There is controversy concerning the use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEI) or angiotensin II type-I receptor blockers (ARB) for treating hypertensive patients with Covid-19. It has been hypothesized that these drugs might increase the risk of severe Covid-19, but some authors suggested that blocking the renin-angiotensin system might actually decrease this risk.
MethodsRetrospective cohort study of all the consecutive hypertensive patients with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection in a health area. The outcome variable was hospitalization because of severe Covid-19.
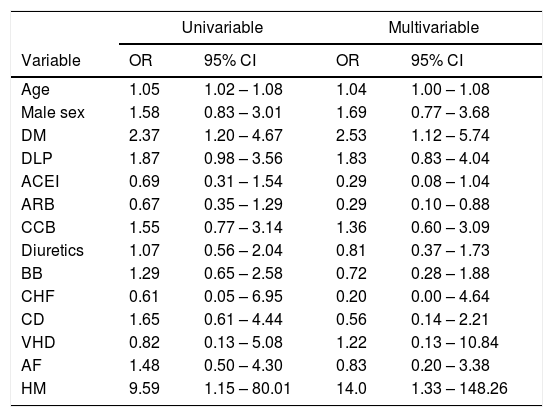
Results539 subjects were diagnosed of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Of these, 157 (29.1%) had hypertension and were included in the study. Sixty-nine cases (43.9%) were hospitalized because of severe Covid-19. In multivariable analysis older age, diabetes and hypertensive myocadiopathy were related to a higher risk of hospital admission. ARB treatment was associated with a significantly lower risk of hospitalization (HR: 0.29, 95% CI: 0.10 – 0.88). A similar albeit not significant trend was observed for ACEI.
ConclusionARB or ACEI treatment was not associated with a worse clinical outcome in consecutive hypertensive patients infected by SARS-CoV-2.
Existe controversia respecto al uso de los inhibidores de la enzima convertidora de angiotensina (IECA) o los bloqueadores de los receptores tipo I de la angiotensina II (ARA-II) para el tratamiento de la hipertensión arterial en COVID-19. Se ha sugerido que estos fármacos podrían tanto aumentar como reducir el riesgo de COVID-19 grave.
Pacientes y métodoEstudio de cohortes retrospectivo de pacientes consecutivos de un área sanitaria, con hipertensión e infección por SARS-CoV-2. Variable de resultados: ingreso hospitalario por COVID-19 grave.
ResultadosFueron diagnosticados 539 sujetos por infección por SARS-CoV-2. De estos, 157 (29,1%) eran hipertensos y se incluyeron en el estudio. Se ingresaron 69 (43,9%) pacientes por COVID-19 grave. En el análisis multivariante, la edad más elevada, la diabetes y la miocardiopatía hipertensiva se relacionaron con el riesgo de ingreso hospitalario. El tratamiento con ARA-II se asoció con un riesgo significativamente más bajo de ingreso (HR: 0,29, IC 95%: 0,10-0,88). Una tendencia similar, aunque no significativa, se encontró para los IECA.
Conclusiónel tratamiento con ARA-II o IECA no se asoció con una peor evolución clínica en pacientes hipertensos consecutivos infectados por SARS-CoV-2.