Postoperative pain is common in hospitals. Clinical practice guidelines for the control of postoperative pain (CPGPP) have been developed to improve its treatment. The objective of this study was to evaluate the prevalence and intensity of postoperative pain and analgesic norms, before and after the implementation of a CPGPP.
Material and methodAn observational study was carried out that included 2 cross-sectional studies in 2 separate periods, before and after implementation of the CPGPP. Adult patients postoperated on the first day of admission in the surgery plants were included. Demographic, clinical and pharmacological variables were collected from clinical histories. The intensity of the pain was collected through individual interviews with patients.
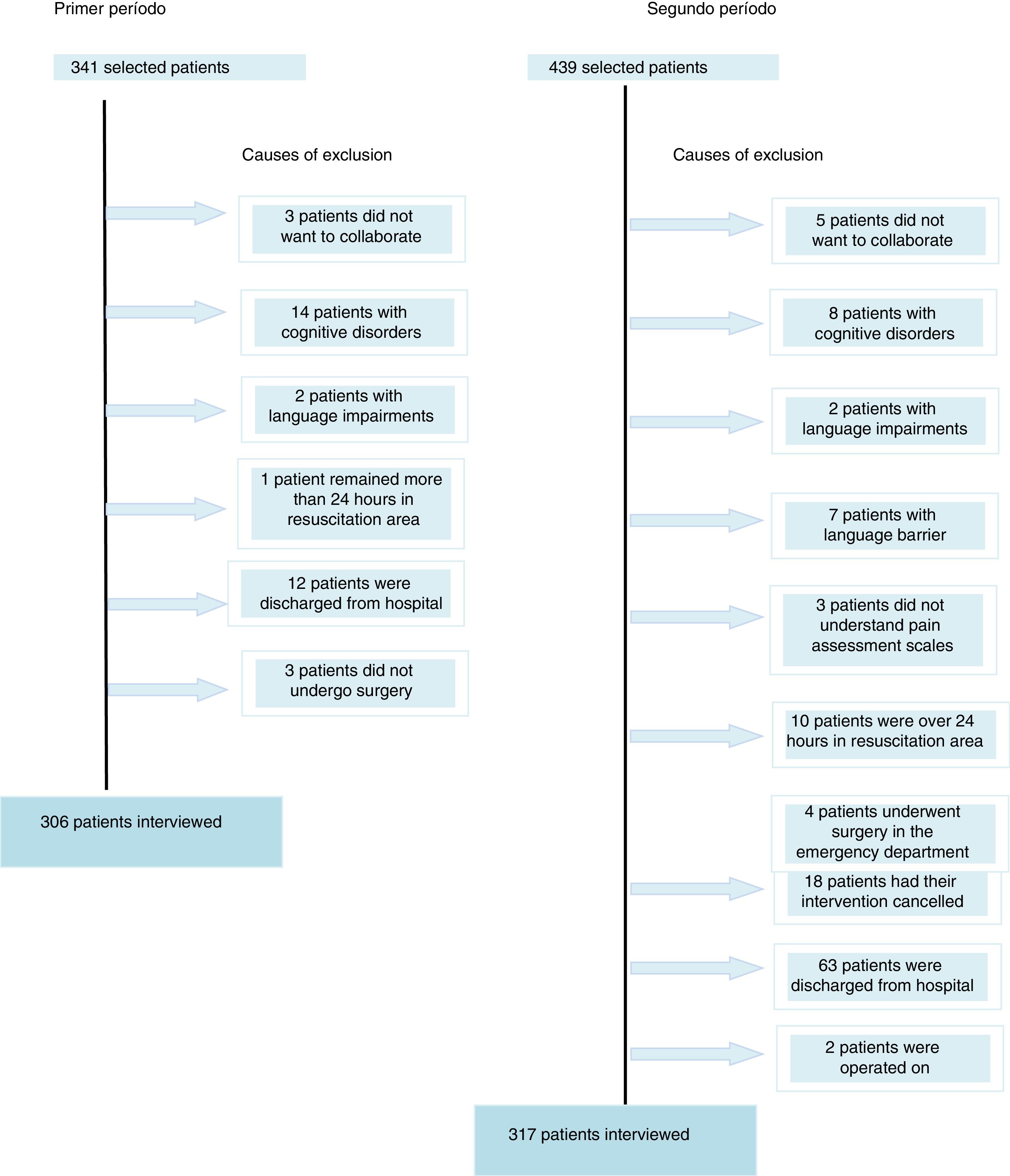
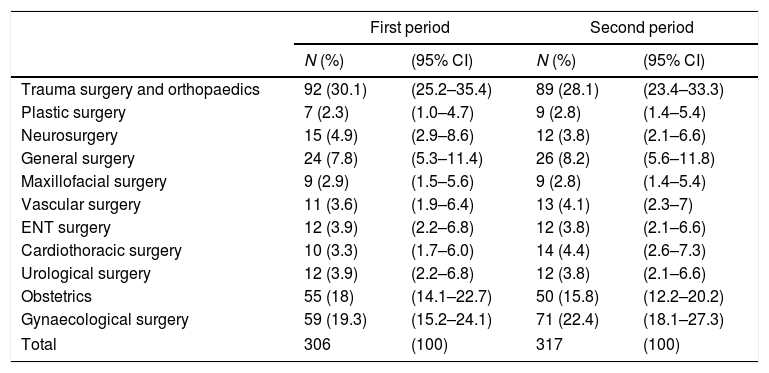
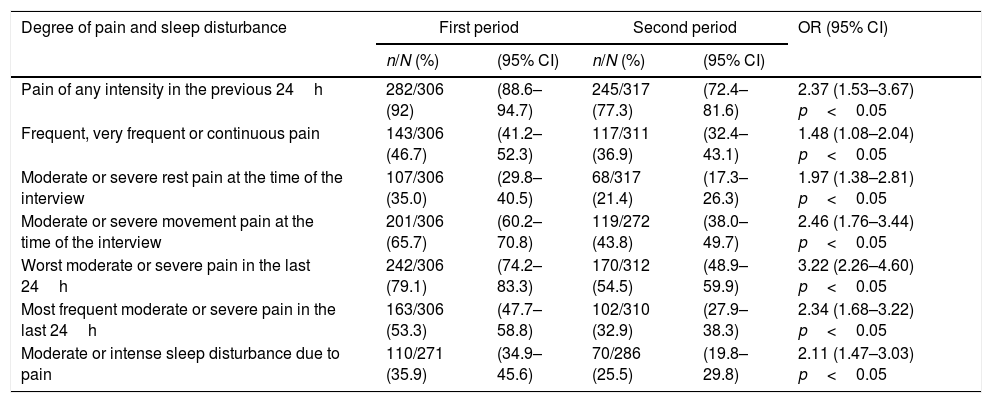
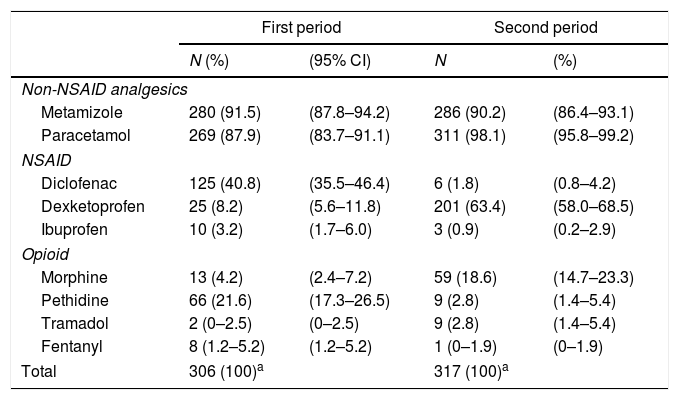
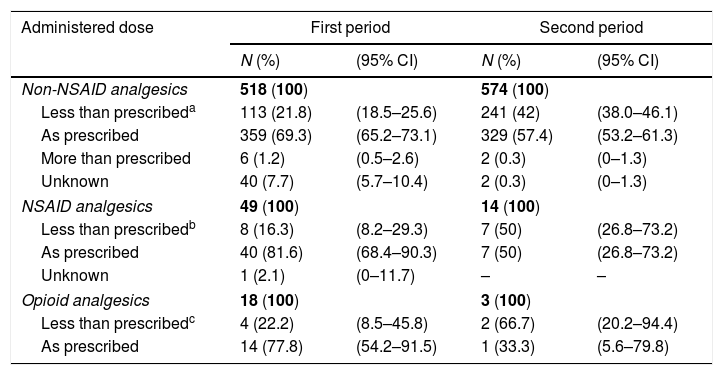
ResultsWe included 306 patients in the first period and 317 in the second. There were no differences between patients’ demographic and clinical variables and the 2 periods. The prevalence of pain was 92% (IC 95%: 87%–95%) in the first period and 77% (IC 95%: 72%–82%) in the second (p<0.05). The most frequent pain in the last 24h was moderate or intense in 53% (IC 95%: 48%–59%) of patients in the first period and in 33% (IC 95%: 28%–38%) of the patients in the second (p<0.05).
ConclusionsAfter the implementation of the CPGPP, a decrease in the prevalence and intensity of pain in patients was observed, but without reaching an optimal level. Continued pain training and assessment measures are therefore necessary for proper pain treatment over time.
El dolor postoperatorio es frecuente en los hospitales. Se han desarrollado guías de práctica clínica para el control del dolor postoperatorio (GPCDP) y para mejorar su tratamiento. El objetivo fue evaluar la prevalencia e intensidad del dolor postoperatorio y las pautas analgésicas, antes y después de la implementación de una GPCDP.
Material y métodoEstudio observacional que incluyó 2estudios transversales realizados en 2períodos (anterior y posterior a la implementación de una GPCDP). Incluyó a pacientes adultos postoperados el primer día de ingreso en plantas de cirugía. Las variables demográficas, clínicas y farmacológicas se recogieron de las historias clínicas; la intensidad del dolor, mediante entrevista con los pacientes.
ResultadosSe incluyó a 306 pacientes en el primer período y 317 en el segundo. No hubo diferencias respecto a las variables demográficas y clínicas de los pacientes en los 2períodos. La prevalencia del dolor fue del 92% (IC 95%: 87-95%) en el primer período y del 77% (IC 95%: 72-82%) en el segundo (p<0,05). El dolor más frecuente en las últimas 24h fue moderado o intenso en el 53% (IC 95%: 48-59%) de los pacientes en el primer período y en el 33% (IC 95%: 28-38%) de los pacientes en el segundo (p<0,05).
ConclusionesTras la implementación de la GPCDP se observó un descenso de la prevalencia e intensidad del dolor de los pacientes, pero sin llegar a ser óptimo. Son necesarias medidas continuadas de formación y evaluación del dolor para un tratamiento adecuado a lo largo del tiempo.