The identification of biomarkers of disease progression continues to be a necessity in the approach to multiple sclerosis (MS), a disabling neurological disease more common in young adults, which can have different phenotypes, among which relapsing-remitting (RRMS), primary progressive (PPMS) and secondary progressive (SPMS). Among biomarkers, the determination of neurofilament light chain (NfL) levels in both cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and serum have been shown to predict the severity of MS. Therefore, the objective of the present work was to evaluate the levels of NfL in patients in different stages of MS.
MethodologyA descriptive study was carried out, which included 70 patients diagnosed with MS; plasma NfL levels were analyzed using the adsorption enzyme immunoassay kit and the levels of the MS patients were compared with the levels of control patients.
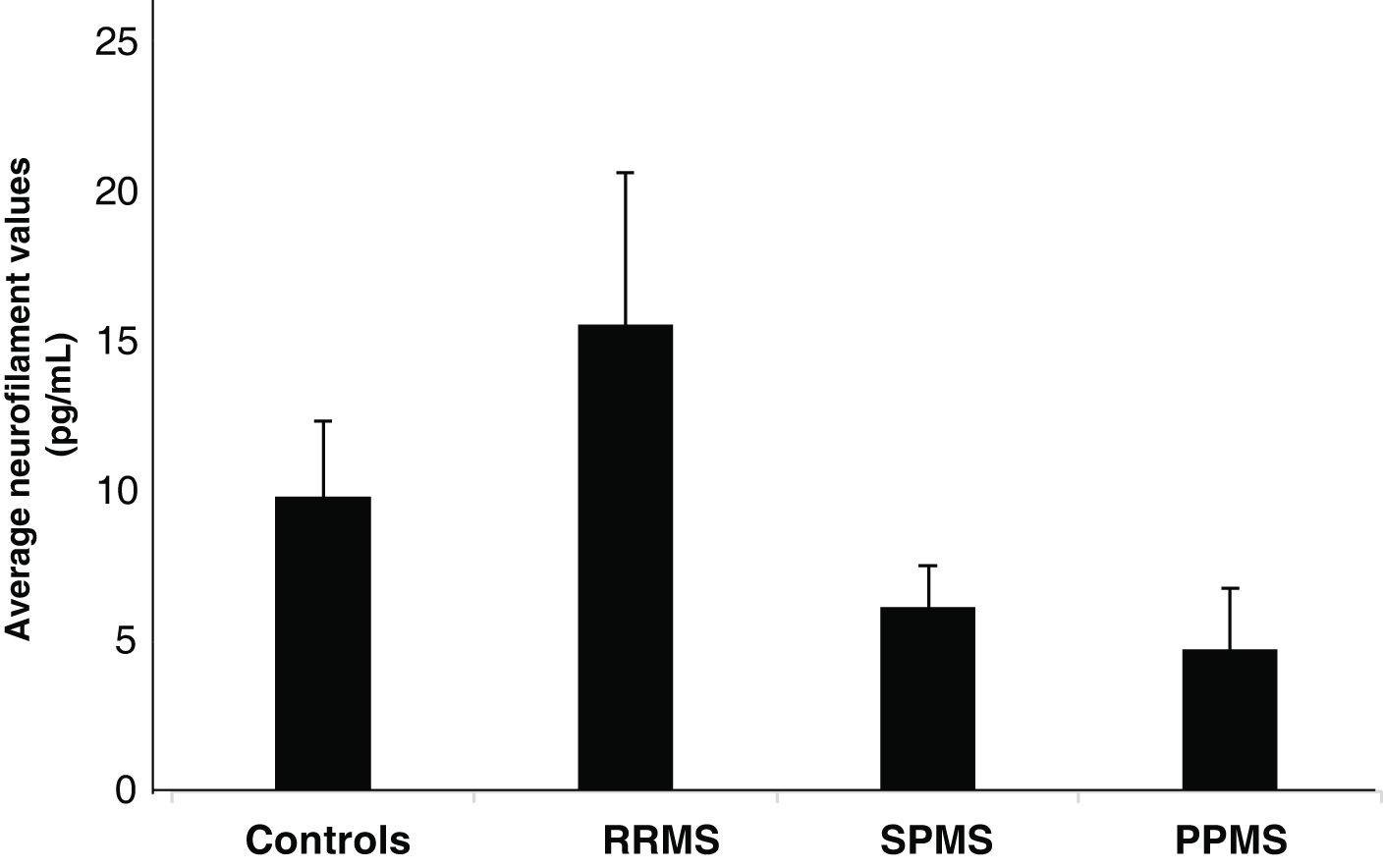
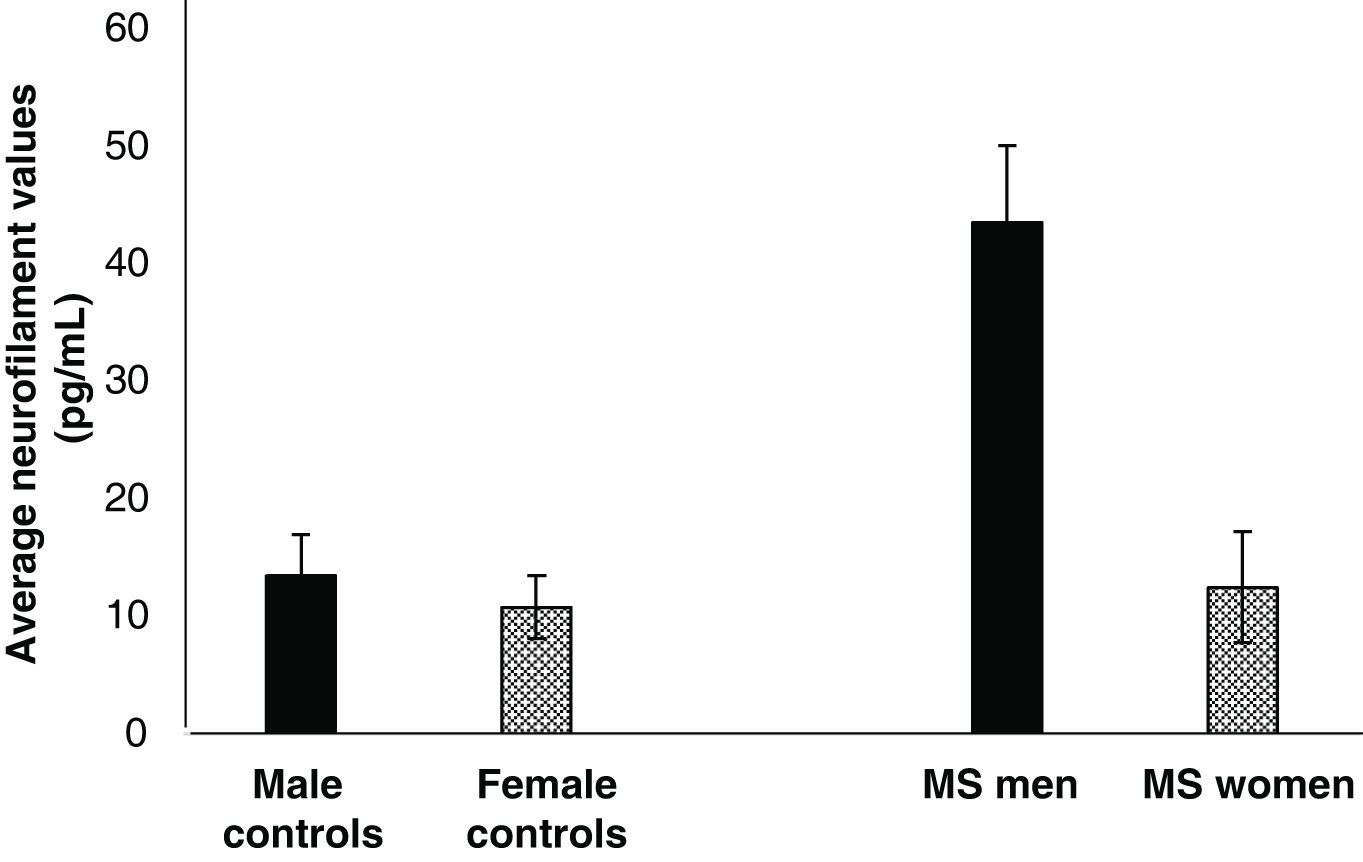
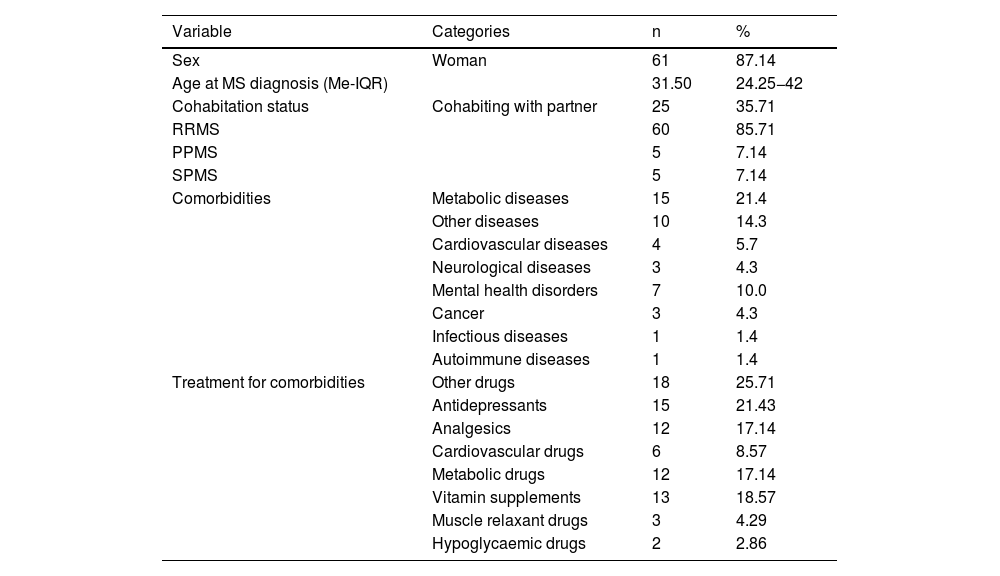
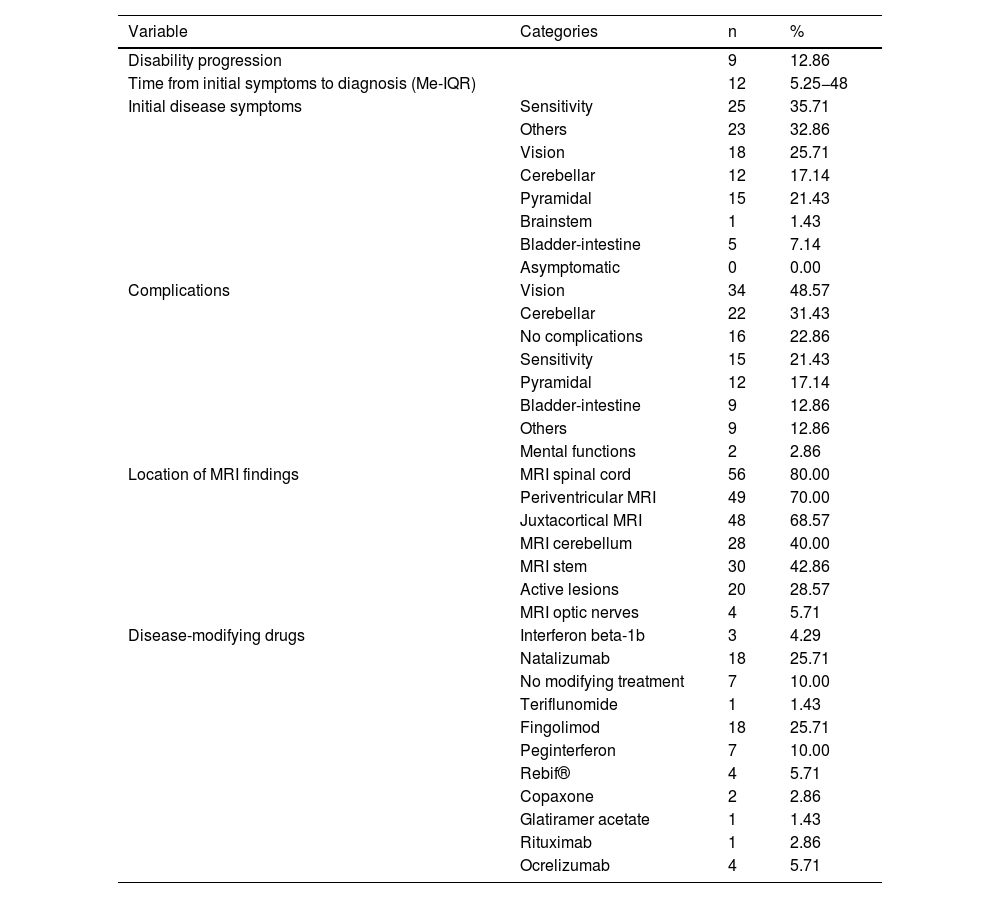
ResultsIn patients with MS, 87,14% were women, 21,43% were taking antidepressant drugs, 48,57% had vision complications.and 80% had spinal injuries. It was found that patients with RRMS phenotype and of male sex have higher levels of NfL.
ConclusionsThe results show an increase in NfL in RRMS and in male patients, which suggests that there may be greater neuroaxonal deterioration in men and that they have this disease phenotype. However, future studies aimed at optimizing, standardizing, and implementing new technologies are necessary to address the predictive value of these biomarkers that can contribute to the management of the disease.
La identificación de biomarcadores de progresión de la enfermedad continúa siendo una necesidad en el abordaje de la esclerosis múltiple (EM), una enfermedad neurológica discapacitante más frecuente en adultos jóvenes, la cual puede tener diferentes fenotipos entre los cuales se destacan el remitente recurrente (EMRR), primaria progresiva (EMPP) y secundaria progresiva (EMSP). Entre los biomarcadores, la determinación tanto en líquido cefalorraquídeo (LCR) como en suero de niveles de los neurofilamentos de cadena ligera (NfL) han mostrado predecir la severidad de la EM. Por lo tanto, el objetivo del presente trabajo fue evaluar los niveles de NfL en pacientes en diferentes estadios de la EM.
MetodologíaSe realizó un estudio descriptivo, que incluyó 70 pacientes con diagnóstico de EM; se analizaron los niveles plasmáticos de NfL utilizando el kit de enzimoinmunoanálisis de adsorción y los niveles de los pacientes con EM fueron comparados con los niveles de pacientes controles.
ResultadoEn los pacientes con EM el 87,14% fueron mujeres, el 21,43% tomaban fármacos antidepresivos, el 48,57% tenían complicaciones de visión y el 80% tenían lesiones en medula. Se encontró que, pacientes con fenotipo EMRR y de sexo masculino presentan mayores niveles de NfL.
ConclusionesLos resultados muestran un incremento de los NfL en EMRR y en pacientes de sexo masculino, lo cual sugiere que puede existir un mayor deterioro neuroaxonal en hombres y que tengan este fenotipo de la enfermedad. Sin embargo, se hace necesario futuros estudios dirigidos a la optimización, estandarización e implementación de nuevas tecnologías para abordar el valor predictivo de estos biomarcadores que puedan aportar al manejo de la enfermedad.
Article
Diríjase al área privada de socios de la web de la SEDENE, (https://sedene.com/revista-de-sedene/ ) y autentifíquese.