La esclerosis lateral amiotrófica (ELA) es una enfermedad neurodegenerativa progresiva que causa pérdida de la función motora y está asociada con alteraciones cognitivas y conductuales. Los pacientes con ELA dependen de los cuidadores/as primarios, quienes enfrentan altos niveles de estrés emocional, incluyendo ansiedad, depresión y sobrecarga.
ObjetivoEvaluar el estrés emocional en los cuidadores/as primarios de pacientes con ELA mediante la medición de los niveles de ansiedad, depresión y sobrecarga.
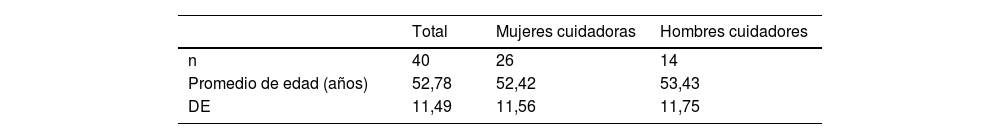
MétodoEstudio descriptivo, cuantitativo y transversal. Se incluyó una muestra de 40 cuidadores/as primarios. Se utilizaron la Escala de Autoevaluación de Ansiedad de Zung (SAS-15), la Escala de Autoevaluación de Depresión de Zung (SDS) y el Cuestionario de Sobrecarga del Cuidador de Zarit (ZBI).
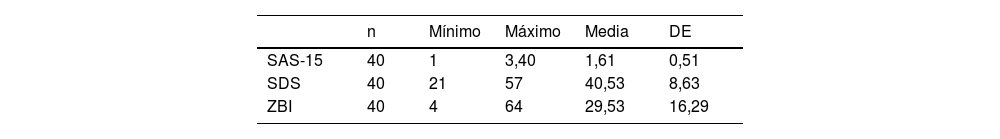
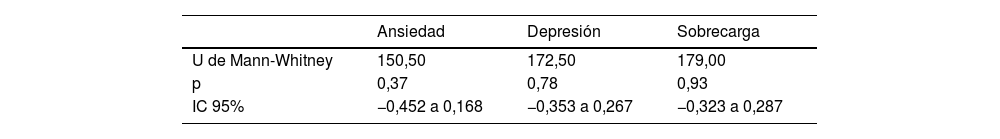
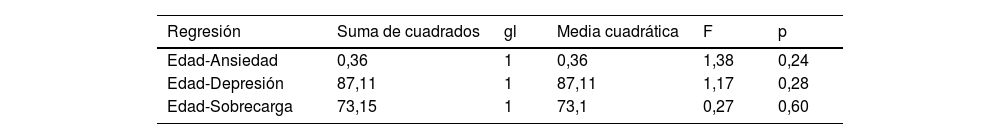
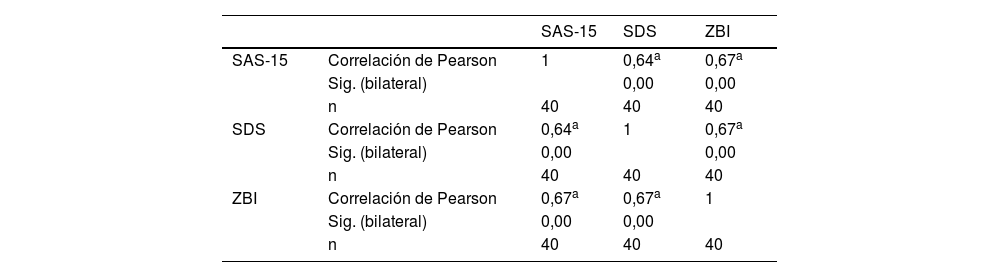
ResultadosLos cuidadores/as presentaron niveles de ansiedad entre leves y moderados, con un valor promedio de 1,61 en la SAS-15, constatando la presencia de estrés emocional. Los niveles de depresión fueron normales y no se observó sobrecarga significativa. No se hallaron diferencias estadísticamente significativas entre hombres y mujeres, ni la edad influyó en los resultados. Se observaron correlaciones positivas significativas entre los niveles de ansiedad y depresión (r=0,64; p<0,05), ansiedad y sobrecarga (r=0,67; p<0,05) y entre depresión y sobrecarga (r=0,67; p<0,05).
ConclusionesEl estrés emocional es prevalente entre los cuidadores/as primarios de pacientes con ELA, siendo la ansiedad el aspecto más afectado. Los resultados destacan la necesidad de abordar el bienestar psicológico de los cuidadores/as.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that causes loss of motor function and is associated with cognitive and behavioral disturbances. ALS patients are dependent on primary caregivers, who face high levels of emotional stress, including anxiety, depression and burden.
ObjectiveTo assess emotional stress in primary caregivers of ALS patients by measuring levels of anxiety, depression and burden.
MethodDescriptive, quantitative, cross-sectional study. A sample of 40 primary caregivers was included. The Zung Self-Rating Anxiety Scale (SAS-15), the Zung Self-Rating Depression Scale (SDS) and the Zarit Burden Interview (ZBI) were used.
ResultsThe caregivers presented mild to moderate levels of anxiety, with an average value of 1.61 on the SAS-15, indicating the presence of emotional stress. Depression levels were normal, and no significant burden was observed. No statistically significant differences were found between men and women, nor did age influence the results. Significant positive correlations were observed between levels of anxiety and depression (r=.64; P<.05), anxiety and burden (r=.67; P<.05) and between depression and burden (r=.67; P<.05).
ConclusionsEmotional stress is prevalent among primary caregivers of ALS patients, with anxiety being the most affected aspect. The results highlight the need to address the psychological well-being of caregivers.
Artículo
Diríjase al área privada de socios de la web de la SEDENE, (https://sedene.com/revista-de-sedene/ ) y autentifíquese.