The pathological classification of hippocampal sclerosis is based on the loss of neurons in the substructures of the hippocampus. This study aimed to evaluate these substructures in patients with hippocampal sclerosis by magnetic resonance imaging and to compare the usefulness of this morphological analysis compared to that of volumetric analysis of the entire hippocampus.
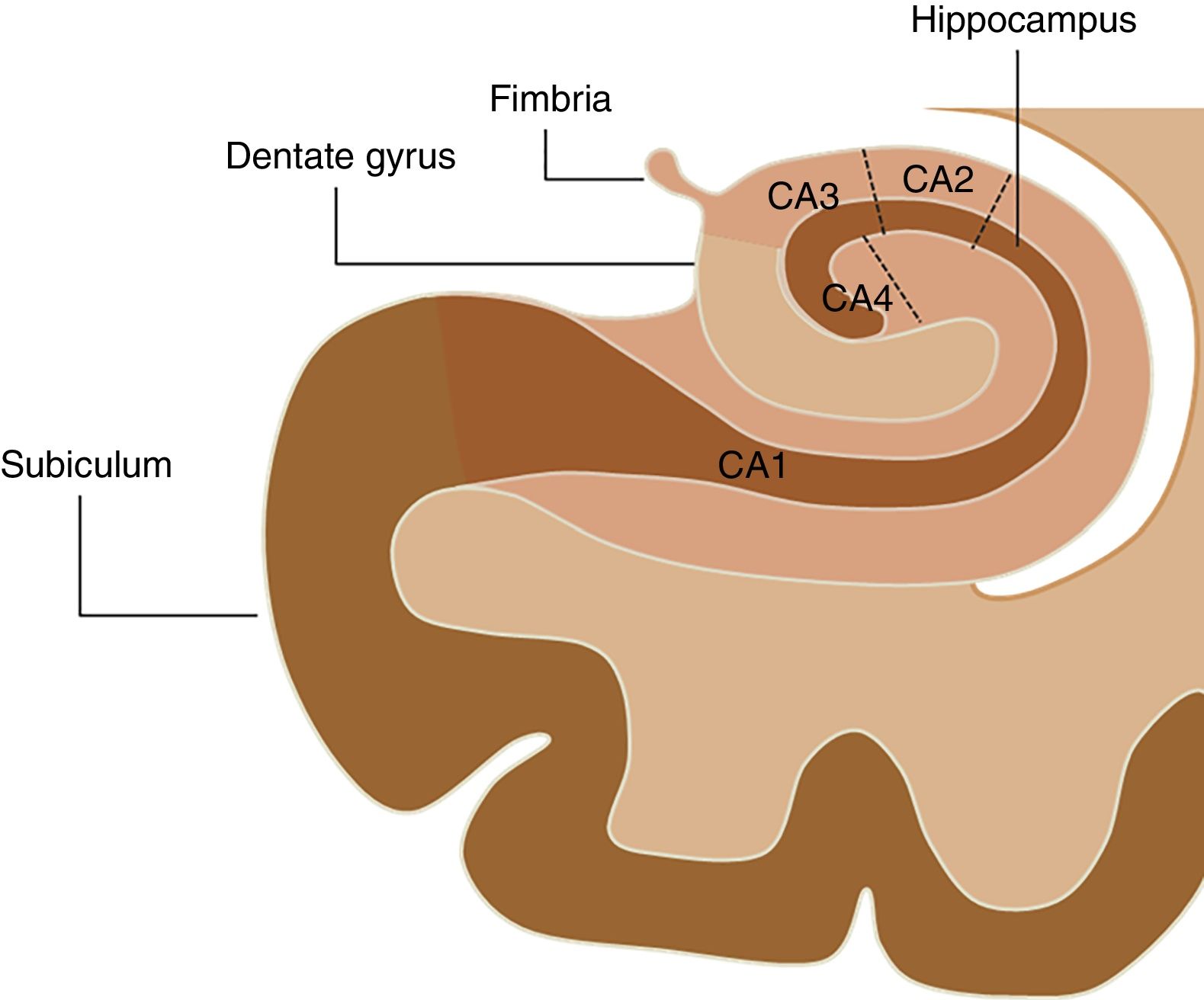
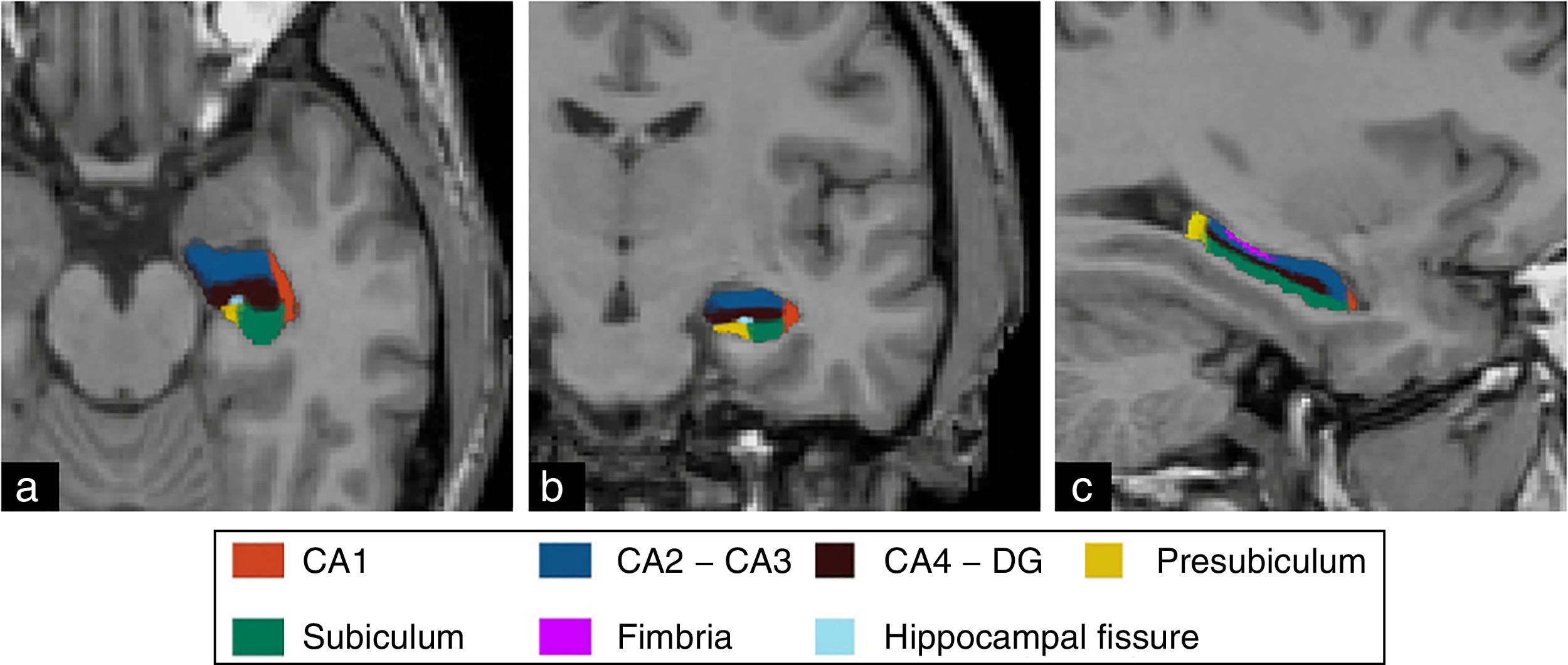
Material and methodsWe included 25 controls and 25 patients with hippocampal sclerosis whose diagnosis was extracted from the institutional epilepsy board. We used FreeSurfer to process the studies and to obtain the volumetric data. We evaluated overall volume and volume by substructure: fimbria, subiculum, presubiculum, hippocampal sulcus, CA1, CA2–CA3, CA4, and dentate gyrus (DG). We considered p<0.05 statistically significant.
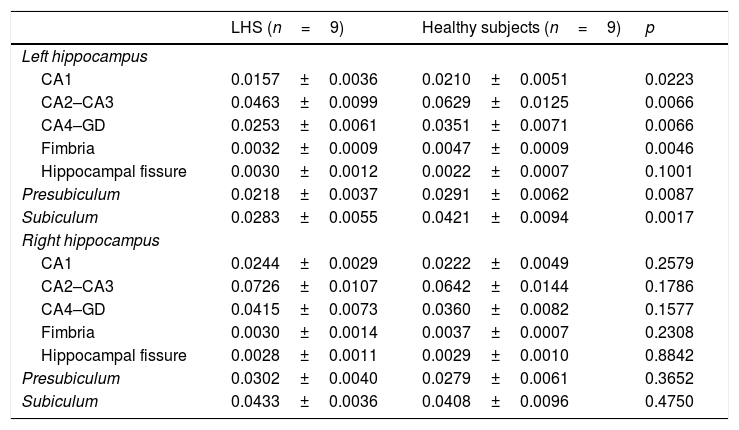
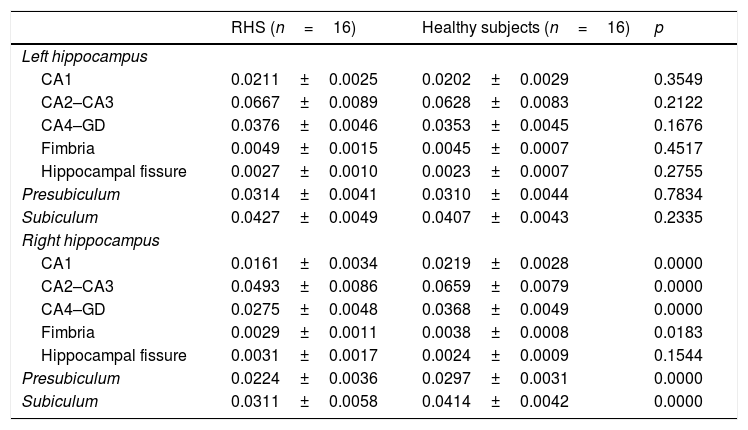
ResultsWe observed statistically significant decreases in the volume of the hippocampus ipsilateral to the epileptogenic focus in 19 (76.0%) of the 25 cases. With the exception of the hippocampal sulcus, we observed a decrease in all ipsilateral hippocampal substructures in patients with right hippocampal sclerosis (CA1, p=0.0223; CA2–CA3, p=0.0066; CA4–GD, p=0.0066; fimbria, p=0.0046; presubiculum, p=0.0087; subiculum, p=0.0017) and in those with left hippocampal sclerosis (CA1, p<0.0001; CA2–CA3, p<0.0001; CA4–GD, p<0.0001; fimbria, p=0.0183; presubiculum, p<0.0001; subiculum, p<0.0001). In four patients with left hippocampal sclerosis, none of the substructures had statistically significant alterations, although a trend toward atrophy was observed, mainly in CA2–CA3 and CA4–GD.
ConclusionThe findings suggest that it can be useful to assess the substructures of the hippocampus to improve the performance of diagnostic imaging in patients with hippocampal sclerosis.
Evaluar las subestructuras hipocampales utilizando resonancia magnética en pacientes con esclerosis hipocampal (EH), comparando los resultados con el análisis morfológico y la volumetría global del hipocampo.
MétodoSe incluyeron 25 controles y 25 pacientes con EH, cuyo diagnóstico fue extraído del informe de la junta institucional de epilepsia. Se utilizó FreeSurfer para el procesamiento de los estudios y la obtención de los datos volumétricos. El volumen fue valorado de manera global y por subestructura: fimbria, subiculum, presubiculum, fisura hipocampal, CA1, CA2-CA3, CA4 y giro dentado (GD). Se consideró p<0,05 como estadísticamente significativo.
ResultadosSe observó una disminución estadísticamente significativa en el hipocampo homolateral al foco epileptógeno en 19 de los 25 casos (76,0%). A excepción de la fisura hipocampal, se observó una disminución en todas las subestructuras hipocampales homolaterales en la EH derecha (CA1, p=0,0223; CA2–CA3, p=0,0066; CA4–GD, p=0,0066; fimbria, p=0,0046; presubiculum, p=0,0087; subiculum, p=0,0017) y la EH izquierda (CA1, p<0,0001; CA2–CA3, p<0,0001; CA4–GD, p<0,0001; fimbria, p=0,0183; presubiculum, p<0,0001; subiculum, p<0,0001). En cuatro casos de EH izquierda, ninguna de las subestructuras presentó alteración estadísticamente significativa; sin embargo, se observó una tendencia de atrofia, principalmente en CA2–CA3 y CA4–GD.
ConclusiónLos hallazgos sugieren la utilidad de la evaluación de las subestructuras hipocampales para mejorar el desempeño de la imagen en el diagnóstico de la EH.