To analyze the usefulness of diffusion magnetic resonance (MR) sequences before and after prostatic artery embolization (PAE) in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
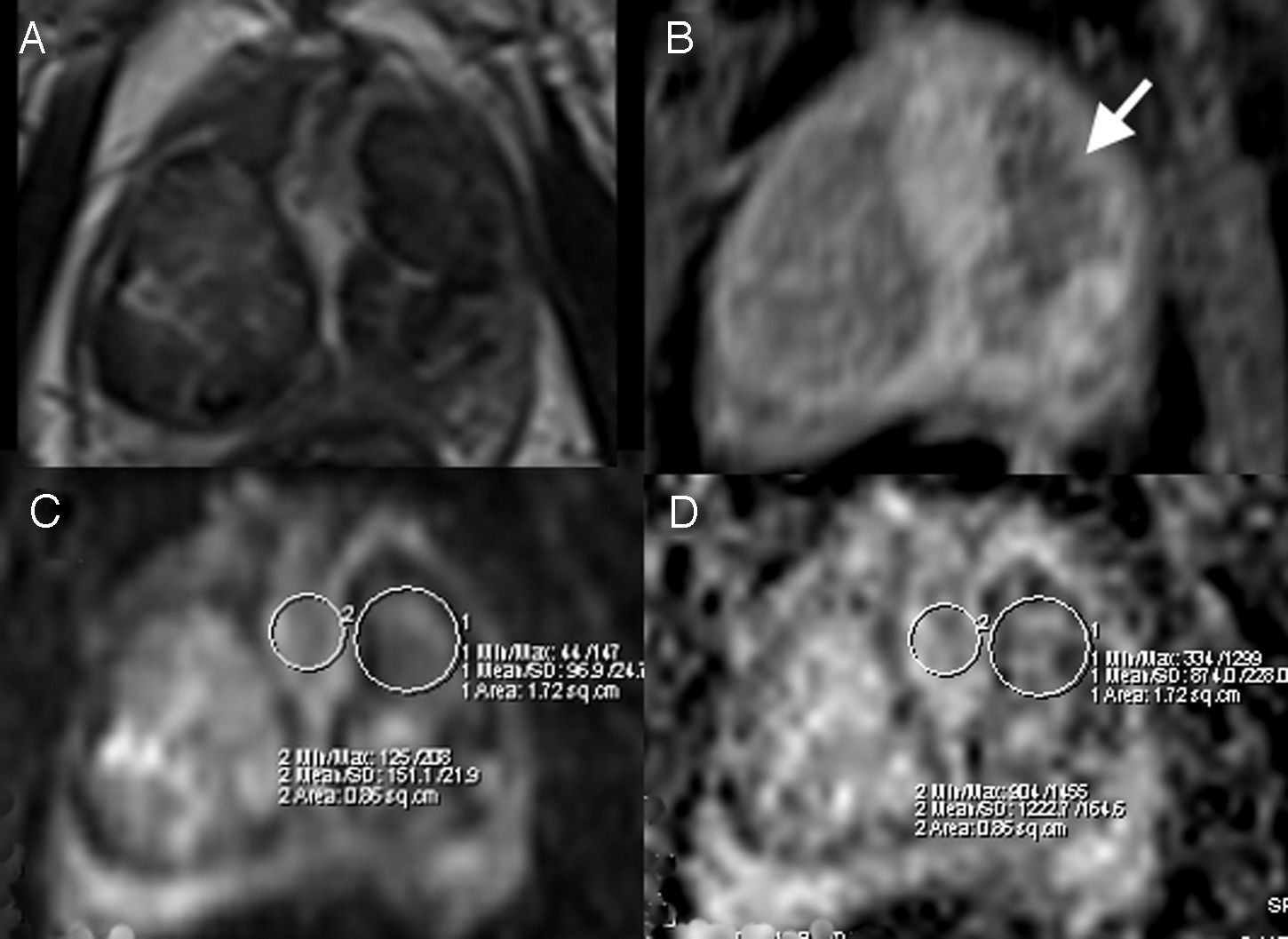
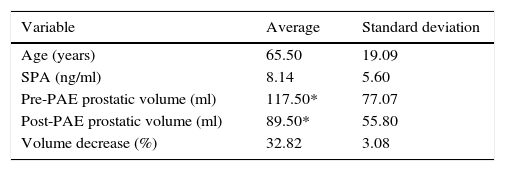
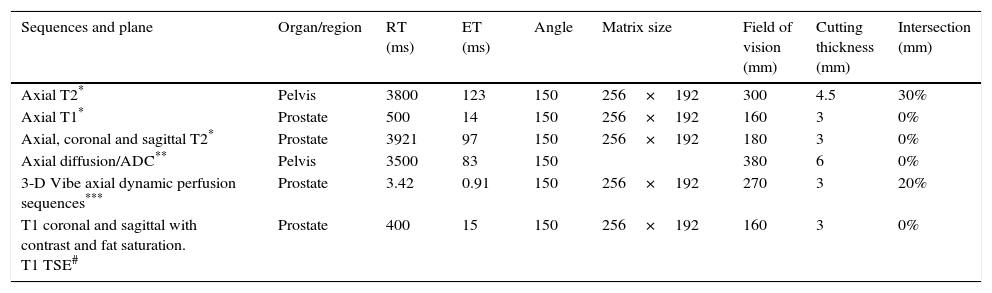
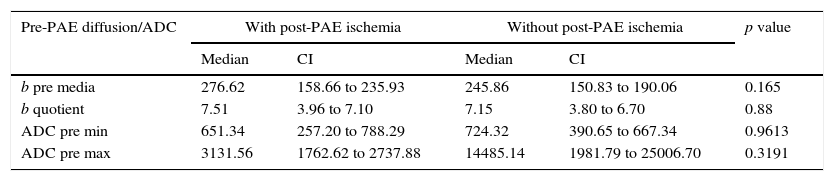
Material and methodsWe analyzed MR studies done before (7–10 days) and after (30 days) PAE in 19 patients with BPH treated with PAE between June 2012 and December 2013. We used 1.5Tesla scanners with body surface coils. In pre-PAE MR studies, we recorded mean b40 values and minimum (min) and maximum (max) apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values. In post-PAE MR studies, we recorded b40, b400, and b1000 values and min, mean, and max ADC values. We compared diffusion behavior/ADC before and after PAE and areas without ischemia. We correlated these with decreased prostatic volume (PV).
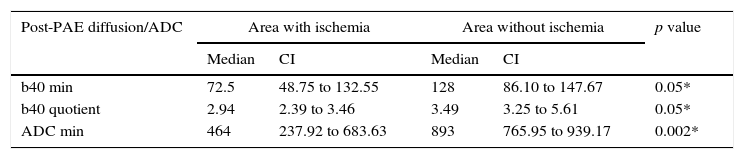
ResultsWe identified ischemia with contrast in 8 (42.1%) patients. No significant difference was found in mean b40 (p=0.1650) or in the b40 ratio (p=0.8868) between patients with ischemia and those without before PAE. Min b40, b40 ratio, and min ADC values differed significantly between ischemic areas and nonischemic areas within patients [p=0.048 (b40 min and ratio) and p=0.002 (min ADC)]. No significant correlation was found between the percentage decrease in PV and mean b40 (p=0.8490) or b40 ratio (p=0.8573).
ConclusionPost-PAE ischemia generates objective changes in diffusion and ADC values that enable ischemic sectors to be differentiated from nonischemic sectors. Future studies should analyze whether it is possible to subjectively differentiate between these areas through the visualization of nonischemic sectors and the feasibility of replacing them with contrast to detect ischemia.
Analizar la utilidad de la difusión en resonancia magnética (RM) antes y después de la embolización de arterias prostáticas (EAP) en pacientes con hiperplasia prostática benigna (HPB).
Material y métodoSe analizaron RM pre-EAP (7–10 días) y post-EAP (30 días) en 19 pacientes con HPB tratados con EAP entre junio de 2012 y diciembre de 2013. Se utilizaron equipos de 1,5 Tesla y bobina corporal de superficie. En RM pre-EAP se registraron valores b40 media, coeficiente de difusión aparente (CDA) mínimo (mín) y máximo (máx). En RM post-EAP se determinaron b40, b400, b1000 y CDA mín, media y máx. Se comparó el comportamiento en difusión/CDA antes y después del procedimiento y en áreas sin isquemia. Se correlacionó con la disminución de volumen prostático (VP).
ResultadosSe identificó isquemia con contraste en 8 pacientes (42,1%). Al comparar pacientes con isquemia vs. sin isquemia, la diferencia en b40 media (p=0,1650) y b40 cociente (p=0,8868) pre-EAP no fue significativa. Encontramos diferencia significativa entre valores b40 mín, b40 cociente y CDA mín de áreas isquémicas y no isquémicas del mismo paciente (p=0,048 [b40 mín y cociente] y 0,002 para CDA mín). No se encontró una correlación significativa para b40 media (p=0,8490) y b40 cociente (p=0,8573) al compararla con el porcentaje de reducción de VP.
ConclusiónLa isquemia post-EAP genera cambios objetivos en difusión y CDA que permitirían diferenciarla de sectores no isquémicos. Futuros trabajos deberán analizar si es posible una diferenciación subjetiva mediante visualización de sectores no isquémicos y la factibilidad de reemplazar las secuencias con contraste para detectar isquemia.