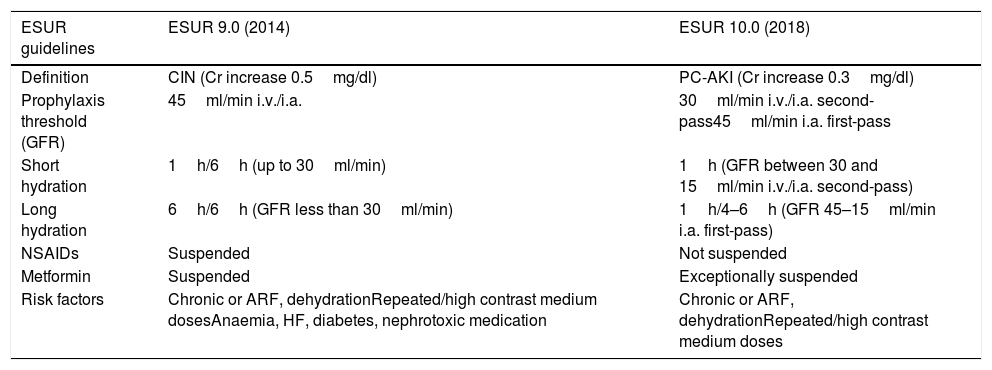
The European Society of Urogenital Radiology (ESUR) updated its guidelines for prophylaxis against postcontrast acute kidney injury (PC-AKI) in 2018 (ESUR 10.0). These guidelines drastically reduce the indications for prophylaxis against PC-AKI after iodine-based contrast administration, lowering the cutoff for administering prophylaxis to glomerular filtration rates <30ml/min/1.73m2 and eliminating most of the prior risk factors. Moreover, in cases where prophylaxis is considered necessary, the periods of hydration are shorter than in the previous version. These guidelines have been approved by most radiological societies, although they have also been criticised for excessive relaxation regarding risk factors, especially by the nephrological community. In this article, we critically review the changes to the guidelines.
La European Society of Urogenital Radiology (ESUR) ha actualizado la guía de profilaxis de la lesión renal aguda poscontraste (LRA-PC) yodado en 2018, guía ESUR 10.0. Esta guía reduce drásticamente las indicaciones de la realización de la profilaxis de la LRA-PC yodado, rebajando el dintel de realización de profilaxis a filtrados glomerulares menores de 30 ml/min/1,73m2 y eliminando la mayoría de los considerados factores de riesgo previamente. En los casos en que se considera necesario, las pautas de hidratación indicadas son más cortas que en la guía previa. Esta guía ha sido suscrita por la mayoría de las sociedades radiológicas, pero también ha sido criticada por su excesiva relajación en cuanto a los factores de riesgo, especialmente por la comunidad nefrológica. En este artículo revisamos los cambios que supone esta guía en relación con la anterior y planteamos las críticas a la misma.