The aim of this study was to investigate the frequency of fibromyalgia (FM) in axial spondyloarthritis (ax-SpA) patients using the current FM diagnostic criteria (2016 Revised Fibromyalgia Diagnostic Criteria). Additionally, we aimed to investigate the relationship between FM severity and disease activity, functional status, and quality of life (QoL).
Materials and methodsDisease activity, functional disability and QoL were evaluated. FM severity was measured with the fibromyalgia impact questionnaire (FIQ).
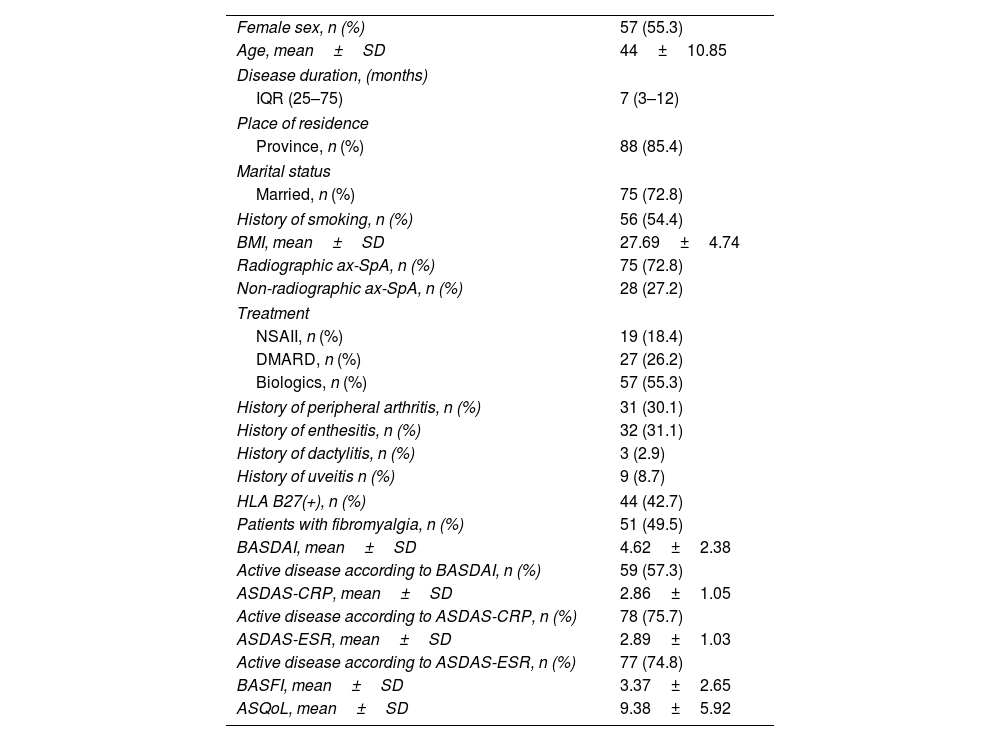
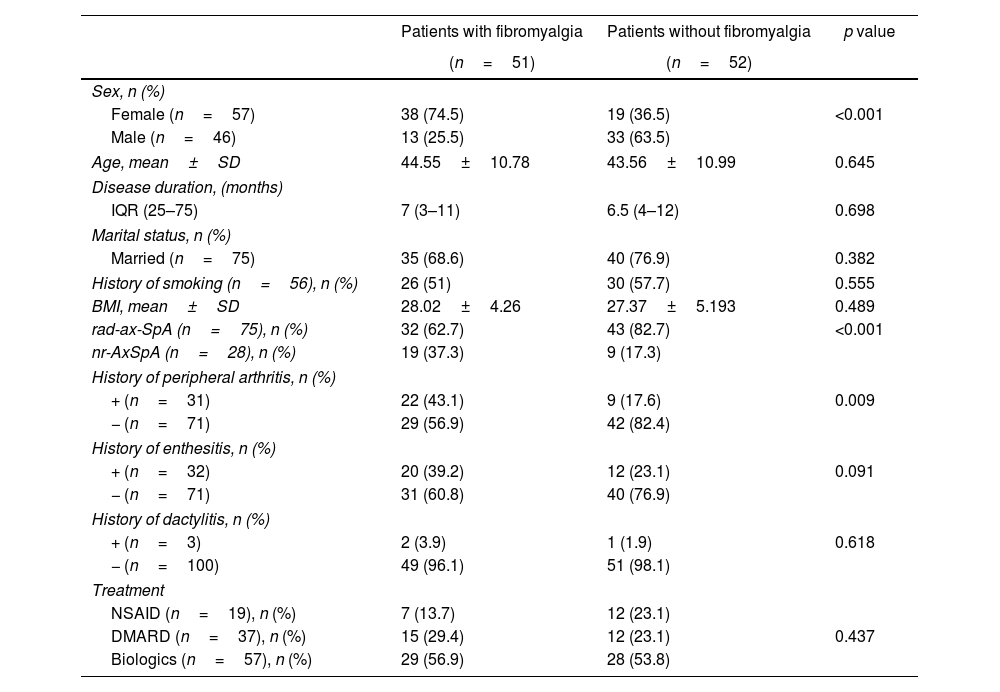
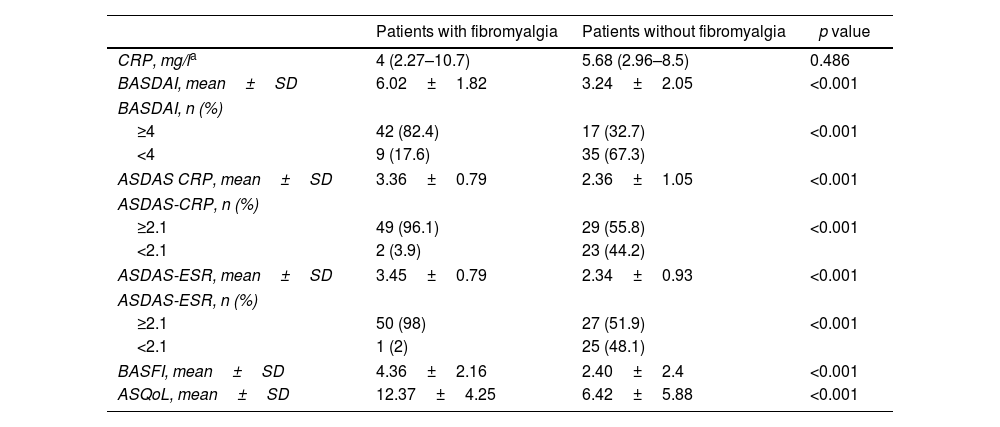
ResultsOne hundred and three patients with ax-SpA (55.3% female; mean age 44±10.85 years) were included. FM was detected in 49.5% of the patients. While FM was detected in 71% of patients with a history of peripheral arthritis, FM was present in 59.2% of patients without (p = 0.009). FM-ax-SpA patients showed higher disease activity except for C-reactive protein; functional status and QoL were statistically worse in patients with FM-SpA. Significant positive correlations were found between FIQ and disease activity, functional disability and QoL (p<.001).
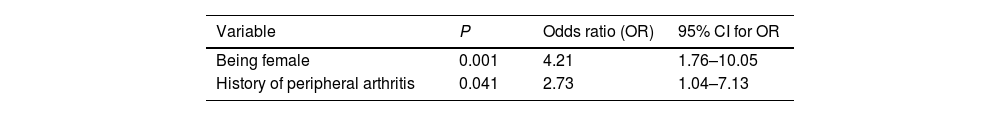
ConclusionsThe most effective features associated with the presence of FM were detected as gender and a history of peripheral arthritis. Presence of FM may cause an overestimation of disease activity, FM severity correlates with disease activity.
El objetivo de este estudio fue investigar la frecuencia de fibromialgia (FM) en pacientes con espondiloartritis axial (ax-SpA), para lo cual se utilizaron los criterios de diagnóstico de FM actuales (2016 Revised Fibromyalgia Diagnostic Criteria). Además, nuestro objetivo también fue investigar la relación entre la gravedad de la FM y la actividad de la enfermedad, el estado funcional y la calidad de vida (CV).
Materiales y métodosSe evaluó la actividad de la enfermedad, la discapacidad funcional y la calidad de vida. La gravedad de la FM se midió con el cuestionario de impacto de la fibromialgia (FIQ).
ResultadosSe incluyeron 103 pacientes con ax-SpA (55,3% mujeres; edad media 44 ± 10,85 años). Mientras que la FM se detectó en 71% de los pacientes con antecedentes de artritis periférica, estuvo presente en 59,2% de los pacientes sin esta última condición (0,009). Los pacientes con FM-ax-SpA mostraron una mayor actividad de la enfermedad, con excepción de la proteína C reactiva; el estado funcional y la calidad de vida fueron estadísticamente peores en pacientes con FM-SpA, y se encontraron correlaciones positivas significativas entre el FIQ y la actividad de la enfermedad, la discapacidad funcional y la CV (p < 0,001).
ConclusiónLas características más efectivas asociadas con la presencia de FM fueron el género y los antecedentes de artritis periférica. La presencia de FM puede causar una sobreestimación de la actividad de la enfermedad, en tanto que la gravedad de la FM se correlaciona con la actividad de la enfermedad.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora