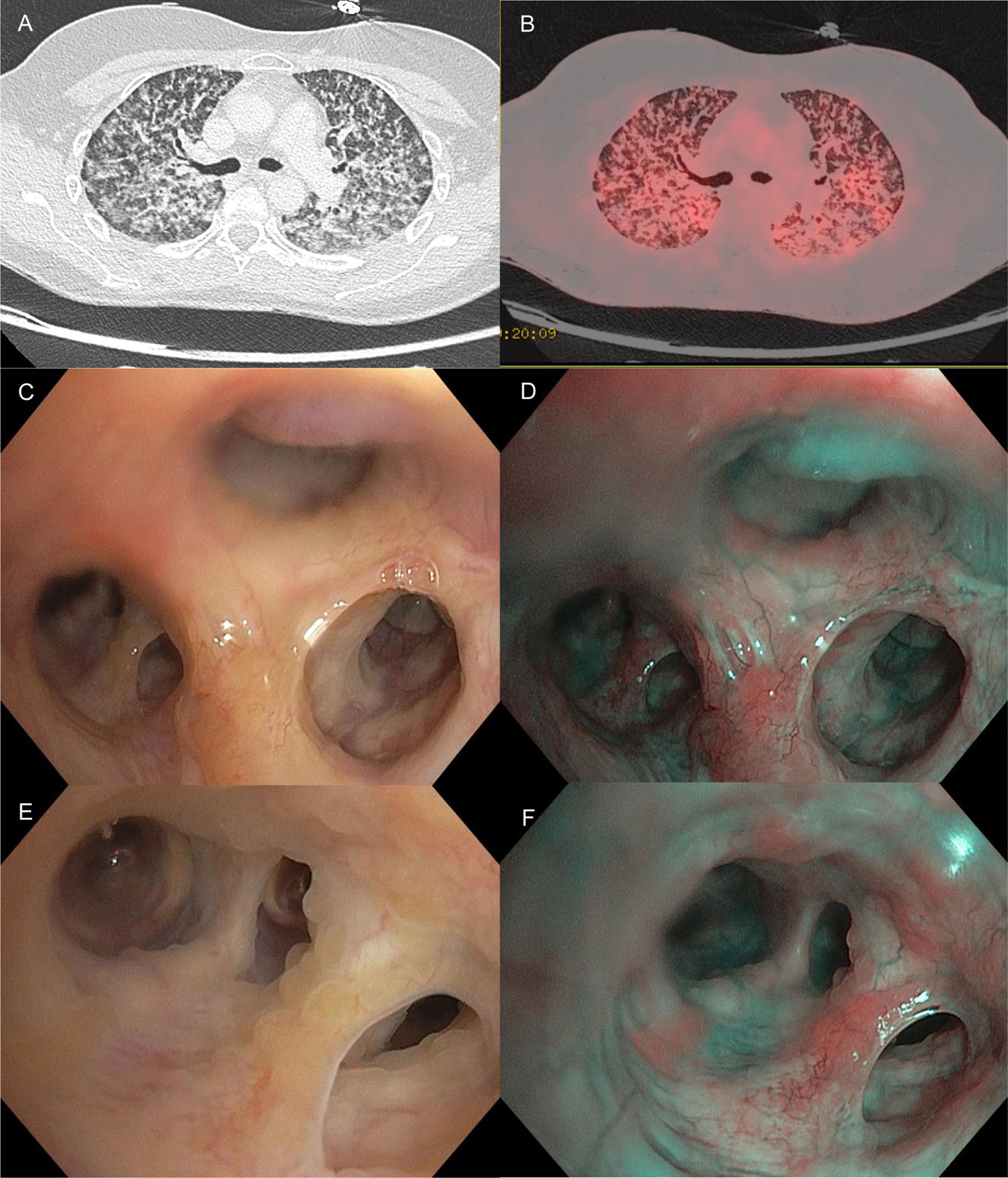
A 48-year-old female, former smoker, without respiratory symptoms, was incidentally found to have diffuse pulmonary abnormalities. Chest CT revealed upper lobe– predominant diffuse parenchymal changes with confluent micronodules in a lymphangitic distribution, without thoracic lymphadenopathy (Fig. 1A), and PET-CT demonstrated diffuse pulmonary hypermetabolism (Fig. 1B). Flexible bronchoscopy revealed pale, nodular bronchial mucosa with a cobblestone pattern, highlighted by saline (Fig. 1C and E), while narrow-band imaging (NBI) showed predominantly hypovascular nodules coalescing and increased submucosal vascularity (Fig. 1D and F). Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) demonstrated lymphocytosis (39%) with markedly elevated CD4+/CD8+ ratio (12.2). Endobronchial biopsy (EBB) and transbronchial lung biopsy (TBLB) in right upper lobe (RUL) were performed. Histopathologic of EBB from abnormal mucosa (Fig. 1C and D) showed non-necrotizing epithelioid granulomas with multinucleated giant cells, confirmed by TBLB. Microbiologic studies were negative. These findings established the diagnosis of endobronchial sarcoidosis. This case highlights the utility of NBI in assessing atypical bronchial mucosa, complementing standard bronchoscopy in non-malignant conditions. While EBB has an overall diagnostic yield of ∼40%, this rate increases in presence of endobronchial abnormalities such as cobblestoning and nodularity, as observed in our case. The recognition of the patterns may facilitate prompt diagnosis and avoid others procedures.
Multimodal imaging and bronchoscopic findings in endobronchial sarcoidosis. (A) Chest CT shows diffuse parenchymal changes with confluent micronodules in a lymphangitic distribution, predominantly involving the upper lobes. (B) PET-CT demonstrates diffuse pulmonary hypermetabolism. (C) Flexible bronchoscopy reveals pale and nodular mucosal changes in right upper lobe. (D) NBI of segment B1 shows mixed abnormal vascular patterns. (E) Bronchoscopic view of the cobblestoning pattern highlighted by saline. (F) NBI confirms hypovascular nodules coalescing and increased submucosal vascularity.
The authors declare that artificial intelligence (AI) tools (e.g., ChatGPT by OpenAI) were used solely to improve the grammar and clarity of the English language.
Informed consentInformed consent was obtained from the patient for the publication of their clinical data and images.
FundingNo funding was granted or solicited for this research.
Authors’ contributionsAll the authors have made significant contributions to the conception, drafting and critical revision of the manuscript.
Conflicts of interestAuthors declare not conflict of interest.
Uncited references1,2.