To determine whether pancreatic iodine concentrations quantified by dual-energy CT differ between patients with acute pancreatitis and those without imaging or laboratory findings indicative of pancreatic disease.
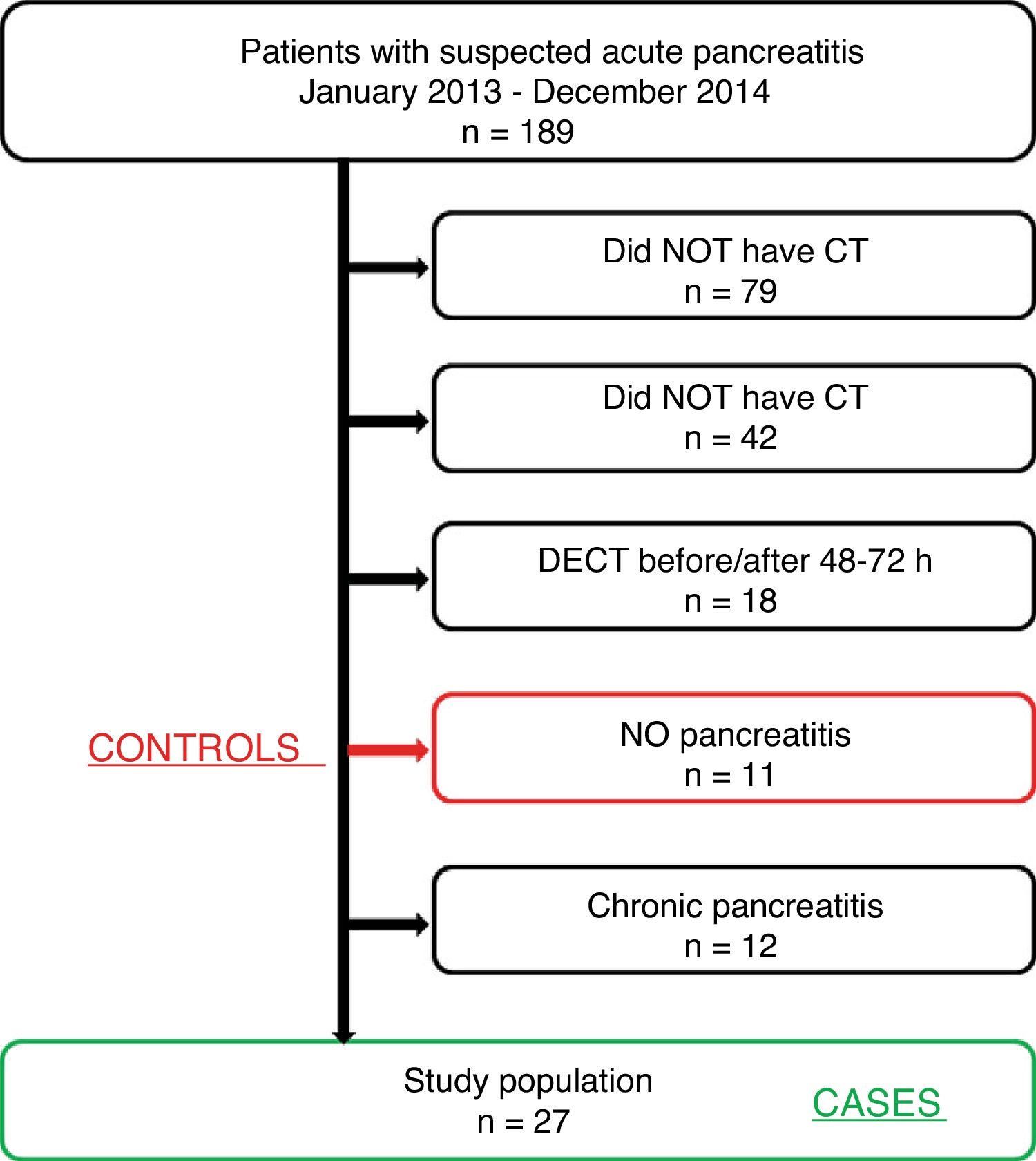
Material and methodsWe compared findings on single-phase dual-energy CT images acquired 55s after the intravenous administration of contrast material in 27 patients with acute pancreatitis who underwent the examination 48–72h after the onset of symptoms versus in 11 patients (controls) with no imaging findings suggestive of pancreatic disease and normal amylase and lipase who underwent the examination with the same protocol for other purposes. Imaging post-processing included the generation of iodine maps. Three regions of interest were selected (pancreatic head, body, and tail) to obtain iodine concentrations (mg/ml) to compare between groups. Iodine concentrations were also calculated a second time by normalising the density of iodine with the aorta.
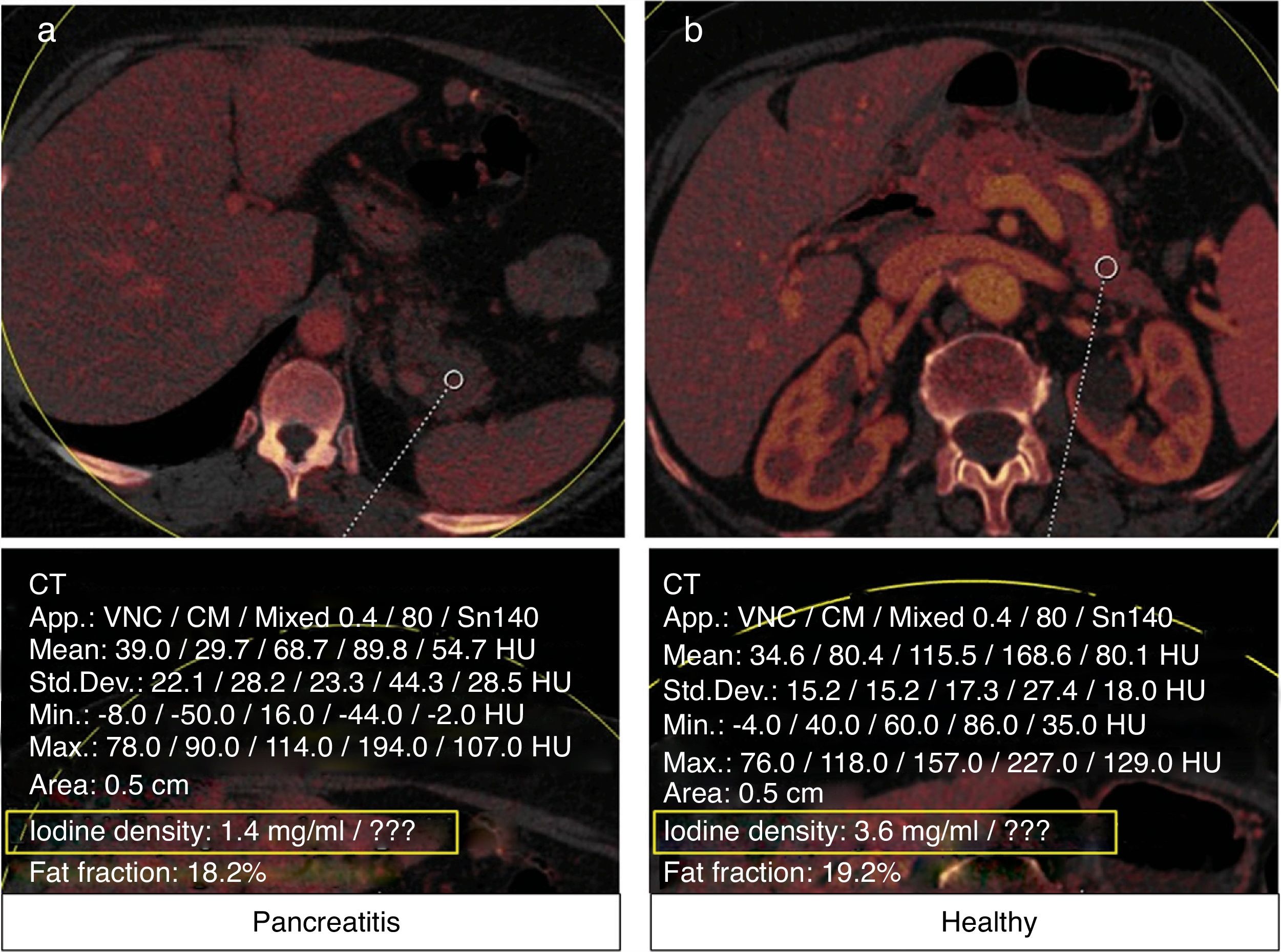
ResultsThe mean density of iodine was 2.5mg/ml in patients with pancreatitis vs. 3.65mg/ml in controls (p=0.02). In three patients with glandular necrosis, the density of iodine was 1.53mg/ml.
ConclusionsThe concentration of iodine in the pancreas measured with dual-energy CT differs significantly between patients with initial-stage acute pancreatitis and those without imaging or laboratory findings indicative of pancreatic disease.
Determinar si existen diferencias en la concentración de iodo cuantificada con TC de doble energía en el páncreas de pacientes con pancreatitis aguda y pacientes sin signos analíticos ni en imagen de patología pancreática.
Material y métodosSe estudian 27 casos de pancreatitis aguda a los que se realizó una TC con energía dual a las 48-72 horas del inicio de los síntomas, realizada con contraste intravenoso y una sola fase con un retraso de 55 segundos. Se compara con un grupo control de 11 pacientes con una TC realizada con el mismo protocolo, pero sin datos radiológicos de pancreatitis y amilasa y lipasa normales. Mediante posprocesado se obtienen reconstrucciones con mapa de iodo y se realizan tres regiones de interés en cabeza, cuerpo y cola pancreática para obtener los valores de concentración de iodo (mg/ml) y se comparan entre ambos grupos. Se hace un segundo cálculo normalizando la densidad de iodo con la aorta.
ResultadosEn las pancreatitis, el valor medio de densidad de iodo es 2,5mg/ml. En el grupo de los controles es de 3,65mg/ml (p = 0,02). Hay tres casos con necrosis glandular en los que la densidad de iodo es 1,53mg/ml.
ConclusionesExisten diferencias significativas en la concentración de iodo del páncreas medida en TC con energía dual entre pacientes con pancreatitis aguda en fases iniciales y pacientes sin signos analíticos ni en imagen de patología pancreática.