidad del 91,43% y 85,71%, con un ABC de 0,907 y 0,806 respectivamente.
ConclusiónTanto DVNO como LUS pueden utilizarse para evaluar la gravedad y las complicaciones de la preeclamsia. La detección temprana puede utilizarse para tratar, guiar la fluidoterapia y supervisar la respuesta al tratamiento.